Embed an Authenticated Chart using a Custom JWT Provider
On this page
Many websites use authentication systems that generate JWTs to represent a signed-in user. If your website produces JWTs, you can configure Charts to validate the existing tokens to authorize the rendering of embedded charts. Alternatively, if your site does not already use JWTs as a part of the authentication process, you can write code to generate JWTs explicitly for the purpose of authorizing chart renders.
This tutorial shows the latter approach. The example shows you how to generate a simple JWT for a logged in user and send it to Charts.
Charts uses the details you provided when you configure a provider to validate JWTs it receives with requests to render embedded charts. If the token is invalid or does not conform to the details you provided, Charts doesn't render the authenticated chart view.
Prerequisites
You must be an Atlas Project Owner to configure embedding authentication providers for your linked Charts instance.
Procedures
Enable Authenticated Embedding for a Chart
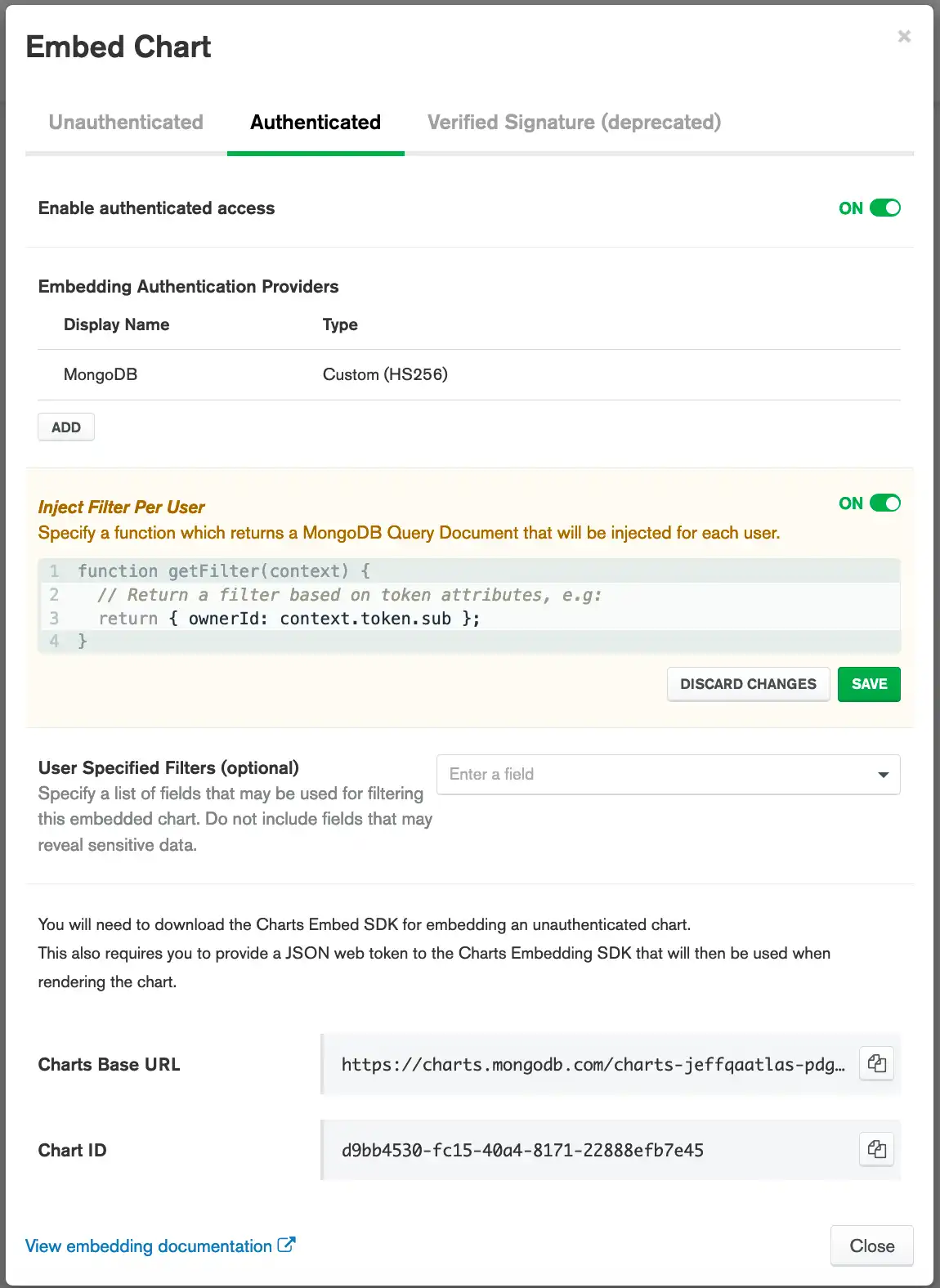
Enable authenticated embedding to generate a Charts Base URL and a chart ID. You will need your Charts Base URL and chart ID to display your chart on a web page.
Select a chart.
From the dashboard, click at the top-right of the chart to access its embedding information. Select Embed chart from the dropdown menu.
Note
If a chart is on a dashboard that has embedding enabled, the Embed Chart option is automatically enabled. Therefore, you can't select the Embed chart option for charts within dashboards that have embedding enabled.
(Optional) Specify a filter function to inject per user.
You can specify a function to inject a MongoDB filter document for each user who views the chart. This is useful for rendering user-specific charts.
Example
The following filter function only renders data where the
ownerId field of a document matches the value of
the Embedding Authentication Provider's token's sub field:
function getFilter(context) { return { ownerId: context.token.sub }; }
Configure Charts to use your Custom JWT Provider
Note
When you configure authentication using a custom JWT provider, you can choose the signing algorithm. This tutorial uses the HS256 signing algorithm. If you select the RS256 signing algorithm, you can also choose one of the following signing keys:
JSON web key (JWK) or JSON web key set (JWKS) URL: Charts retrieves the key from the JWK or JWKS file at the specified URL. Charts then uses the key to validate the JSON web token. If there are multiple keys in the file, Charts tries each key until it finds a match.
PEM public key: Charts uses the specified public key to verify the JSON web token.
Go to the Embedding page.
Click Embedding under the Development heading in the sidebar.
The Embedding page displays.
Go to the Authentication Settings view.
Note
You must be a Project Owner to access the Authentication Settings page. As a non-admin user, you can still use embedded charts, but you must get a key from a Project Owner.
Click the Authentication Settings tab.
The Authentication Settings tab displays.
Add the authentication provider.
From the Authentication providers section, click Add.
Provide the following values to configure Charts to validate the JWT for the tutorial.
FieldValueName
Enter
charts-jwt-tutorial.Provider
Select Custom JSON Web Token.
Signing Algorithm
Select HS256.
Signing Key
Enter
topsecret.Click Save.
Create a Web App to Display your Chart
If you already have an app in which to display your chart, you're all set. If not, proceed with the remaining steps.
MongoDB offers a pre-built sample that shows you how to use the Embedding SDK to authenticate an embedded chart using a JWT.
Clone the GitHub repository and follow the instructions in the Readme file to begin using the app. You can customize it to use the chart you created earlier.
Customize the Node.js App
In your application server code, generate and return a JWT. The implementation varies based on your authentication provider.
Warning
Generate JWTs server-side to protect your signing keys from exposure.
The app.js file in the sample application uses a simple web
service and the jsonwebtoken package to generate and return a
JWT signed using the HS256 algorithm when a user logs in to the
application with these credentials:
User name:
adminPassword:
password
1 const express = require("express"); 2 const bodyParser = require("body-parser"); 3 const cors = require("cors"); 4 const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken"); 5 const config = require("./config.js"); 6 7 const app = express(); 8 const port = 8000; 9 10 // Configuring body parser middleware 11 app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false })); 12 app.use(bodyParser.json()); 13 app.use(cors()); 14 15 app.post("/login", (req, res) => { 16 const loginDetails = req.body; 17 // mock a check against the database 18 let mockedUsername = "admin"; 19 let mockedPassword = "password"; 20 21 if ( 22 loginDetails && 23 loginDetails.username === mockedUsername && 24 loginDetails.password === mockedPassword 25 ) { 26 let token = jwt.sign({ username: loginDetails.username }, config.secret, { 27 expiresIn: "24h" // expires in 24 hours 28 }); 29 res.json({ bearerToken: token }); 30 } else { 31 res.status(401).send(false); 32 } 33 }); 34 35 app.listen(port, () => console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}!`));
Note
Your application must handle refreshing or issuing new tokens before they expire.
In the sample application, the signing key topsecret is defined in a file
in your application named config.js:
module.exports = { secret: "topsecret" };
Embed a chart.
Create a new object from the
ChartsEmbedSDKclass. Provide:The value of the
baseUrlproperty with the URL that points to your Charts instance. To embed one of your charts in the sample application, replace this value with the :guilabel:Base URLfrom your Embed Chart dialog.The
chartIdproperty to specify the unique identifier of the chart you want to embed. To embed one of your charts in the sample application, replace this value with the :guilabel:Chart IDfrom your Embed Chart dialog.The
getUserTokenproperty to specify the function that generates and returns a JWT from your authentication provider.Any optional properties you want to provide. For a list of all properties you can use when you embed charts using the SDK, see SDK option reference.
In the
src/index.jsfile in the sample application, theloginfunction in thegetUserTokenproperty calls the web service you created to generate a JWT. If login is successful, that function returns a valid JWT to thegetUserTokenproperty.1 import ChartsEmbedSDK from "@mongodb-js/charts-embed-dom"; 2 import "regenerator-runtime/runtime"; 3 4 document 5 .getElementById("loginButton") 6 .addEventListener("click", async () => await tryLogin()); 7 8 function getUser() { 9 return document.getElementById("username").value; 10 } 11 12 function getPass() { 13 return document.getElementById("password").value; 14 } 15 16 async function tryLogin() { 17 if (await login(getUser(), getPass())) { 18 document.body.classList.toggle("logged-in", true); 19 await renderChart(); 20 } 21 } 22 23 async function login(username, password) { 24 const rawResponse = await fetch("http://localhost:8000/login", { 25 method: "POST", 26 headers: { 27 Accept: "application/json", 28 "Content-Type": "application/json" 29 }, 30 body: JSON.stringify({ username: username, password: password }) 31 }); 32 const content = await rawResponse.json(); 33 34 return content.bearerToken; 35 } 36 37 async function renderChart() { 38 const sdk = new ChartsEmbedSDK({ 39 baseUrl: "https://localhost/mongodb-charts-iwfxn", // ~REPLACE~ with the Base URL from your Embed Chart dialog 40 chartId: "d98f67cf-374b-4823-a2a8-f86e9d480065", // ~REPLACE~ with the Chart ID from your Embed Chart dialog 41 getUserToken: async function() { 42 return await login(getUser(), getPass()); 43 } 44 }); For each chart that you want to embed, invoke the
CreateChartmethod of the object you just created. To embed one of your charts in the sample application, replace the value of theidproperty with the :guilabel:Chart IDfrom your Embed Chart dialog.The following example shows an invocation of the
CreateChartmethod in thesrc/index.jsfile in the sample application.const chart = sdk.createChart({ chartId: "d98f67cf-374b-4823-a2a8-f86e9d480065" }); // ~REPLACE~ with the Chart ID from your Embed Chart dialog
Deploy and test your application.
Charts renders the chart if it can validate the token it received with the request to render the chart. If the token isn't valid, Charts doesn't render the chart and displays an error code.
For more information on the Charts embedding error codes, see Embedded Error Codes.