Modify the Score
The following score modifying options are available to all operators. For details and examples, click any of the following options:
boost
The boost option multiplies a result's base score by a given number
or the value of a numeric field in the documents. For example, you can
use boost to increase the importance of certain matching documents
in the result.
Note
You can't use the
boostandconstantoptions together.The
boostoption withpathis the same as multiplying using thefunctionoption with a path expression.
Fields
The boost option takes the following fields:
Field | Type | Necessity | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
value | float | Conditional | Number to multiply the default base score by. Value must be a
positive number. Either value or path is required, but
you can't specify both. |
path | string | Conditional | Name of the numeric field whose value to multiply the default
base score by. Either path or value is required, but you
can't specify both. |
undefined | float | Optional | Numeric value to substitute for path if the numeric field
specified through path is not found in the documents. If
omitted, defaults to 0. You can specify this only if you
specify path. |
Examples
The following examples use the movies collection in the
sample_mflix database. If you have the sample dataset on your cluster, you can create the Atlas Search
default index and run the example queries on your cluster.
The sample compound queries demonstrate how to increase the
importance of one search criteria over another. The queries include a
$project stage to exclude all fields except title and
score.
In the following example, the compound operator uses
text operator to search for the term Helsinki
in the plot and title fields. The query for the title
field uses score with the boost option to multiply the
score results by 3, as specified in the value field.
1 db.movies.aggregate([ 2 { 3 "$search": { 4 "compound": { 5 "should": [{ 6 "text": { 7 "query": "Helsinki", 8 "path": "plot" 9 } 10 }, 11 { 12 "text": { 13 "query": "Helsinki", 14 "path": "title", 15 "score": { "boost": { "value": 3 } } 16 } 17 }] 18 } 19 } 20 }, 21 { 22 "$limit": 5 23 }, 24 { 25 "$project": { 26 "_id": 0, 27 "title": 1, 28 "plot": 1, 29 "score": { "$meta": "searchScore" } 30 } 31 } 32 ])
This query returns the following results, in which the score
for documents where the title matches the query term is
multiplied by 3 from its base value:
[ { plot: 'Epic tale about two generations of men in a wealthy Finnish family, spanning from the 1960s all the way through the early 1990s. The father has achieved his position as director of the ...', title: 'Kites Over Helsinki', score: 12.2470121383667 }, { plot: 'Alex is Finlander married to an Italian who works as a taxi driver in Berlin. One night in his taxi come two men with a briefcase full of money. Unluckily for Alex, they are being chased by...', title: 'Helsinki-Naples All Night Long', score: 9.56808090209961 }, { plot: 'The recession hits a couple in Helsinki.', title: 'Drifting Clouds', score: 4.5660295486450195 }, { plot: 'Two teenagers from Helsinki are sent on a mission by their drug dealer.', title: 'Sairaan kaunis maailma', score: 4.041563034057617 }, { plot: 'A murderer tries to leave his criminal past in East Helsinki and make a new life for his family', title: 'Bad Luck Love', score: 3.6251673698425293 } ]
In the following example, the compound operator
uses text operator to search for the term
Helsinki in the plot and title fields. The query
against the title field uses score with the boost
option to multiply the score results by the numeric field
imdb.rating in path. If the numeric field isn't found in
the specified path, the operator multiplies the score of the
documents by 3.
1 db.movies.aggregate([ 2 { 3 "$search": { 4 "compound": { 5 "should": [{ 6 "text": { 7 "query": "Helsinki", 8 "path": "plot" 9 } 10 }, 11 { 12 "text": { 13 "query": "Helsinki", 14 "path": "title", 15 "score": { 16 "boost": { 17 "path": "imdb.rating", 18 "undefined": 3 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 }] 23 } 24 } 25 }, 26 { 27 "$limit": 5 28 }, 29 { 30 "$project": { 31 "_id": 0, 32 "title": 1, 33 "plot": 1, 34 "score": { "$meta": "searchScore" } 35 } 36 } 37 ])
This query returns the following results, in which the score
for documents where the title field matches the query term is
multiplied from its base value by the value of the numeric field
imdb.rating or 3, if the field isn't found in the
documents:
[ { plot: 'Epic tale about two generations of men in a wealthy Finnish family, spanning from the 1960s all the way through the early 1990s. The father has achieved his position as director of the ...', title: 'Kites Over Helsinki', score: 24.902257919311523 }, { plot: 'Alex is Finlander married to an Italian who works as a taxi driver in Berlin. One night in his taxi come two men with a briefcase full of money. Unluckily for Alex, they are being chased by...', title: 'Helsinki-Naples All Night Long', score: 20.411907196044922 }, { plot: 'The recession hits a couple in Helsinki.', title: 'Drifting Clouds', score: 4.5660295486450195 }, { plot: 'Two teenagers from Helsinki are sent on a mission by their drug dealer.', title: 'Sairaan kaunis maailma', score: 4.041563034057617 }, { plot: 'A murderer tries to leave his criminal past in East Helsinki and make a new life for his family', title: 'Bad Luck Love', score: 3.6251673698425293 } ]
constant
The constant option replaces the base score with a specified number.
Note
You must not use the constant and boost options together.
Examples
The following example uses the default index on the
sample_mflix.movies collection to query the plot and title
fields using the compound operator. In the query, the
text operator uses score with the constant option to
replace all score results with 5 for results that match the query
against the title field only.
1 db.movies.aggregate([ 2 { 3 "$search": { 4 "compound": { 5 "should": [{ 6 "text": { 7 "query": "tower", 8 "path": "plot" 9 } 10 }, 11 { 12 "text": { 13 "query": "tower", 14 "path": "title", 15 "score": { "constant": { "value": 5 } } 16 } 17 }] 18 } 19 } 20 }, 21 { 22 "$limit": 5 23 }, 24 { 25 "$project": { 26 "_id": 0, 27 "title": 1, 28 "plot": 1, 29 "score": { "$meta": "searchScore" } 30 } 31 } 32 ])
The above query returns the following results, in which the score for
documents that match the query against the title field only is
replaced with the specified constant value:
1 [ 2 { 3 plot: 'Several months after witnessing a murder, residents of Tower Block 31 find themselves being picked off by a sniper, pitting those lucky enough to be alive into a battle for survival.', 4 title: 'Tower Block', 5 score: 8.15460205078125 6 }, 7 { 8 plot: "When a group of hard-working guys find out they've fallen victim to their wealthy employer's Ponzi scheme, they conspire to rob his high-rise residence.", 9 title: 'Tower Heist', 10 score: 5 11 }, 12 { 13 plot: 'Toru Kojima and his friend Koji are young student boys with one thing in common - they both love to date older women. Koji is a playboy with several women, young and older, whereas Toru is a romantic with his heart set on on certain lady.', 14 title: 'Tokyo Tower', 15 score: 5 16 }, 17 { 18 plot: 'A middle-aged mental patient suffering from a split personality travels to Italy where his two personalities set off all kinds of confusing developments.', 19 title: 'The Leaning Tower', 20 score: 5 21 }, 22 { 23 plot: 'A documentary that questions the cost -- and value -- of higher education in the United States.', 24 title: 'Ivory Tower', 25 score: 5 26 } 27 ]
embedded
Note
You can use this option with the embeddedDocument operator only.
The embedded option allows you to configure how to:
Aggregate the scores of multiple matching embedded documents.
Modify the score of an embeddedDocument operator after aggregating the scores from matching embedded documents.
Note
The Atlas Search embeddedDocuments
type, embeddedDocument operator, and embedded
scoring option are in preview. When an Atlas Search index on a replica set or
single MongoDB shard reaches two billion index objects,
Atlas Search transitions the index to a failed, non-queryable state. A solution
to accommodate this limitation will be in place when this feature is
generally available. To troubleshoot any issues related to using this
feature, contact Support. To request support
for more than two billion index objects, upvote
this request
in the MongoDB Feedback Engine.
Fields
The embedded option takes the following fields:
Field | Type | Necessity | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
aggregate | string | Optional | Configures how to combine scores of matching embedded documents. Value must be one of the following aggregation strategies:
If omitted, this field defaults to |
outerScore | Optional | Specifies the score modification to apply after applying the
aggregation strategy. |
Examples
The following sample query uses an index named default on the
sample_analytics.transactions collection. The index configures an
embeddedDocuments type on documents in the transactions array
and string type for transactions.symbol and
transactions.transaction_code fields.
Example
{ "mappings": { "dynamic": true, "fields": { "transactions": { "dynamic": true, "fields": { "symbol": { "type": "string" }, "transaction_code": { "type": "string" } }, "type": "embeddedDocuments" } } } }
The sample query on the transactions field, which contains an array
of documents, includes a $limit stage to limit the output to 10
results and a $project stage to:
Exclude all fields except
account_idandtransaction_count.Add a field named
scorethat applies an aggregation strategy and further score modification.Note
You can use
functioninside thescoreoption of the embeddedDocument operator'soperator. However, for function score expressions that require thepathoption, the numeric field that you specify as thepathfor the expression must be inside the embeddedDocument operator'spath. For example, in the following example query, the fieldtransactions.amountthat is specified inside thescoreoption of thecompoundoperator on line 24 is inside in theembeddedDocumentoperator's pathtransactionson line 4.
The query searches for accounts that have bought AMD and multiplies
the largest single AMD purchase (by number of shares) by the
log1p value of the number of transactions that the account has made
in this period. It ranks the accounts based on the following:
Number of
AMDbought in a single transactionNumber of transactions in the last period
1 db.transactions.aggregate({ 2 "$search": { 3 "embeddedDocument": { 4 "path": "transactions", 5 "operator": { 6 "compound": { 7 "must": [ 8 { 9 "text": { 10 "path": "transactions.symbol", 11 "query": "amd" 12 } 13 }, 14 { 15 "text": { 16 "path": "transactions.transaction_code", 17 "query": "buy" 18 } 19 } 20 ], 21 "score": { 22 "function": { 23 "path": { 24 "value": "transactions.amount", 25 "undefined": 1.0 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 }, 31 "score": { 32 "embedded": { 33 "aggregate": "maximum", 34 "outerScore": { 35 "function": { 36 "multiply": [ 37 { 38 "log1p": { 39 "path": { 40 "value": "transaction_count" 41 } 42 } 43 }, 44 { 45 "score": "relevance" 46 } 47 ] 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 }, 55 { "$limit": 10 }, 56 { 57 "$project": { 58 "_id": 0, 59 "account_id": 1, 60 "transaction_count": 1, 61 "score": { $meta: "searchScore" } 62 } 63 })
Atlas Search ranks accounts that have made many transactions in the last
period and bought many AMD in a single transaction highly.
1 [ 2 { account_id: 467651, transaction_count: 99, score: 19982 }, 3 { account_id: 271554, transaction_count: 96, score: 19851.822265625 }, 4 { account_id: 71148, transaction_count: 99, score: 19840 }, 5 { account_id: 408143, transaction_count: 100, score: 19836.76953125 }, 6 { account_id: 977774, transaction_count: 98, score: 19822.64453125 }, 7 { account_id: 187107, transaction_count: 96, score: 19754.470703125 }, 8 { account_id: 492843, transaction_count: 97, score: 19744.998046875 }, 9 { account_id: 373169, transaction_count: 93, score: 19553.697265625 }, 10 { account_id: 249078, transaction_count: 89, score: 19436.896484375 }, 11 { account_id: 77690, transaction_count: 90, score: 19418.017578125 } 12 ]
function
The function option allows you to alter the final score of the
document using a numeric field . You can specify the numeric field for
computing the final score through an expression. If the final result of the function score
is less than 0, Atlas Search replaces the score with 0.
Note
You can use function inside the score option of the
embeddedDocument operator's operator. However, for
function score expressions that require the path option, the
numeric field that you specify as the path for the expression
must be inside the embeddedDocument operator's path.
Expressions
Use the following expressions with the function option
to alter the final score of the document:
Arithmetic expressions, which add or multiply a series of numbers.
Constant expressions, which allow a constant number in the function score.
Gaussian decay expressions, which decay, or reduces, the scores by multiplying at a specified rate.
Path expressions, which incorporate an indexed numeric field value into a function score.
Score expressions, which return the relevance score assigned by Atlas Search.
Unary expressions, which are expressions that take a single argument. In Atlas Search, you can calculate the log10(x) or log10(x+1) of a specified number.
An arithmetic expression adds or multiplies a series of numbers. For example, you can use arithmetic expression to modify relevance ranking through a numeric field from a data enrichment pipeline. It must include one of the following options:
Option | Type | Description | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
add | array of expressions | Adds a series of numbers. Takes an array of
expressions, which can
have negative values. Array length must be greater than or
equal to ExampleArithmetic Expression Syntax Atlas Search uses the
| ||||||||||||
multiply | array of expressions | Multiplies a series of numbers. Takes an array of
expressions, which can
have negative values. Array length must be greater than or
equal to ExampleArithmetic Expression Syntax Atlas Search uses the
|
Note
You can't replace an arithmetic expression that evaluates to
undefined with a constant value.
A constant expression allows a constant
number in the function score. For example, you can use
constant to modify relevance ranking through a numeric value
from a data enrichment pipeline. It must include the following
option:
Option | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
constant | float | Number that indicates a fixed value. Atlas Search supports
negative values. |
Example
{ "function": { "constant": -23.78 } }
A gaussian decay expression allows you to decay, or reduce by
multiplying, the final scores of the documents based on the
distance of a numeric field value from a specified origin point.
decay is computed as:
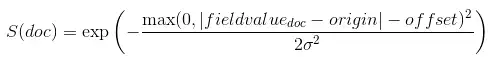
where sigma is computed to assure that the score takes the value
decay at distance scale from origin±offset:
For example, you can use gauss to adjust the relevant score
of documents based on document freshness, or date influencing
higher ranking. gauss takes the following options:
Field | Type | Necessity | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
decay | double | Optional | Rate at which you want to multiply the scores. Value must
be a positive number between For documents whose numeric field value (specified using
|
offset | double | Optional | Number to use to determine the distance from origin. The
decay operation is performed only for documents whose
distances are greater than origin plus or minus
(±) offset. If ommitted, defaults to 0. |
origin | double | Required | Point of origin from which to calculate the distance. |
path | Required | Name of the numeric field whose value you want to use to
multiply the base score. | |
scale | double | Required | Distance from origin plus or minus (±) offset
at which scores must be multiplied. |
Example
{ "function": { "gauss": { "path": { "value": "rating", "undefined": 50 }, "origin": 95, "scale": 5, "offset": 5, "decay": 0.5 } } }
Suppose the max rating is 100. Atlas Search uses the rating
field in the documents to decay the score:
Retains the current score for documents with rating between
90to100.Multiplies the current score by
0.5for documents with a rating lower than90.Multiplies the current score by
0.25for documents with a rating lower than85, and so on.
A path expression incorporates an indexed numeric field value
into a function score. It can either be a string or an
object.
If string, the value is the name of the numeric field to
search over for the path expression.
Example
{ "function": { "path": "rating" } }
Atlas Search incorporates the numeric value of the rating
field in the final score of the document.
If object, the path expression takes the following options:
Option | Type | Necessity | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
value | string | Required | Name of numeric field. Field can contain negative numeric
values. |
undefined | float | Optional | Value to use if the numeric field specified using
value is missing in the document. If omitted, defaults
to 0. |
Example
{ "function": { "path": {"value": "quantity", "undefined": 2} } }
Atlas Search incorporates numeric value of the quantity field
or 2, if the quantity field is not present in the
document, in the final score of the document.
A path expression can't be an array and can't contain
regex or wildcard in the path.
A score expression represents the relevance score, which is the score Atlas Search assigns documents based on relevance, of the query. It is the same as the current score of the document. It must include the following option:
Option | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
score | string | Value of relevance score of the query. Value must be
relevance. |
Example
{ "function": { "score": "relevance" } }
A unary expression is an expression that takes a single argument.
In Atlas Search, you can use unary expressions to calculate the log10(x)
or log10(x+1) of a specified number. For example, you can use
log1p to influence the relevance score by document popularity
score. It must include one of the following options:
Option | Type | Description | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
log | Calculates the log10 of a number. ExampleThe following example uses the arithmetic expression
Unary Expression Syntax If the specified expression evaluates to less than or
equal to ExampleIn the following example, log10 of Unary Expression Syntax | |||||||||||||||||||
log1p | Adds ExampleThe following example uses the path expression. Atlas Search
adds Unary Expression Syntax |
Examples
The following examples use the default index on the
sample_mflix.movies collection to query the title field. The
sample queries include a $limit stage to limit the output to 5
results and a $project stage to exclude all fields except title
and score.
Example
In this example, the text operator uses score
with the function option to multiply the following:
Numeric value of the path expression, which is the value of the
imdb.ratingfield in the documents or2, if theimdb.ratingfield is not in the documentRelevance score, or the current score of the document
db.movies.aggregate([{ "$search": { "text": { "path": "title", "query": "men", "score": { "function":{ "multiply":[ { "path": { "value": "imdb.rating", "undefined": 2 } }, { "score": "relevance" } ] } } } } }, { $limit: 5 }, { $project: { "_id": 0, "title": 1, "score": { "$meta": "searchScore" } } }])
This query returns the following results, in which
the score is replaced with the specified function value:
{ "title" : "Men...", "score" : 23.431293487548828 } { "title" : "12 Angry Men", "score" : 22.080968856811523 } { "title" : "X-Men", "score" : 21.34803581237793 } { "title" : "X-Men", "score" : 21.34803581237793 } { "title" : "Matchstick Men", "score" : 21.05954933166504 }
Example
In the following example, the text operator uses score
with the function option to replace the current score of
the document with the constant numeric value of 3.
db.movies.aggregate([ { "$search": { "text": { "path": "title", "query": "men", "score": { "function":{ "constant": 3 } } } } }, { $limit: 5 }, { $project: { "_id": 0, "title": 1, "score": { "$meta": "searchScore" } } } ])
This query returns the following results, in which
the score is replaced with the specified function value:
{ "title" : "Men Without Women", "score" : 3 } { "title" : "One Hundred Men and a Girl", "score" : 3 } { "title" : "Of Mice and Men", "score" : 3 } { "title" : "All the King's Men", "score" : 3 } { "title" : "The Men", "score" : 3 }
Example
In the following example, the text operator uses score
with the function option to decay the relevance score
of the documents in the result.
The query specifies that for documents whose imdb.rating
field value or 4.6, if the imdb.rating field is not
present in the documents, is scale distance, which is
5, away from origin, which is 9.5, plus or minus
offset, which is 0, Atlas Search must multiply the score
using decay, which starts at 0.5. This query includes
a $limit stage to limit the output to up to 10
results and a $project stage to add the
imdb.rating field in the results.
db.movies.aggregate([ { "$search": { "text": { "path": "title", "query": "shop", "score": { "function":{ "gauss": { "path": { "value": "imdb.rating", "undefined": 4.6 }, "origin": 9.5, "scale": 5, "offset": 0, "decay": 0.5 } } } } } }, { "$limit": 10 }, { "$project": { "_id": 0, "title": 1, "imdb.rating": 1, "score": { "$meta": "searchScore" } } } ])
This query returns the following results:
[ { title: 'The Shop Around the Corner', imdb: { rating: 8.1 }, score: 0.9471074342727661 }, { title: 'Exit Through the Gift Shop', imdb: { rating: 8.1 }, score: 0.9471074342727661 }, { title: 'The Shop on Main Street', imdb: { rating: 8 }, score: 0.9395227432250977 }, { imdb: { rating: 7.4 }, title: 'Chop Shop', score: 0.8849083781242371 }, { title: 'Little Shop of Horrors', imdb: { rating: 6.9 }, score: 0.8290896415710449 }, { title: 'The Suicide Shop', imdb: { rating: 6.1 }, score: 0.7257778644561768 }, { imdb: { rating: 5.6 }, title: 'A Woman, a Gun and a Noodle Shop', score: 0.6559237241744995 }, { title: 'Beauty Shop', imdb: { rating: 5.4 }, score: 0.6274620294570923 } ]
To compare the results of the Gaussian expressions used in the previous query with the relevance score that is returned in the results by Atlas Search, run the following query:
db.movies.aggregate([ { "$search": { "text": { "path": "title", "query": "shop" } } }, { "$limit": 10 }, { "$project": { "_id": 0, "title": 1, "imdb.rating": 1, "score": { "$meta": "searchScore" } } } ])
This query returns the following results:
[ { title: 'Beauty Shop', imdb: { rating: 5.4 }, score: 4.111973762512207 }, { imdb: { rating: 7.4 }, title: 'Chop Shop', score: 4.111973762512207 }, { title: 'The Suicide Shop', imdb: { rating: 6.1 }, score: 3.5363259315490723 }, { title: 'Little Shop of Horrors', imdb: { rating: 6.9 }, score: 3.1020588874816895 }, { title: 'The Shop Around the Corner', imdb: { rating: 8.1 }, score: 2.762784481048584 }, { title: 'The Shop on Main Street', imdb: { rating: 8 }, score: 2.762784481048584 }, { title: 'Exit Through the Gift Shop', imdb: { rating: 8.1 }, score: 2.762784481048584 }, { imdb: { rating: 5.6 }, title: 'A Woman, a Gun and a Noodle Shop', score: 2.0802340507507324 } ]
Example
In the following example, the text operator uses score
with the function option to replace the relevance score
of the query with the value of the numeric field
imdb.rating or 4.6, if the imdb.rating field isn't
present in the documents.
db.movies.aggregate([{ "$search": { "text": { "path": "title", "query": "men", "score": { "function":{ "path": { "value": "imdb.rating", "undefined": 4.6 } } } } } }, { $limit: 5 }, { $project: { "_id": 0, "title": 1, "score": { "$meta": "searchScore" } } }])
This query returns the following results, in which
the score is replaced with the specified function value:
{ "title" : "12 Angry Men", "score" : 8.899999618530273 } { "title" : "The Men Who Built America", "score" : 8.600000381469727 } { "title" : "No Country for Old Men", "score" : 8.100000381469727 } { "title" : "X-Men: Days of Future Past", "score" : 8.100000381469727 } { "title" : "The Best of Men", "score" : 8.100000381469727 }
Example
In the following example, the text operator uses score
with the function option to return the relevance score,
which is the same as the current score, of the documents.
db.movies.aggregate([{ "$search": { "text": { "path": "title", "query": "men", "score": { "function":{ "score": "relevance" } } } } }, { "$limit": 5 }, { "$project": { "_id": 0, "title": 1, "score": { "$meta": "searchScore" } } }])
This query returns the following results, in which
the score is replaced with the specified function value:
{ "title" : "Men...", "score" : 3.4457783699035645 } { "title" : "The Men", "score" : 2.8848698139190674 } { "title" : "Simple Men", "score" : 2.8848698139190674 } { "title" : "X-Men", "score" : 2.8848698139190674 } { "title" : "Mystery Men", "score" : 2.8848698139190674 }
Example
In the following example, the text operator uses score
with the function option to calculate the log10 of the
imdb.rating field or 10, if the imdb.rating field
is not present in the document.
db.movies.aggregate([{ "$search": { "text": { "path": "title", "query": "men", "score": { "function": { "log": { "path": { "value": "imdb.rating", "undefined": 10 } } } } } } }, { "$limit": 5 }, { "$project": { "_id": 0, "title": 1, "score": { "$meta": "searchScore" } } }])
This query returns the following results, in which
the score is replaced with the specified function value:
{ "title" : "12 Angry Men", "score" : 0.9493899941444397 } { "title" : "The Men Who Built America", "score" : 0.9344984292984009 } { "title" : "No Country for Old Men", "score" : 0.9084849953651428 } { "title" : "X-Men: Days of Future Past", "score" : 0.9084849953651428 } { "title" : "The Best of Men", "score" : 0.9084849953651428 }