$rankFusion and $scoreFusion stages are available as Preview features. To learn more, see Preview Features.Important
$rankFusion is only available for deployments that use MongoDB
8.0 or higher.
Definition
$rankFusion$rankFusionfirst executes all input pipelines independently and then de-duplicates and combines the input pipeline results into a final ranked results set.$rankFusionoutputs a ranked set of documents based on the ranks the input documents appear in their input pipelines and the pipeline weights. This stage uses the Reciprocal Rank Fusion algorithm to rank the combined results of the input pipelines.Use
$rankFusionto search for documents in a single collection based on multiple criteria and retrieve a final ranked results set that factors in all specified criteria.
Syntax
The stage has the following syntax:
{ $rankFusion: { input: { pipelines: { <myPipeline1>: <expression>, <myPipeline2>: <expression>, ... } }, combination: { weights: { <myPipeline1>: <numeric expression>, <myPipeline2>: <numeric expression>, ... } }, scoreDetails: <bool> } }
Command Fields
$rankFusion takes the following fields:
Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Object | Defines the input that |
input.pipelines | Object | Contains a map of pipeline names to the aggregation stages that define
that pipeline. For more information on input pipeline restrictions, see Input Pipelines and Input Pipeline Names. |
| Object | Optional. Defines how to combine the |
combination.weights | Object | Optional. Contains a map from If you do not specify a weight, the default value is 1. |
| Boolean | Default is false. Specifies if |
Behavior
Collections
You can only use $rankFusion with a single collection. You cannot use this
aggregation stage at a database scope.
De-Duplication
$rankFusion de-duplicates the results across multiple input pipelines in the
final output. Each unique input document appears at most once in the
$rankFusion output, regardless of the number of times that the document
appears in input pipeline outputs.
Input Pipelines
Each input pipeline must be both a Selection Pipeline and a Ranked Pipeline.
Selection Pipeline
A Selection Pipeline retrieves a set of documents from a collection without
performing any modifications after retrieval. $rankFusion compares documents
across different input pipelines which requires that all input pipelines output
the same unmodified documents.
Note
If you want to modify the documents that you search for with $rankFusion,
perform those modifications after the $rankFusion stage.
A selection pipeline must only contain the following stages:
Type | Stages |
|---|---|
Search Stages |
If you use |
Ordering Stages | |
Pagination Stages |
Ranked Pipeline
A ranked pipeline sorts or orders documents. $rankFusion uses the order of
ranked pipeline results to influence the output ranking. Ranked pipelines must
meet one of the following criteria:
Begin with one of the following ordered stages:
Contain an explicit
$sortstage.
Input Pipeline Names
Pipeline names in input must meet the following restrictions:
Must not be an empty string
Must not start with a
$Must not contain the ASCII null character delimiter
\0anywhere in the stringMust not contain a
.
Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) Formula
$rankFusion orders results according to the Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF)
Formula. This stage places the RRF score for each document in the score
metadata field of the output results. The RRF formula ranks documents with a
combination of the following factors:
The placement of documents in input pipeline results
The number of times that a document appears in different input pipelines
The
weightsof input pipelines.
For example, if a document has a high ranking in multiple pipeline result sets, the RRF score for that document would be higher than if that same document has the same ranking in some input pipelines, but is not present (or has a lower ranking) in the other pipelines
The Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) Formula is equivalent to the following algebraic operation:
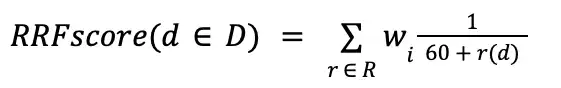
Note
In this formula, 60 is a sensitivity parameter that MongoDB determined.
The below table contains the variables that the RRF formula uses:
Variable | Description |
|---|---|
D | The set of result documents for the whole operation. |
d | The document that the RRF score is being computed for. |
R | The set of ranks for input pipelines that |
r(d) | The rank of document |
w | The weight of the input pipeline that |
Each term in the summation represents the appearance of a document d in one
of the input pipelines. The total RRF score for d is the summation of
each of these terms across all the input pipelines that d appears in.
RRF Calculation Example
Consider a $rankFusion pipeline stage with one $search and one
$vectorSearch input pipeline.
All input pipelines output the same 3 documents: Document1, Document2,
and Document3.
The $search pipeline ranks the documents in the following order:
Document3Document2Document1
The $vectorSearch pipeline ranks the documents in the following order:
Document1Document2Document3.
rankFusion computes the RRF score for Document1 through the following
operation:
RRFscore(Document1) = 1/(60 + search_rank_of_Document1) + (1/(60 + vectorSearch_rank_of_Document1)) RRFscore(Document1) = 1/63 + 1/61 RRFscore(Document1) = 0.0322664585
The score metadata field for Document1 is 0.0322664585.
scoreDetails
If you set scoreDetails to true, $rankFusion creates a
scoreDetails metadata field for each document. The scoreDetails field
contains information about the final ranking.
Note
When you set scoreDetails to true, $rankFusion sets the
scoreDetails metadata field for each document but does not automatically
output the scoreDetails metafield.
To view the scoreDetails metadata field, you must either:
use a
$projectstage after$rankFusionto project thescoreDetailsfielduse a
$addFieldsstage after$rankFusionto add thescoreDetailsfield to your pipeline output
The scoreDetails field contains the following subfields:
Field | Description |
|---|---|
| The numerical value of the RRF score for this document. |
| A description of how |
| An array where each array entry contains information about the input pipelines that output this document. |
Each array entry in the details field contains the following subfields:
Field | Description |
|---|---|
| The name of the input pipeline that output this document. |
| The rank of this document in the input pipeline. Rank is |
| The weight of the input pipeline. |
| Optional. If the input pipeline outputs a |
| Optional. If the input pipeline outputs a |
| The |
Warning
MongoDB does not guarantee any specific output format for
scoreDetails.
For example, the following code blocks shows the scoreDetails field for a
$rankFusion operation with $search, $vectorSearch, and $match
input pipelines:
{ value: 0.030621785881252923, description: "value output by reciprocal rank fusion algorithm, computed as sum of weight * (1 / (60 + rank)) across input pipelines from which this document is output, from:" details: [ { inputPipelineName: 'search', rank: 2, weight: 1, value: 0.3876491287, description: "sum of:", details: [... omitted for brevity in this example ...] }, { inputPipelineName: 'vector', rank: 9, weight: 3, value: 0.7793490886688232, details: [ ] }, { inputPipelineName: 'match', rank: 10, weight: 1, details: [] } ] }
Explain Results
MongoDB converts $rankFusion operations into a set of existing aggregation
stages that, in combination, compute the output result prior to query execution.
The Explain Results for a $rankFusion operation
show the full execution of the underlying aggregation stages that
$rankFusion uses to compose the final result.
Examples
This example uses a collection with embeddings and text fields. Create
search and vectorSearch type indexes on the collection.
The following index definition automatically indexes all the
dynamically indexable fields in the collection for running
$search queries against the indexed fields.
db.embedded_movies.createSearchIndex( "search_index", { mappings: { dynamic: true } } )
The following index definition indexes the field with the embeddings in
the collection for running $vectorSearch queries against
that field.
db.embedded_movies.createSearchIndex( "vector_index", "vectorSearch", { "fields": [ { "type": "vector", "path": "<FIELD_NAME>", "numDimensions": <NUMBER_OF_DIMENSIONS>, "similarity": "dotProduct" } ] } );
The following aggregation pipeline uses $rankFusion with the following input
pipelines:
Pipeline | Number of Documents Returned | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | Runs a vector search on the field indexed as |
| 20 | Runs a full-text search for the same term and limits the results to 20 documents. |
1 db.embedded_movies.aggregate( [ 2 { 3 $rankFusion: { 4 input: { 5 pipelines: { 6 searchOne: [ 7 { 8 "$vectorSearch": { 9 "index": "<INDEX_NAME>", 10 "path": "<FIELD_NAME>", 11 "queryVector": <QUERY_EMBEDDINGS>, 12 "numCandidates": 500, 13 "limit": 20 14 } 15 } 16 ], 17 searchTwo: [ 18 { 19 "$search": { 20 "index": "<INDEX_NAME>", 21 "text": { 22 "query": "<QUERY_TERM>", 23 "path": "<FIELD_NAME>" 24 } 25 } 26 }, 27 { "$limit": 20 } 28 ], 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 }, 33 { $limit: 20 } 34 ] )
This operation performs the following actions:
Executes the
inputpipelinesCombines the returned results
Outputs the first 20 documents which are the top 20 ranked results of the
$rankFusionpipeline
The C# examples on this page use the sample_mflix database
from the Atlas sample datasets. To learn how to create a
free MongoDB Atlas cluster and load the sample datasets, see
Get Started in the MongoDB .NET/C#
Driver documentation.
The following Movie class models the documents in the sample_mflix.movies
collection:
public class Movie { public ObjectId Id { get; set; } public int Runtime { get; set; } public string Title { get; set; } public string Rated { get; set; } public List<string> Genres { get; set; } public string Plot { get; set; } public ImdbData Imdb { get; set; } public int Year { get; set; } public int Index { get; set; } public string[] Comments { get; set; } [] public DateTime LastUpdated { get; set; } }
Note
ConventionPack for Pascal Case
The C# classes on this page use Pascal case for their property names, but the
field names in the MongoDB collection use camel case. To account for this difference,
you can use the following code to register a ConventionPack when your
application starts:
var camelCaseConvention = new ConventionPack { new CamelCaseElementNameConvention() }; ConventionRegistry.Register("CamelCase", camelCaseConvention, type => true);
To use the MongoDB .NET/C# driver to add a $rankFusion stage to an aggregation
pipeline, call the RankFusion() method on a PipelineDefinition object.
Before running the following example, you must create a MongoDB
Search index named default. Include the following code in your
application to create a search index on the movies collection:
var collection = client.GetDatabase("sample_mflix").GetCollection<Movie>("movies"); var index = new BsonDocument { { "mappings", new BsonDocument { { "dynamic", true } } } }; collection.SearchIndexes.CreateOne(index, "default");
The following example creates a pipeline stage that executes two pipelines, searchPlot and searchGenre,
that perform $search operations by using the default search index. The
$rankFusion stage then ranks the search results based on each $search
pipeline's assigned weight and returns the ordered results. The pipeline includes
the scoreDetails field in the return documents by enabling the ScoreDetails
option in the RankFusionOptions instance passed to the RankFusion() method.
var searchPipelines = new Dictionary<string, PipelineDefinition<Movie, Movie>> { { "searchPlot", new EmptyPipelineDefinition<Movie>() .Search( Builders<Movie>.Search.Text(Builders<Movie>.SearchPath.Single(m => m.Plot), "space")) }, { "searchGenre", new EmptyPipelineDefinition<Movie>() .Search( Builders<Movie>.Search.Text(Builders<Movie>.SearchPath.Single(m => m.Genres), "adventure")) } }; var weights = new Dictionary<string, double> { { "searchPlot", 0.4 }, { "searchGenre", 0.6 } }; var pipeline = new EmptyPipelineDefinition<Movie>() .RankFusion(searchPipelines, weights, new RankFusionOptions<Movie> { ScoreDetails = true });
The Node.js examples on this page use the sample_mflix database from the
Atlas sample datasets. To learn how to create a free
MongoDB Atlas cluster and load the sample datasets, see Get Started in the MongoDB Node.js driver documentation.
To use the MongoDB Node.js driver to add a $rankFusion stage to an aggregation
pipeline, use the $rankFusion operator in a pipeline object.
Before running the following example, you must create a MongoDB
Search index named default. Include the following code in your
application to create a search index on the movies collection:
const index = { name: "default", definition: { mappings: { dynamic: true } } } const result = collection.createSearchIndex(index);
The following example creates a pipeline stage that executes two pipelines, searchPlot and searchGenre, that
perform $search operations by using the default
search index. The $rankFusion stage then ranks the search
results based on each $search pipeline's assigned weight and
returns the ordered results. The $addFields stage
includes the scoreDetails field in the return documents. The
example then runs the aggregation pipeline:
const pipeline = [ { $rankFusion: { input: { pipelines: { searchPlot: [ { $search: { index: "default", text: { query: "space", path: "plot"} } } ], searchGenre: [ { $search: { index: "default", text: { query: "adventure", path: "genres" } } } ] } }, combination: { weights: {searchPlot: 0.6, searchGenre: 0.4} }, scoreDetails: true } }, { $addFields: { scoreDetails: { $meta: "searchScoreDetails" } } } ]; const cursor = collection.aggregate(pipeline); return cursor;