You can deploy MongoDB Search and Vector Search in your Kubernetes cluster to build powerful search experiences directly within your applications. Using MongoDB Search and Vector Search, you can build both traditional text search and AI-powered vector search capabilities that automatically sync with an on-premises MongoDB database. This eliminates the need to maintain separate systems in sync while providing advanced search features. To learn more, see:
To enable the search capabilities such as full-text and semantic search
in on-prem deployments, you must deploy the MongoDB Search and
Vector Search process (mongot) and connect it with your MongoDB
database deployment (mongod). Deployment of mongot is optional
and is needed only if you plan to leverage the search features it offers.
The MongoDB Database processes (mongod) acts as the proxy for all
search queries for mongot. The mongod forwards the query to
mongot, which processes the query. The mongot returns the query
results to the mongod, which then forwards the results to you. You
never interact directly with the mongot.
Each mongot process has its own persistent volume that is not shared
with the database or other search nodes. Storage is used to maintain
indexes that are built from the data continuously sourced from the
database. The index definitions (metadata) are stored in the database
itself.
The mongot performs the following actions:
Manages the index.
The
mongotis responsible for updating the index definitions in the database.Sources the data from the database.
The
mongotnodes establish permanent connections to the database in order to update indexes from the database in real time.Processes search queries.
When
mongodreceives a$search,$searchMeta, or$vectorSearchquery, it directs the query to one of themongotnodes. Themongotthat receives the query processes the query, aggregates the data, and returns the results tomongod, which it forwards to the user.
The mongot components are tightly coupled with a single MongoDB
replica set and cannot be shared across multiple databases or replica
sets. That means a replica set deployment has its own dedicated search
nodes.
Network connectivity between mongot and mongod goes in both
directions:
mongotestablishes connection to the replica set to source the data used to build indexes and run queries.mongodconnects tomongotto forward search related operations such as index management and querying the data.
MongoDB Search and Vector Search Deployment
There are not many differences between the search deployment architecture with or without the Kubernetes Operator. The Kubernetes Operator simplifies the steps required to deploy fully functioning search nodes, especially when the database is also managed by the Kubernetes Operator.
To deploy, you apply the MongoDBSearch Custom Resource (CR), which
the Kubernetes Operator picks up and starts deploying mongot pods and
requests persistent storage specified in the spec. The MongoDB Search
and Vector Search deployed using the Kubernetes Operator can target MongoDB
replica set deployed by the Kubernetes Operator inside the same Kubernetes cluster
or a completely independent external MongoDB database. To learn how to
deploy and configure mongot to use:
A MongoDB replica set in Kubernetes, see Install and use With MongoDB Community Edition or Install and Use Search With MongoDB Enterprise Edition
An external MongoDB replica set, see Install and Use MongoDB Search and Vector Search With External MongoDB Enterprise Edition.
Pre-Requisites
In order to leverage MongoDB Search and Vector Search in your:
MongoDB Community deployment, you must have a fully functional MongoDB 8.2+ replica set deployed inside a Kubernetes cluster using the Kubernetes Operator.
MongoDB Enterprise deployment, you must have a fully functional MongoDB 8.2+ replica set deployed in one of the following ways:
Inside a Kubernetes cluster using the Kubernetes Operator
Outside a Kubernetes cluster
Cloud Manager or Ops Manager Instance
Before you begin, consider the following:
You must have a working
StorageClassfor the creation of persistent volumes in the|k8s| cluster. Without this, yourPersistentVolumeClaimsmight remain pending and MongoDB might not have durable storage.You must have a correctly configured cluster networking. Services such as ClusterIP, NodePort, or LoadBalancer must be able to route traffic. If external clients need access, set up an ingress or load balancer.
Your database and search nodes must have enough CPU, memory, and disk space allocated because MongoDB database, and MongoDB Search and Vector Search workloads are resource-intensive. We recommend using requests and limits in your Pod specs to avoid eviction or throttling.
Your Kubernetes version must be supported by the MongoDB operator or Helm chart you want to use. Some CRDs or APIs differ across versions. To learn more, see MongoDB Controllers for Kubernetes Operator Compatibility.
You must create any required RBAC roles and role bindings so that the Kubernetes Operator and processes running within the Pods can manage resources.
Configuration Tasks
The following table shows the configuration tasks that the Kubernetes Operator automatically performs and the actions that you must take to successfully deploy MongoDB Search and Vector Search in Kubernetes and connect to a MongoDB replica set in Kubernetes or an external MongoDB replica set.
Task | (Inside Kubernetes) Performed by | (External MongoDB) Performed by |
|---|---|---|
Deploy Ops Manager inside Kubernetes | Kubernetes Operator | Kubernetes Operator |
Deploy Cloud Manager or Ops Manager outside Kubernetes | You | You |
Deploy MongoDB replica set | Kubernetes Operator | You |
Create MongoDBSearch custom resource | You | You |
Provide connection string to MongoDB replica set | Kubernetes Operator | You |
Create | Kubernetes Operator | Kubernetes Operator |
Set necessary replica set parameters in each | Kubernetes Operator | You |
Create user for | Kubernetes Operator and you by applying MongoDBUser resource | You |
Configure MongoDB replica set with a user that has necessary permissions to query search | You | You |
Create MongoDB Search and Vector Search indexes | You | You |
Expose search pods externally for connecting from each | Not necessary | You |
Expose mongod pods externally for connecting from | Not necessary | You |
The following diagram shows the deployment architecture of a single MongoDB Search and Vector Search instance with a MongoDB Enterprise replica set in a Kubernetes cluster.
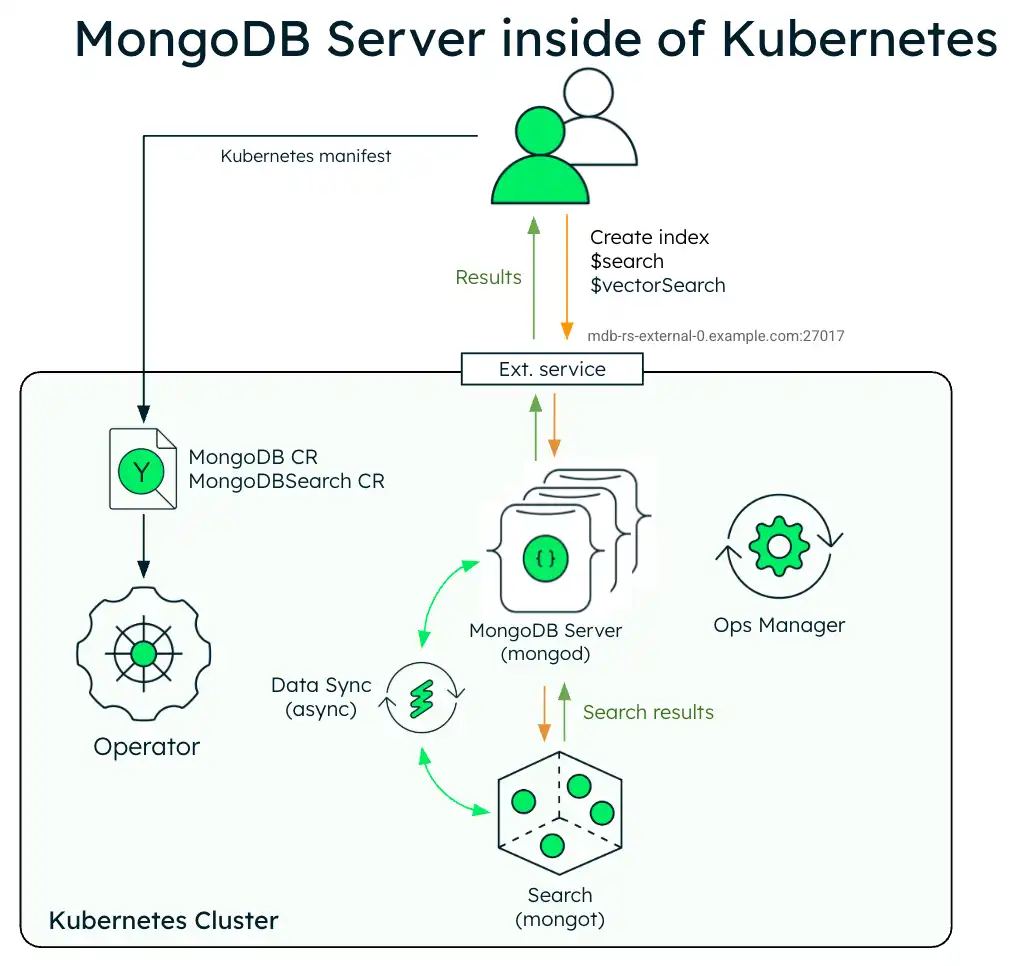
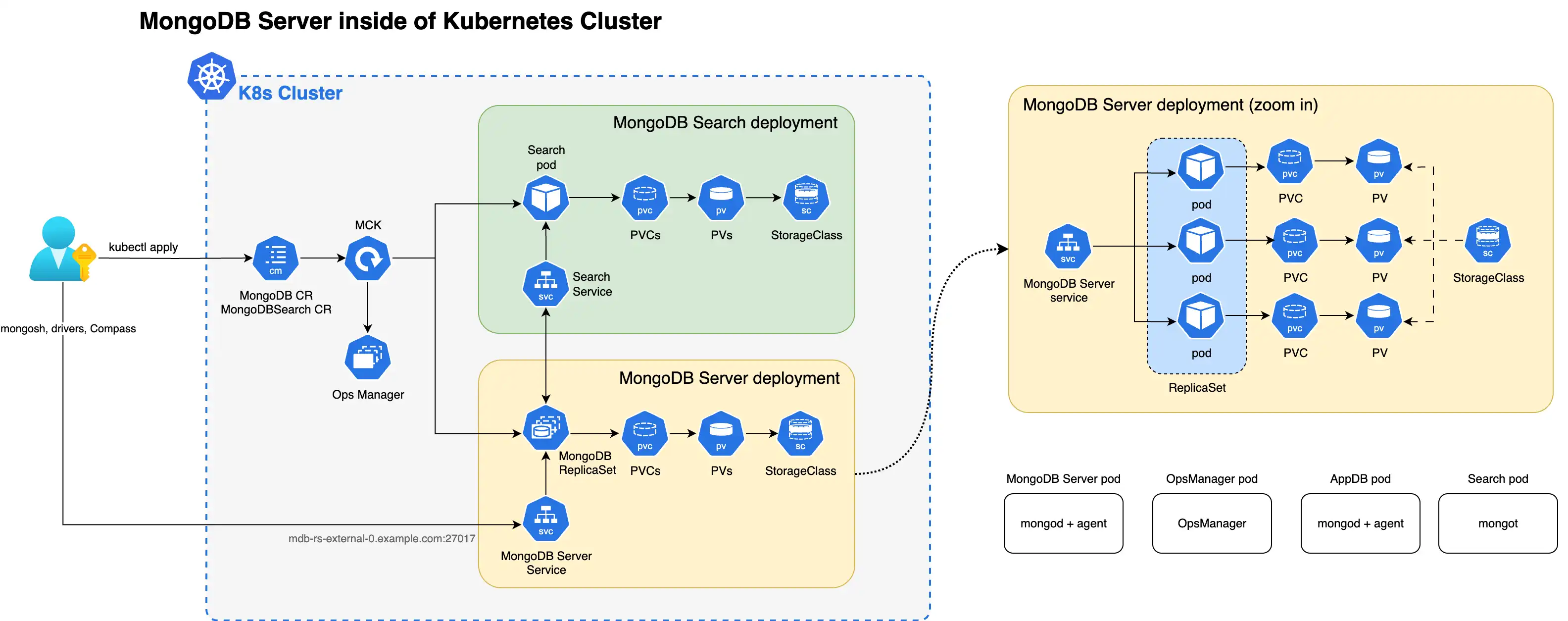
The following diagram shows the components that the Kubernetes Operator deploys in a Kubernetes cluster for MongoDB Search and Vector Search with a MongoDB Enterprise Edition replica set.
When both the mongot and mongod processes are deployed inside
the Kubernetes cluster, the Kubernetes Operator performs configuration for both
processes automatically. Specifically, the Kubernetes Operator performs the
following operations:
Finds the MongoDB CR referenced by MongoDBSearch using
spec.source.mongodbResourceRef, or by a naming convention by looking for MongoDB CR with the same name as MongoDBSearch.Generates
mongotconfiguration in a YAML file and saves it to a config map named<MongoDBSearch.metadata.name>-search-config.The Config map is mounted by the search pods and the YAML configuration is used by
mongot's process on startup. The generated YAML contains all the information about how to connect to the replica set, TLS settings, and so on.Deploys MongoDB Search and Vector Search stateful set named
<MongoDBSearch.metadata.name>-searchwith storage and resource requirements configured according to thespec.persistenceandspec.resourceRequirementssettings in the CR.Updates configuration of every
mongodprocess by adding the necessarysetParameteroptions, including the hostnames and port numbers of the mongot hosts. necessarysetParameteroptions, including the hostnames and port numbers of the MongoDB replica set members.
You must perform the following actions:
Create a user in the replica set using a
MongoDBUsercustom resource. Themongotuses the credentials of this user to connect to the replica set to source the data:The user name is arbitrary (in the examples, we use
search-sync-source-user), but it must have thesearchCoordinatorrole set.The username and password of this user is passed in
MongoDBSearch.spec.source.usernameandMongoDBSearch.spec.source.passwordSecretRefrespectively.The password secret can refer to the same secret containing user password that was used to create
MongoDBUserspec (inMongoDBUser.spec.source.passwordSecretKeyRef).
Configure and apply the MongoDBSearch custom resource.
To learn more about the CR settings for the
mongot process, see MongoDB Search and Vector Search Settings.
The following diagram shows the deployment architecture of MongoDB Search and Vector Search in a Kubernetes cluster using an external MongoDB Enterprise Edition replica set.
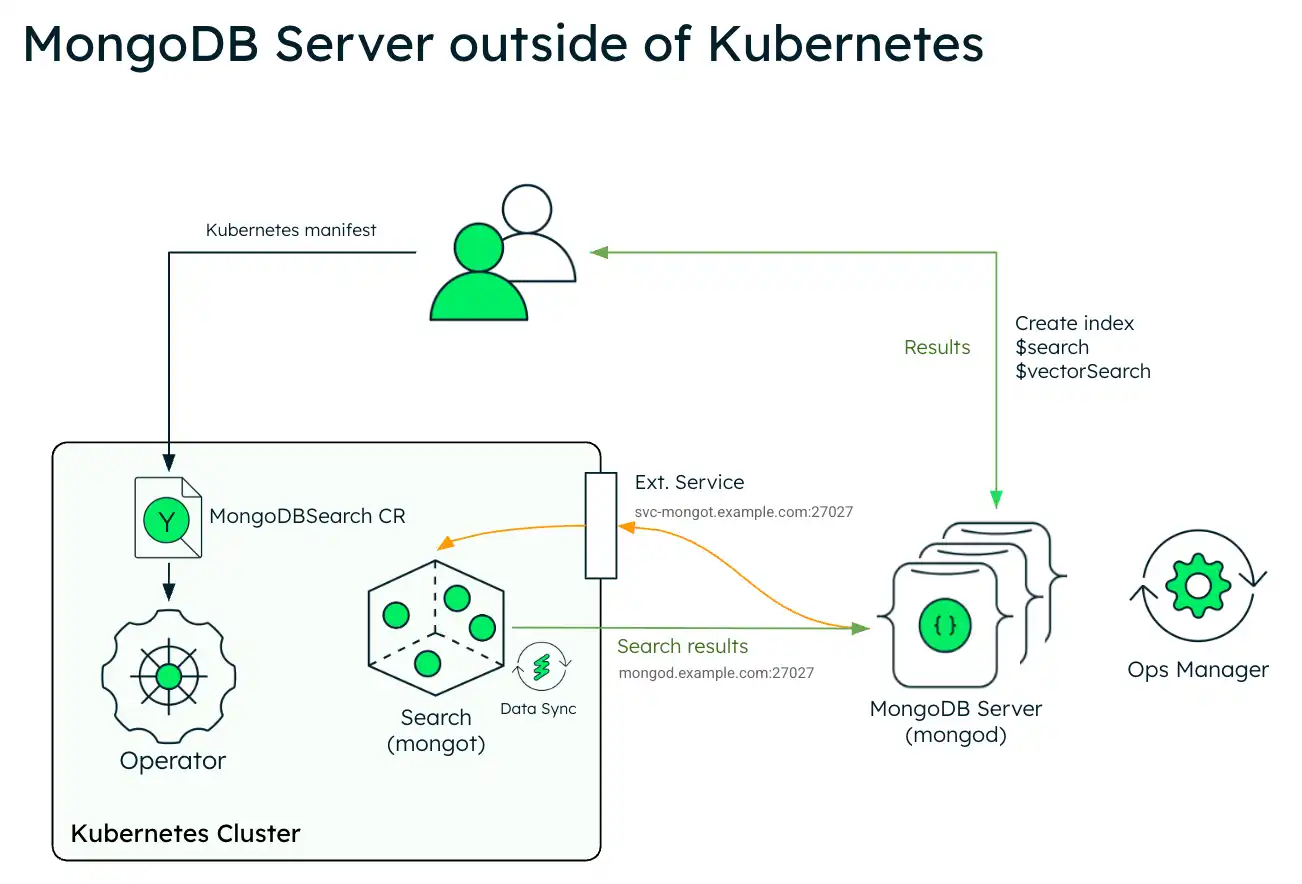
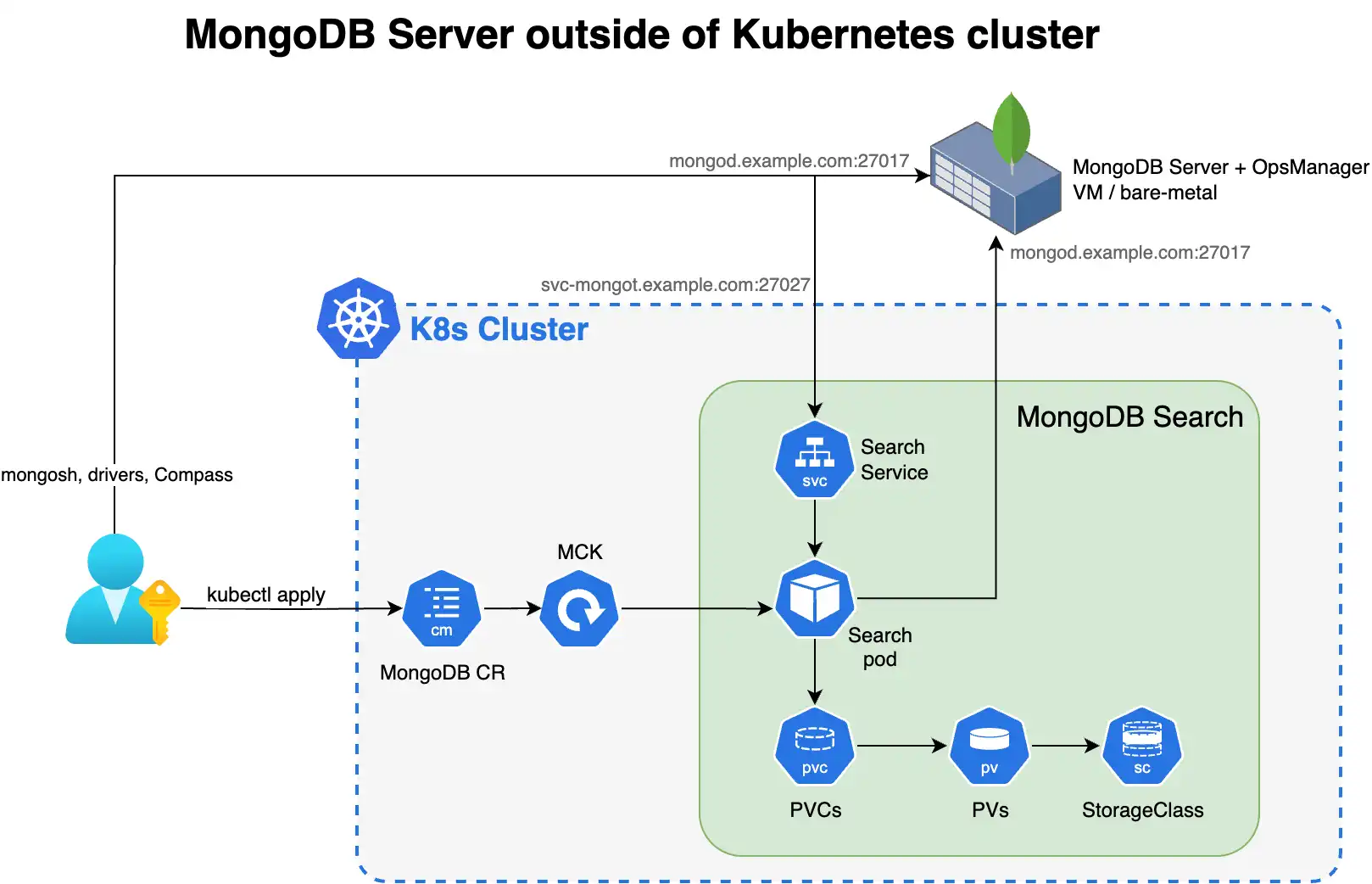
The following diagram shows the components that the Kubernetes Operator deploys in a Kubernetes cluster for MongoDB Search and Vector Search.
In order to leverage MongoDB Search and Vector Search when you have
your MongoDB deployment outside of Kubernetes, you deploy mongot using
the Kubernetes Operator and you must perform some steps manually. The
Kubernetes Operator handles configuration of the search pods. However,
when the MongoDB replica set is outside of Kubernetes, you must
reconfigure your MongoDB nodes and the networking.
You are responsible for the following manual configurations:
External MongoDB Configuration
Configure the following parameter using
setParameteron everymongodprocess in your external replica set. When configuring, replace<search-service-hostname>:27028with the actual resolvable hostname and port of your MongoDBSearch service.setParameter: mongotHost: "<search-service-hostname>:27028" searchIndexManagementHostAndPort: "<search-service-hostname>:27028" skipAuthenticationToSearchIndexManagementServer: false searchTLSMode: "disabled" # or "requireTLS" for TLS deployments useGrpcForSearch: true Create a user in the external replica set for the search synchronization process. This user must have the
searchCoordinatorrole.- userName: "search-sync-source" password: "<your-search-sync-password>" database: "admin" roles: - role: "searchCoordinator" db: "admin"
Kubernetes Configuration
Configure and apply the MongoDBSearch CR with
spec.source.externalpointing to your external MongoDB hosts.Create a Kubernetes secret for the search synchronization user's password.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: search-sync-source-password stringData: password: "your-search-sync-password" Configure networking and DNS to ensure bi-directional connectivity between your external MongoDB and the search pods. Your external MongoDB environment must be able to resolve your search service hostname (
<search-service-hostname>).
To learn more about the CR settings for the
mongot process to connect to an external mongod process, see
MongoDB Search and Vector Search Settings.
Security
The following image illustrates the security configuration for the
mongot process. If the MongoDB server is inside of the Kubernetes
cluster, the Kubernetes Operator automatically sets up keyfile authentication
for MongoDB Search and Vector Search. If the MongoDB server is
external, you must create a Kubernetes Secret containing the replica set's
keyfile credential and reference it in the MongoDBSearch CR.
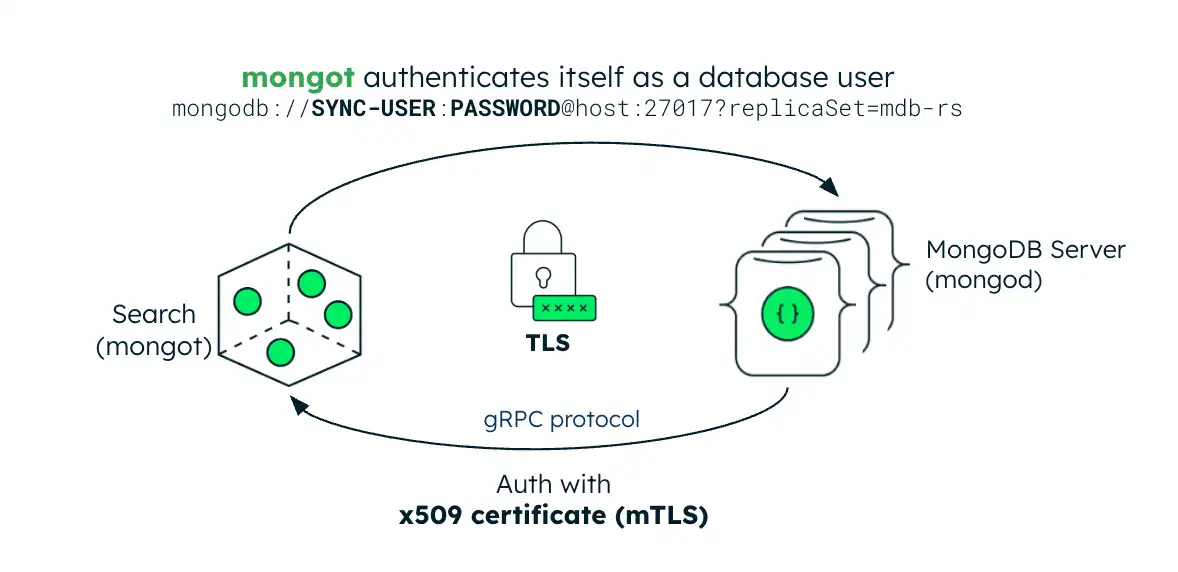
Authentication
The mongot process authenticates mongod connections using mTLS.
When you enable TLS, the mongot process uses the MongoDB server's
TLS certificate as the client certificate for authentication. This
certificate is verified against the CA certificate that mongot is
configured with. For authentication to work properly, you must configure
both mongot and mongod with TLS enabled.
When configured to index a MongoDB resource within the same Kubernetes
cluster, the Kubernetes Operator automatically propagates the mongod CA
certificate to mongot and enables mTLS for search query connections
if both the MongoDB and MongoDBSearch resources are configured for
TLS. If the MongoDB replica set is deployed outside Kubernetes, you must
create a Kubernetes Secret containing the replica set's CA certificate and
reference it in the MongoDBSearch.spec.source.external.tls.ca field to
enable mTLS authentication for search query requests.
Transport Layer Security
MongoDBSearch can protect data and credentials in transit using TLS.
For index management commands and search queries, specify (even an empty
object, {}) spec.security.tls field and provide a TLS
certificate in a Kubernetes Secret in the
spec.security.tls.certificateKeySecretRef field. This TLS
certificate must be issued and signed by the same CA that issued the CA
certificate that the MongoDB replica set uses.
When both MongoDBSearch and MongoDB are deployed by the
Kubernetes Operator, the underlying mongot and mongod configuration
is largely handled by the Kubernetes Operator itself. When the MongoDB
replica set is deployed outside of Kubernetes, the
.spec.source.external.tls field must be populated with a Kubernetes
Secret containing the same CA certificate mongod is configured with,
and mongod configuration itself must have the searchTLSMode
parameter set to requireTLS.