Atlas for the Edge
Reliable data where you need it, when you need it
Edge computing powers critical, real-time use cases that drive operational efficiency, machine learning, disaster recovery, autonomous vehicles and more. With Atlas for the Edge, you benefit from the power of reliable data where you need it, when you need it.Unlock speed, for your users and your teams
Unify your edge data with ease
Enjoy the flexibility to deploy MongoDB at any edge location to improve availability, performance, and costs. Atlas for the Edge unifies across your local data sources and devices to provide a single, reliable, and real-time source of truth.Real-time data processing for mobile, edge, and IoT
Handle data from millions of devices such as sensors, smart devices, mobile phones, and kiosks with Atlas Stream Processing. Deploy automatic anomaly detection or predictive maintenance on time series collections with real-time reporting and alerting.Easily secure edge applications
Leverage the enterprise-grade security built into the leading developer data platform. Data is encrypted in-flight, on-devices, and at-rest. Deploy fine-grained role-based access for sensitive data with built-in identity management, or integrate with a third party identity management solution.Core platform capabilities
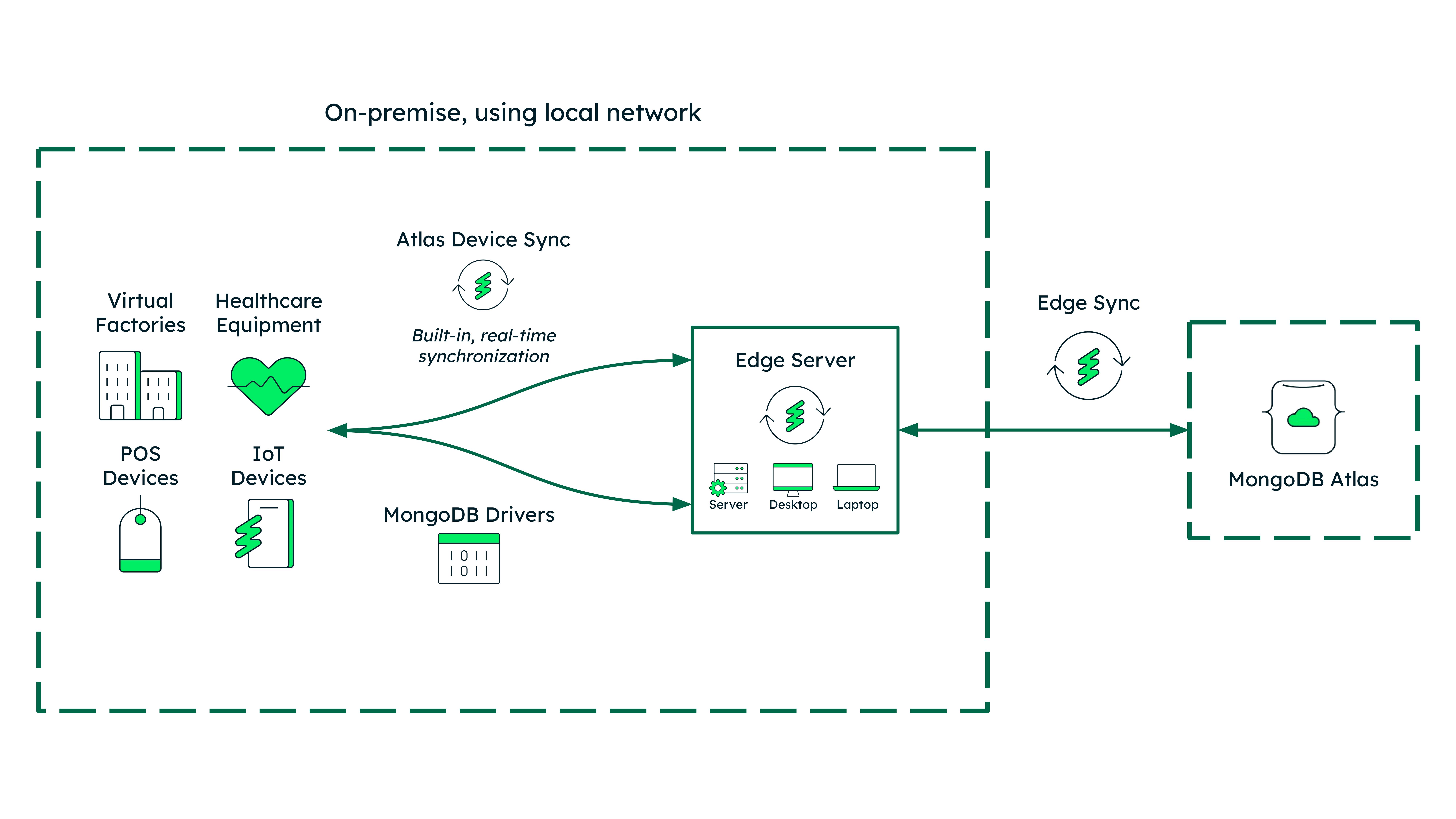
Deploy Atlas Edge Server anywhere
From popular edge servers on the market to edge infrastructure provided by cloud providers, deploy MongoDB anywhere, and leverage Atlas Edge Server to connect it to Atlas.
Sync your data sources
Automatically merge conflicting updates from on-premise data centers, edge devices, and the cloud to a single source of truth with Atlas Device Sync.
Unify on a single, powerful platform
Integrate your distributed data sources to a single place in Atlas and leverage powerful platform capabilities like Stream Processing, Time Series, and more.
Always-on availability
A tiered architecture with data on an Atlas Edge Server, plus data on-device, ensures network fault tolerance at edge locations. Edge devices can continue functioning over a local network.
Lightning fast user experiences
Store and process data locally, on edge devices and servers using Atlas Device Sync to ensure real-time and offline user experiences use up-to-date data.
Machine learning at the edge
Deploy machine learning models at the edge to utilize real-time data without delays.
“Atlas for the Edge allowed us to move faster while providing enterprise-grade experiences. Atlas Device Sync enables real-time updates and high reliability. Machine learning models distributed down to devices can then provide low-latency inference, computer vision, and augmented reality.”


Introducing Atlas for the Edge
Edge computing is exciting but comes with significant challenges. Read about our announcement of Atlas for the Edge and how leading enterprises are leveraging the solution for their business-critical initiatives.FAQ
What is edge computing?
What are the benefits of edge computing?
Edge computing offers significant opportunities for organizations that require distributed applications to reach end users with minimal latency. The distributed computing framework and data storage patterns leveraged in edge computing architectures, including processing data locally, results in:
- Low latency data processing and access
- Network fault tolerance (tolerance to disconnection)
- Real-time data synchronization that enable time-sensitive use cases
- High volume local data and data processing
- Data privacy
- Processing power
- Computing tasks
Edge computing addresses many key business pain points and can be strategic for many businesses for these reasons.
What are some challenges with edge computing?
Edge computing comes with significant challenges including:
- Wide array of vendors, each for a specific purpose
- Implementing security protocols
- Limited computing resources
- Network bandwidth restrictions
Data storage also presents challenges when dealing with edge computing:
- Modern edge strategies require specialized technical skills and expertise to manage the complexity and volume of data resulting from these distributed architectures to deliver meaningful value.
- Many edge deployments require stitching together solutions from multiple vendors, resulting in complex and fragile systems often built with legacy technology that is limited by one-way data movement or require specialized skills to manage and operate.
- Physical edge devices require careful optimization due to their limitations — like limited data storage, network access, and power — which comes with trade-offs between performance and availability, and even then, edge deployments can still encounter unreliable network connectivity and bandwidth limitations, along with security vulnerabilities of devices.
What are some examples of edge computing? What is edge computing useful for?
Examples of edge computing include:
- Edge devices such as sensors or machinery - data generated on the factory floor is sent and synced to the cloud, processed in flight with something like Atlas Stream Processing
- Autonomous vehicles are also edge devices that collect critical data, leverage machine learning models locally, and sync with the cloud
- Medical monitoring devices that have patient data that should be accessible
- Sensors at remote locations like oil rigs
- Self-checkout kiosks that need to keep client data synced with backend data
- Connected devices
- Automation and machine learning