A geração aumentada de recuperação (RAG) é uma arquitetura usada para aumentar modelos de linguagem grandes (LLMs) com dados adicionais para que eles possam gerar respostas mais precisas. Você pode implementar RAG em seus aplicativos de IA generativa combinando um LLM com um sistema de recuperação com base na MongoDB Vector Search.
Começar
Para experimentar rapidamente o RAG com o MongoDB Vector Search, use o Construtor de demonstração do chatbot no MongoDB Search Playground. Para saber mais, consulte Construtor de Demonstrações do chatbot no Search Playground.
Para implementar seu próprio sistema RAG com o MongoDB Vector Search, consulte o tutorial nesta página.
Por que usar a RAG?
Ao usar LLMs, você pode encontrar as seguintes limitações:
Dados obsoletos: os LLMssão treinados em um conjunto de dados estático até um determinado ponto no tempo. Isso significa que eles têm uma base de conhecimento limitada e podem usar dados desatualizados.
Sem acesso a dados adicionais: os LLMs não têm acesso a dados locais, personalizados ou específicos de domínio. Portanto, eles podem não ter conhecimento sobre domínios específicos.
Alucinações: quando baseados em dados incompletos ou desatualizados, os LLMs podem gerar respostas imprecisas.
Você pode resolver essas limitações seguindo as seguintes etapas para implementar o RAG:
Ingestão: armazene seus dados personalizados como incorporações vetoriais em um banco de dados vetorial, como MongoDB. Isso permite que você crie uma base de conhecimento de dados atualizados e personalizados.
Recuperação: recupere documentos semanticamente semelhantes do banco de dados com base na pergunta do usuário usando uma solução de pesquisa, como o MongoDB Vector Search. Esses documentos ampliam o LLM com dados adicionais relevantes.
Geração: envie uma solicitação para o LLM. O LLM usa os documentos recuperados como contexto para gerar uma resposta mais precisa e relevante, reduzindo as alucinações.
A RAG é uma arquitetura eficaz para a criação de chatbots de IA, pois permite que os sistemas de IA forneçam respostas personalizadas e específicas de domínio. Para criar chatbots prontos para produção, configure um servidor para rotear as solicitações e construa uma interface de usuário com base na sua implementação RAG.
RAG com a Vector Search do MongoDB
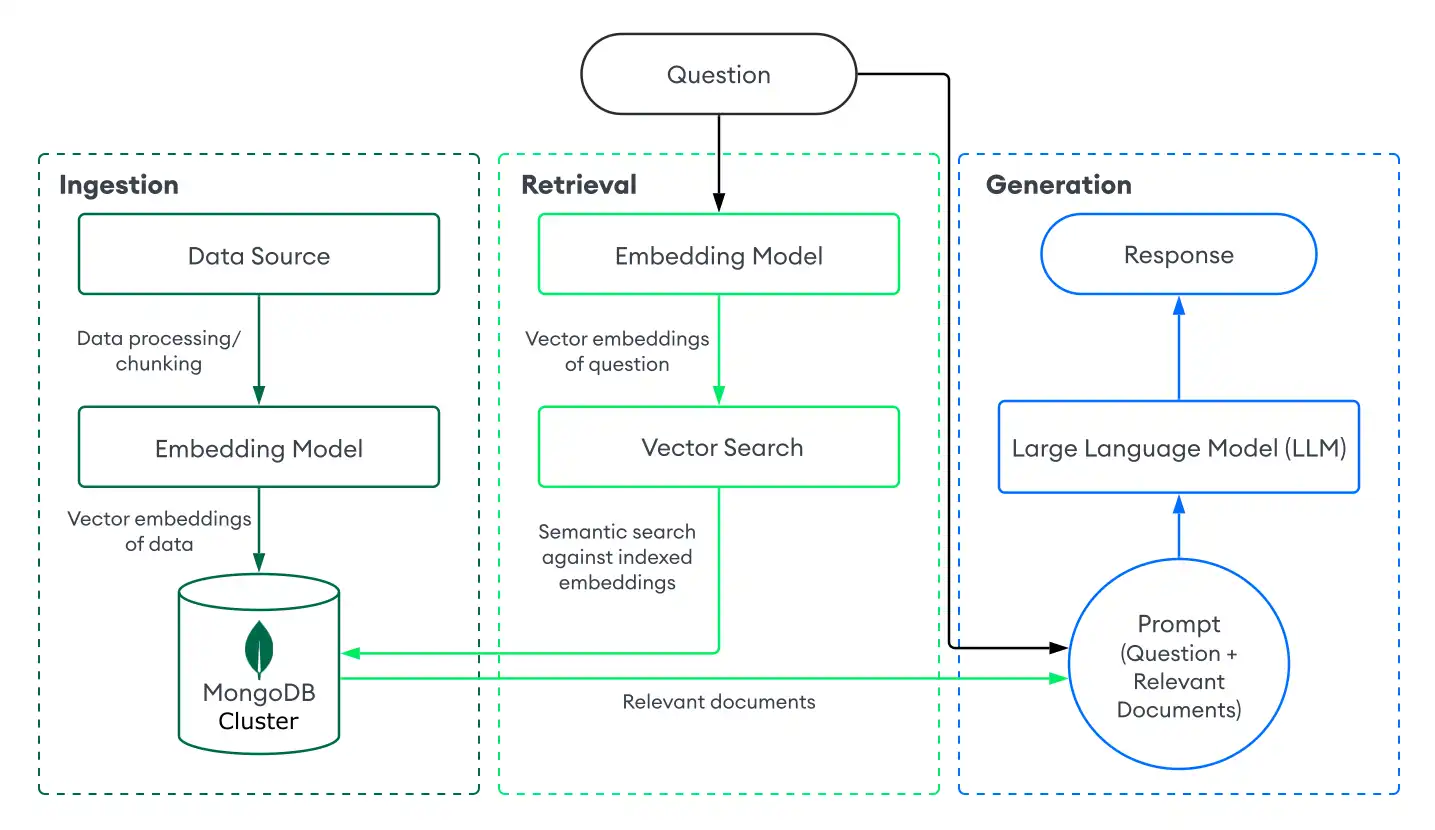
Para implementar o RAG com o MongoDB Vector Search, você ingere dados no MongoDB, recupera documentos com o MongoDB Vector Search e gera respostas usando um LLM. Esta seção descreve os componentes de uma implementação básica ou ingênua de RAG com o MongoDB Vector Search. Para obter instruções passo a passo, consulte Tutorial.
Duração: 5 minutos
Ingestão
A ingestão de dados para RAG envolve o processamento de seus dados personalizados e o armazenamento em um banco de dados vetorial para prepará-los para a recuperação. Para criar um pipeline de ingestão básico com MongoDB como banco de dados vetorial, faça o seguinte:
Prepare seus dados.
Carregue, processe e particione seus dados para prepará-los para o seu aplicativo RAG. O particionamento envolve a divisão dos seus dados em partes menores para gerar uma recuperação ideal.
Converta os dados em incorporações vetoriais.
Converta seus dados em incorporações vetoriais usando um modelo de incorporação. Para aprender mais, consulte Como criar manualmente incorporações vetoriais.
Armazene os dados e incorporações no MongoDB.
Armazene essas incorporações em seu cluster. Você armazena incorporações como um campo junto com outros dados em sua coleção.
Retrieval
A criação de um sistema de recuperação envolve a pesquisa e a devolução dos documentos mais relevantes do seu banco de dados vetorial para aumentar o LLM. Para recuperar documentos relevantes com a Vector Search do MongoDB, converta a pergunta do usuário em incorporações vetoriais e execute uma query de pesquisa vetorial nos dados de sua collection do MongoDB para encontrar documentos com as incorporações mais semelhantes.
Para realizar a recuperação básica com o MongoDB Vector Search, faça o seguinte:
Defina um índice do MongoDB Vector Search na collection que contém suas incorporações vetoriais.
Escolha um dos seguintes métodos para recuperar documentos com base na pergunta do usuário:
Use uma integração do MongoDB Vector Search com uma estrutura ou serviço popular. Essas integrações incluem bibliotecas integradas e FERRAMENTAS que permitem criar facilmente sistemas de recuperação com o MongoDB Vector Search.
Construa seu próprio sistema de recuperação. Você pode definir suas próprias funções e pipelines para executar queries do MongoDB Vector Search específicas para seu caso de uso.
Para saber como criar um sistema básico de recuperação com o MongoDB Vector Search, consulte Tutorial.
Geração
Para gerar respostas, combine seu sistema de recuperação com um LLM. Depois de realizar uma pesquisa vetorial para recuperar documentos relevantes, você fornece a pergunta do usuário junto com os documentos relevantes como contexto para o LLM para que ele possa gerar uma resposta mais precisa.
Escolha um dos seguintes métodos para se conectar a um LLM:
Use uma integração do MongoDB Vector Search com uma estrutura ou serviço popular. Essas integrações incluem bibliotecas integradas e FERRAMENTAS para ajudá-lo a se conectar aos LLMs com o mínimo de configuração.
Chame a API do LLM. A maioria dos provedores de IA oferece APIs para seus modelos generativos que você pode usar para gerar respostas.
Carregue um LLM de código aberto. Se você não tiver chaves de API ou créditos, poderá usar um LLM de código aberto carregando-o localmente a partir do seu aplicação. Para obter um exemplo de implementação, consulte o tutorial Criar uma implementação de RAG local com Vector Search do MongoDB.
Tutorial
O exemplo a seguir demonstra como implementar RAG com um sistema de recuperação alimentado pelo MongoDB Vector Search. Selecione o modelo de incorporação, o LLM e a linguagem de programação de sua preferência para começar:
Próximos passos
Para tutoriais de RAG adicionais, consulte os seguintes recursos:
Para aprender a implementar RAG com frameworks de LLM e serviços de IA populares, consulte Integrações de IA do MongoDB.
Para saber como implementar RAG usando um sistema local do Atlas e modelos locais, consulte Criar uma implementação local do RAG com o MongoDB Vector Search.
Para tutoriais baseados em casos de uso e notebooks interativos em Python, veja o Repositório de docs e notebooks e o Repositório de casos de uso de IA generativa.
Para criar agentes de IA e implementar RAG agente, consulte Criar agentes de IA com MongoDB.
Melhore seus resultados
Para otimizar seus aplicativos RAG, certifique-se de usar um modelo de incorporação poderoso como Voyage AI para gerar incorporações vetoriais de alta qualidade.
Além disso, o MongoDB Vector Search oferece suporte a sistemas avançados de recuperação. Você pode indexar dados vetoriais perfeitamente junto com seus outros dados em seu cluster. Isso permite que você melhore seus resultados pré-filtrando outros campos em sua collection ou realizando pesquisa híbrida que combina pesquisa semântica com resultados de pesquisa de texto completo.
Estratégias de chunking
O chunking divide documentos grandes em segmentos menores antes de gerar incorporações. A estratégia correta de chunking pode melhorar significativamente a qualidade da recuperação do seu aplicação RAG.
Uma estratégia de chunking consiste nos seguintes componentes principais:
Téc
Tamanho do chunk: número máximo de caracteres ou tokens por chunk.
Sobreposição de chunk: número de caracteres ou tokens sobrepostos entre chunks adjacentes. A sobreposição ajuda a preservar o contexto entre os limites de chunks.
Estratégias comuns de chunking incluem:
Estratégia | Melhor para |
|---|---|
Token fixo | Casos de uso simples com estrutura de conteúdo uniforme. |
Token fixo com sobreposição | Clustering de uso geral em que o contexto ultrapassa os limites do chunk. |
Recursivo | Documentos de texto onde você deseja preservar os limites de número e frase. |
Recursivo específico do idioma | Código ou documentação técnica com trechos de linguagem de programação. |
Semântica | Documentos sem limites estruturados claros, como redações ou conteúdo analítico. |
Para experimentar estratégias de agrupamento, use o Construtor de Demonstrações do chatbot no MongoDB Search Playground, que permite experimentar o agrupamento recursivo e o agrupamento de token fixo com sobreposição.
Para obter um tutorial prático que avalia diferentes estratégias de chunking usando a estrutura de Ragas, consulte o bloco de notas Chunking Estratégias no repositório GenAI-showcase.
Você também pode usar os seguintes recursos: