Docs Home → Launch & Manage MongoDB → MongoDB Atlas
Manage Customer Keys with Google Cloud KMS
On this page
- Enable Customer-Managed Keys with Google Cloud KMS
- Example
- Required Access
- Prerequisites
- Enable Customer-Managed Keys for a Project
- Enable Customer Key Management for an Atlas Cluster
- Alerts
- Rotate your GCP Key Version Resource ID
- MongoDB Master Key - MongoDB Responsibility
- Your Google Cloud CMK - Your Responsibility
- Prerequisites
- Procedure
- Alerts
- Related Topics
Note
This feature is not available for
M0free clusters,M2, andM5clusters. To learn more, see Atlas M0 (Free Cluster), M2, and M5 Limits.This feature is not supported on Serverless instances at this time. To learn more, see Serverless Instance Limitations.
You can use a customer-managed key (CMK) from Google Cloud KMS to further encrypt your data at rest in Atlas.
Atlas uses your CMK from Google Cloud KMS to encrypt and decrypt MongoDB Master Keys, which are then used to encrypt cluster database files and cloud providers snapshots. To learn more about how Atlas uses CMKs for encryption, see Enable Customer-Managed Keys with Google Cloud KMS.
When you use your own cloud provider KMS, Atlas automatically rotates MongoDB Master Keys every 90 days. These keys are rotated on a rolling basis and the process does not require the data to be rewritten.
You must configure customer key management for the Atlas project before enabling it on clusters in that project.
Enable Customer-Managed Keys with Google Cloud KMS
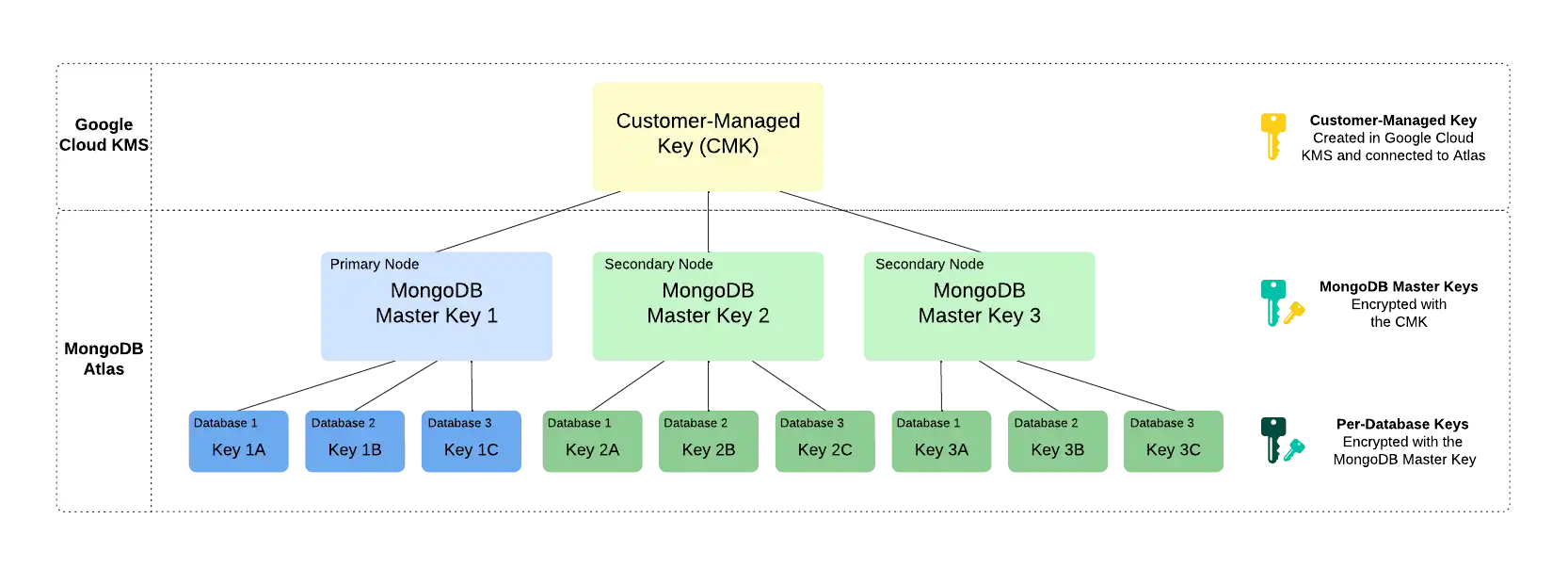
Customer key management in Atlas follows a process called envelope encryption. This process creates multiple layers of encryption by encrypting one key with another key. To enable customer key management, Atlas uses the following encryption keys:
Customer-Managed Key (CMK)Customer-managed keys are encryption keys that you create, own, and manage in Google Cloud KMS. You create the CMK in Google Cloud KMS and connect it to Atlas at the Project level. To learn more about the CMKs used in Google Cloud KMS, see the Google Cloud Documentation.
Atlas uses this key only to encrypt the MongoDB Master Keys.
MongoDB Master KeyEach node in your Atlas cluster creates a MongoDB Master Key. MongoDB Master Keys are encryption keys that a MongoDB Server uses to encrypt files via the WiredTiger storage engine. Atlas saves an encrypted copy of the key locally.
This key is encrypted with the CMK and encrypts the per-database encryption keys.
Per-Database Encryption KeyEach node in your Atlas cluster also creates an encryption key per database in your cluster. Atlas uses these keys to read and write data via WiredTiger, which also encrypts and stores these keys.
This key is encrypted with the MongoDB Master Key.
Example
Consider the following encryption hierarchy for a three-node replica set. Atlas uses the CMK from Google Cloud KMS to encrypt a unique MongoDB Master Key for each node in the cluster. Each node also contains three databases, each of which is encrypted with a unique per-database encryption key. When the cluster starts up, Atlas decrypts the MongoDB Master Key by using the CMK from Google Cloud KMS and supplies this to the MongoDB Server.
Note
If you revoke Atlas's access to the CMK, Atlas shuts down the nodes in your cluster and you can't access your data until you restore access to the CMK.
Required Access
To configure customer key management, you must have Project Owner
access to the project.
Users with Organization Owner access must add themselves to the
project as a Project Owner.
Prerequisites
To enable customer-managed keys with Google Cloud KMS for a MongoDB project, you must have:
Use an M10 or larger cluster.
Use Cloud Backups to encrypt your backup snapshots. Legacy Backups are not supported.
Your Google Cloud Service Account Key.
Your symmetric Encryption Key in Google Cloud KMS.
The Key Version Resource ID associated with your Google Cloud KMS Encryption Key.
A Google Cloud service account with credentials specified in your Service Account Key with sufficient permissions to:
Get the Google Cloud KMS Encryption Key version.
Encrypt data with the Google Cloud KMS Encryption Key version.
Decrypt data with the Google Cloud KMS Encryption Key.
Note
The key, not the key version, handles decryption.
If your Google Cloud KMS configuration requires it, use Accessible Services from GCP from Atlas IP addresses and the public IP addresses or DNS hostnames of your cluster nodes so that Atlas can communicate with your KMS. If the node IP addresses change, you must update your configuration to avoid connectivity interruptions.
Tip
See also:
See the Google Cloud documentation to learn how to:
Enable Customer-Managed Keys for a Project
You must enable customer key management for a project before you can enable it on a cluster in that project.
Navigate to the Advanced page for your project.
If it is not already displayed, select the organization that contains your desired project from the Organizations menu in the navigation bar.
If it is not already displayed, select your desired project from the Projects menu in the navigation bar.
Click Advanced in the sidebar.
Enter the Key Version Resource ID.
Your key version resource ID is the fully-qualified resource name for a CryptoKeyVersion.
Enable Customer Key Management for an Atlas Cluster
After you Enable Customer-Managed Keys for a Project, you must enable customer key management for each Atlas cluster that contains data that you want to encrypt.
Note
You must have the Project Owner role to
enable customer key management for clusters in that project.
For new clusters, toggle the Manage your own encryption keys setting to Yes when you create the cluster.
For existing clusters:
Navigate to the Database Deployments page for your project.
If it is not already displayed, select the organization that contains your desired project from the Organizations menu in the navigation bar.
If it is not already displayed, select your desired project from the Projects menu in the navigation bar.
If the Database Deployments page is not already displayed, click Database in the sidebar.
Optional: Add IP addresses from your cluster nodes.
Depending on your Key Management Service configuration, you may have to add Atlas cluster node IP addresses to your cloud provider KMS list, so that the cluster can communicate with your KMS. To enable communication between the cluster and KMS:
Send a GET request to the
ipAddressesendpoint. The API endpoint returns a list of IP addresses from the existing cluster nodes, similar to the following:{ "groupId": "xxx", // ObjectId "services": { "clusters": [ { "clusterName": "Cluster0", "inbound": [ "3.92.113.229", "3.208.110.31", "107.22.44.69" ], "outbound": [ "3.92.113.229", "3.208.110.31", "107.22.44.69" ] } ] } } Add the returned IP addresses to your cloud provider's IP access list. See the prerequisites for managing customer keys with AWS, Azure, and GCP for more information.
Alerts
Atlas automatically creates an encryption key rotation alert
once you configure customer key management for a project. You can reset this alert at any time by
rotating your GCP Key Version Resource ID.
Rotate your GCP Key Version Resource ID
Note
This feature is not available for
M0free clusters,M2, andM5clusters. To learn more, see Atlas M0 (Free Cluster), M2, and M5 Limits.This feature is not supported on Serverless instances at this time. To learn more, see Serverless Instance Limitations.
MongoDB Master Key - MongoDB Responsibility
When you use your own cloud provider KMS, Atlas automatically rotates MongoDB Master Keys every 90 days. These keys are rotated on a rolling basis and the process does not require the data to be rewritten.
Your Google Cloud CMK - Your Responsibility
Atlas does not automatically rotate the Key Version Resource ID used for Google Cloud key management.
As a best practice, Atlas creates an alert to remind you
to rotate your GCP Key Version Resource ID every 90 days by default when
you enable Encryption at Rest for the
Atlas project. You can configure the time period of this alert.
You can rotate your Google Cloud CMK yourself or configure your Google Cloud KMS instance to automatically rotate your CMK. If you configure automatic Google Cloud CMK rotation, the default time period for rotation is approximately 365 days.
If you have already set up an automatic CMK rotation in Google Cloud and don't want to receive the Atlas alert to rotate your CMK every 90 days, you can modify the default alert period to be greater than 365 days.
Prerequisites
You must create a new Service Account Key in the Google Cloud account associated with your Atlas project.
Procedure
The following procedure documents how to rotate your Atlas project Key Identifier by specifying a new Key Version Resource ID in Atlas.
Navigate to the Advanced page for your project.
If it is not already displayed, select the organization that contains your desired project from the Organizations menu in the navigation bar.
If it is not already displayed, select your desired project from the Projects menu in the navigation bar.
Click Advanced in the sidebar.
Update the GCP Key details.
Click Google Cloud KMS if the Google Cloud KMS tab is not already active.
Expand Encryption Key Credentials if the Encryption Key Credentials dialog is not already displayed.
Enter the GCP Key Version Resource ID in the Key Identifier entry.
Include the fully-qualified resource name for a CryptoKeyVersion.
Example
projects/my-project-0/locations/us-east4/keyRings/my-key-ring-0/cryptoKeys/my-key-0/cryptoKeyVersions/1 The encryption key must belong to the Google Cloud Service Account Key configured for your Atlas project. Click the Service Account Key section to view the currently configured Service Account Key for the project.
Click Update Credentials.
Atlas displays a banner in the Atlas console during the Key Identifier rotation process.
Warning
Do not delete or disable the original Key Version Resource ID until your changes have deployed.
If the cluster uses Back Up Your Database Deployment, do not delete or disable the original Key Version Resource ID until you ensure that no snapshots used that key for encryption.
Alerts
Atlas resets the
encryption key rotation alert
timer at the completion of this procedure.
Related Topics
To enable Encryption at Rest using your Key Management when deploying an Atlas cluster, see Manage Your Own Encryption Keys.
To enable Encryption at Rest using your Key Management for an existing Atlas cluster, see Enable Encryption at Rest.
To learn more about Encryption at Rest using your Key Management in Atlas, see Encryption at Rest using Customer Key Management.
To learn more about MongoDB Encryption at Rest, see Encryption at Rest in the MongoDB server documentation.
To learn more about Encryption at Rest with Cloud Backups, see Storage Engine and Cloud Backup Encryption.