Filter Incoming Queries
Overview
A filter modifies an incoming MongoDB query to return only a subset of the results matched by the query. Adding a filter to a collection allows you to control the shape of queried documents and can improve query performance.
Filters add additional query parameters and omit fields from query results before Atlas App Services runs the query. Every filter has three components:
An "apply when" expression that determines if the filter applies to an incoming request. You can use variables like
%%userand%%requestin the "apply when" expression. However, you cannot use expansions that refer to a document like%%rootbecause App Services evaluates the "apply when" expression before reading any documents.An optional query expression, which merges with the existing query of any request the filter applies to.
An optional projection document, which uses standard MongoDB projection syntax and merges with the existing projection of any request the filter applies to.
How App Services Applies Filters
App Services evaluates and applies filters for all MongoDB requests where rules apply except Device Sync requests. Examples of filterable MongoDB requests include:
A query on a collection.
A write to a document.
A filter applies to a given request if its "apply when" expression evaluates to true given that request's context. If a filter applies to a request, App Services merges the filter's query or projection into the requested operation's existing query and projection.
Multiple filters may apply to a single request.
App Services applies filters to the request before it sends the request to MongoDB.
Example
A collection contains several million documents and has one role with the following "apply when" expression:
{ "owner_id": "%%user.id" }
If no filter is applied, App Services will evaluate a role for each
document that the query matches. We know that App Services will withhold
any document that does not have the user's id as the value of the
owner_id field, so we save time and compute resources by applying
an additional query predicate that excludes those documents before
App Services evaluates any roles:
Apply When | Query | Projection |
|---|---|---|
{ "%%true": true } | { "owner_id": "%%user.id" } | {} |
Define Filters
You can use filters to optimize queries, minimize compute overhead, and secure sensitive data. Filters are most useful for cross-cutting concerns that affect some or all of your queries.
Consider using filters if you want a centralized system to:
Restrict queries to a subset of all documents
Omit sensitive data or unused fields
Example
In a voting app where some users have agreed to anonymously share their vote, you could use the following filter to constrain all queries to an anonymous subset of the existing data:
{ "name": "AnonymizeVotes", "apply_when": true, "query": { "shareVoteAnonymous": true }, "project": { "_id": 0, "age": 1, "vote": 1 } }
{ "_id": ObjectId(...), "name": "sarah", age: 42, "vote": "yes", "shareVoteAnonymous": true } { "_id": ObjectId(...), "name": "andy", age: 22, "vote": "no", "shareVoteAnonymous": true } { "_id": ObjectId(...), "name": "jennifer", age: 37, "vote": "yes", "shareVoteAnonymous": false } { "_id": ObjectId(...), "name": "rick", age: 43, "vote": "no", "shareVoteAnonymous": true } { "_id": ObjectId(...), "name": "tom", age: 64, "vote": "yes", "shareVoteAnonymous": false } { "_id": ObjectId(...), "name": "bob", age: 67, "vote": "yes", "shareVoteAnonymous": true }
{ age: 42, "vote": "yes" } { age: 22, "vote": "no" } { age: 37, "vote": "yes" } { age: 43, "vote": "no" } { age: 64, "vote": "yes" } { age: 67, "vote": "yes" }
Procedure
You can define filters for specific collections in your linked cluster from the App Services UI or by deploying configuration files with Realm CLI:
Note
This guide requires a linked MongoDB Atlas data source.
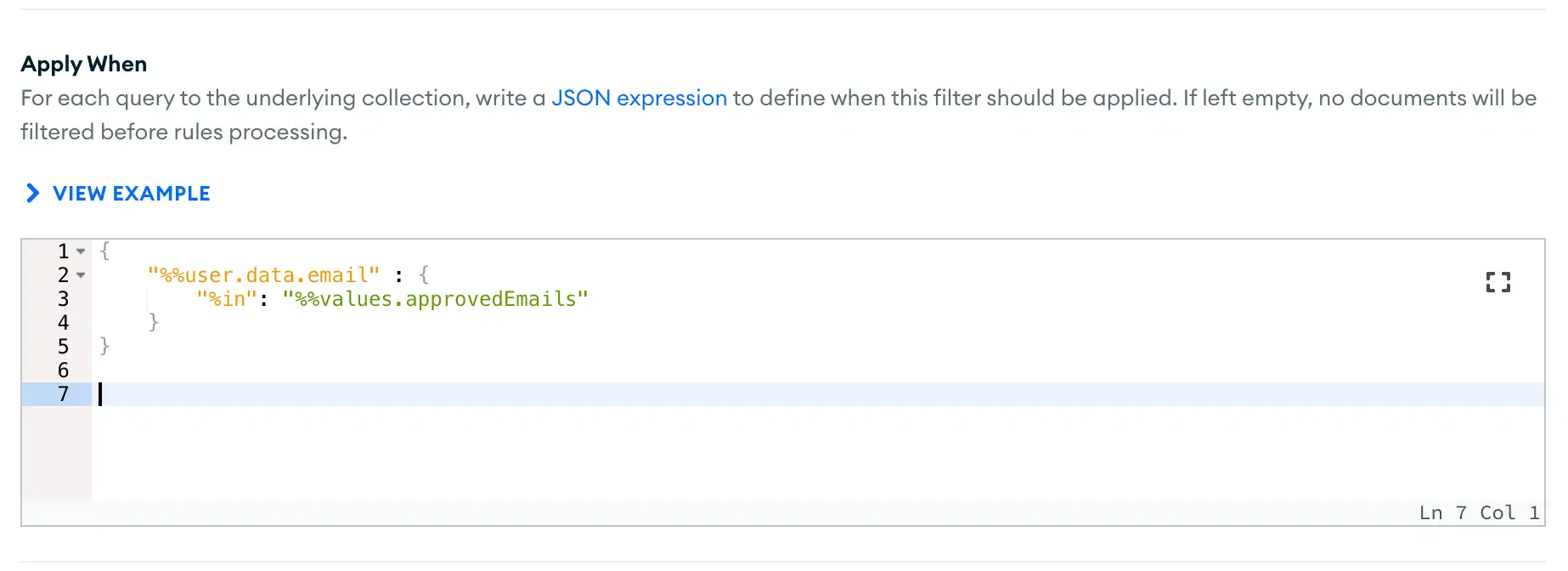
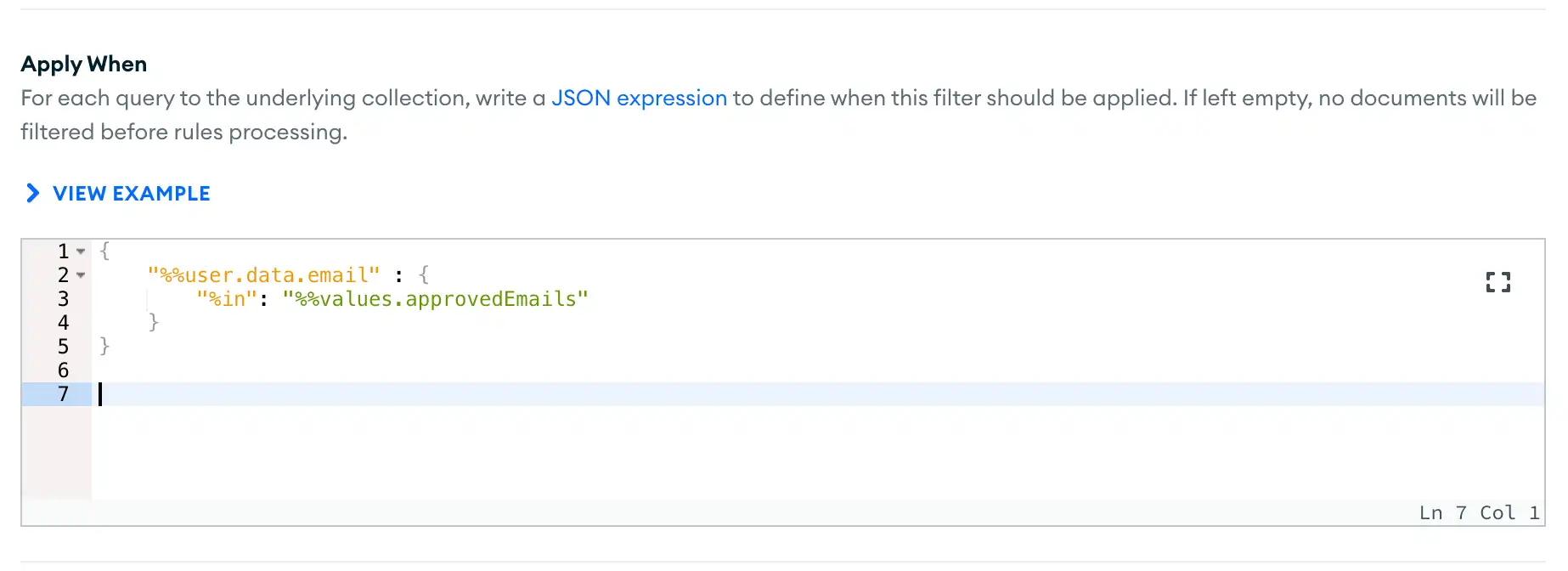
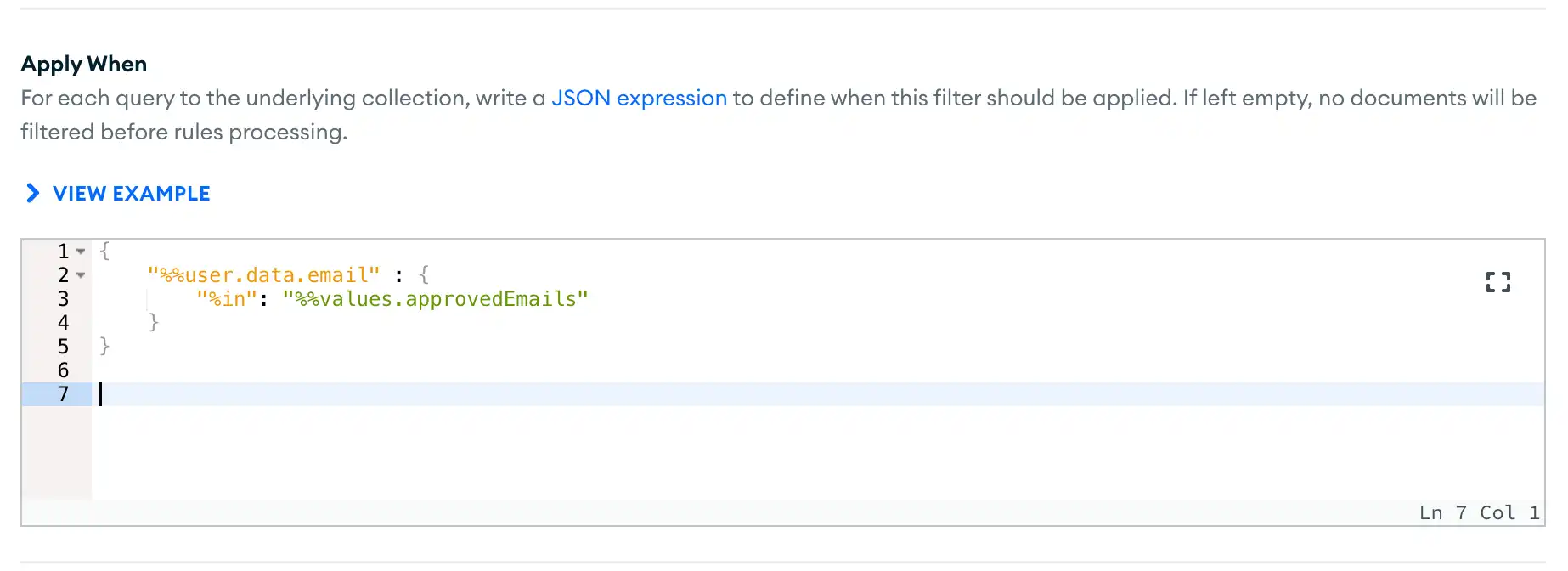
Specify the Apply When Expression
In the Apply When input box, enter a rule expression that defines when the filter applies to a query. If the
expression evaluates to true for an incoming query, App Services adds
the Filter Query parameters to the incoming query.
Important
Atlas App Services evaluates and applies filters before it reads any
documents, so you cannot use MongoDB document expansions in a filter's Apply When expression.
However, you can use other expansions like %%user,
%%values, and %function.
Specify the Filter Query Predicates
In the Query input box, specify a document that contains
additional query predicates to merge into the incoming query when the
filter applies. For example, a filter that withholds documents that
have a score below 20 could use the following filter query:
{ "score": { "$gt": 20 } }
Specify the Filter Projection
In the Projection input box, specify a document that contains a projection document to merge into the incoming query when the filter applies.
For example, a filter that withholds the career_stats and
personal fields from documents could use the following filter
projection:
{ "career_stats": 0, "personal": 0 }
Pull the Latest Version of Your App
To define filters for a collection with appservices, you need a local copy of your application's configuration files.
To pull a local copy of the latest version of your app, run the following:
appservices pull --remote="<Your App ID>"
Tip
You can also download a copy of your application's configuration files from the Deploy > Export App screen in the App Services UI.
Add a Rule Configuration File
To define or modify roles for a collection, open the rules.json
configuration file within the collection's configuration directory.
Tip
Scaffold the Collection
If you haven't already defined rules or a schema for the collection, you
need to manually create its configuration directory and schema.json:
# Create the collection's configuration directory mkdir -p data_sources/<service>/<db>/<collection> # Create the collection's schema file echo '{}' >> data_sources/<service>/<db>/<collection>/rules.json
The configuration file should have the following general form:
{ "database": "<Database Name>", "collection": "<Collection Name>", "roles": [], "filters": [] }
Note
This guide focuses on creating filters for the collection. Check out
the other configuration guides to learn how to define roles and
permissions and enforce
schemas.
Note
Federated data sources do not support rules or schemas. You can only access a Federated data source from a system function.
Add One or More Filters
Add a document to the filters array for each filter that you want
to configure. Filter documents have the following form:
{ "name": "<Filter Name>", "apply_when": { Expression }, "query": { MongoDB Query }, "projection": { MongoDB Projection } }
Field | Description | |
|---|---|---|
namestring | Required. The name of the filter. Filter names are
useful for identifying and distinguishing between filters.
Limited to 100 characters or fewer. | |
apply_whenobject | An expression that determines when this filter applies to an incoming MongoDB operation. ImportantAtlas App Services evaluates and applies filters before it reads any
documents, so you cannot use MongoDB document expansions in a filter's Apply When expression.
However, you can use other expansions like | |
queryobjectDefault: {} | A MongoDB query that App Services merges into a filtered operation's existing query. ExampleA filter withholds documents that have a | |
projectionobjectDefault: {} | A MongoDB projection that App Services merges into a filtered operation's existing projection. ImportantProjection ConflictsMongoDB projections can be either inclusive or exclusive, i.e. they can either return only specified fields or withhold fields that are not specified. If multiple filters apply to a query, the filters must all specify the same type of projection, or the query will fail. ExampleA filter withholds the |
Note
Security Consideration for App Services Filters
While Role-based Permissions and Filters can hide specific documents and fields within a collection there is a potential that data can be exposed if the system allows arbitrary queries to access the collection.
For example, queries or functions that raise errors depending on the values stored in a collection (such as division-by-zero errors) may reveal information about documents, even if a role or filter prevents the querying user from viewing documents directly. Users may also make inferences about the underlying data in other ways (such as by measuring query execution time, which can be affected by the data's distribution).
Be aware that this is possible and audit your data access patterns where neccessary.