This guide describes how to perform semantic search with Voyage AI models. This page includes examples for basic and advanced semantic search use cases, including search with reranking, as well as multilingual, multimodal, contextualized chunk, and large corpus retrieval.
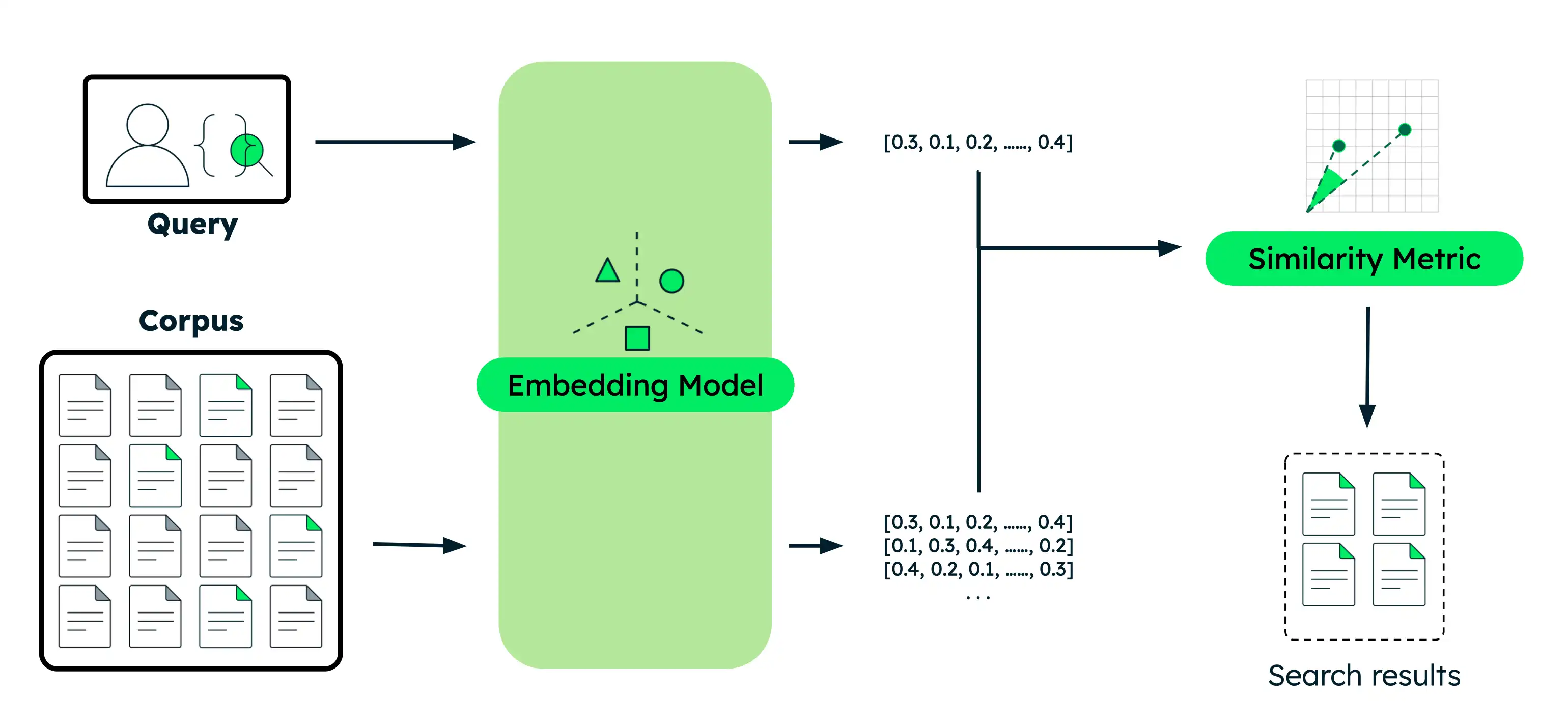
Perform Semantic Search
This section provides code examples for various semantic search use cases with different Voyage AI models. For each example, you perform the same basic steps:
Embed the documents: Convert your data into vector embeddings that capture their meaning. This data can be text, images, document chunks, or a large corpus of text.
Embed the query: Transform your search query into the same vector representation as your documents.
Find similar documents: Compare the query vector against your document vectors to identify the most semantically similar results.
Work with a runnable version of this tutorial as a Python notebook.
Set up your environment.
Before you begin, create a project directory, install libraries, and set your model API key.
Run the following commands in your terminal to create a new directory for this tutorial and install the required libraries:
mkdir voyage-semantic-search cd voyage-semantic-search pip install --upgrade voyageai numpy datasets If you haven't already, follow the steps to create a model API key, then run the following command in your terminal to export it as an environment variable:
export VOYAGE_API_KEY="your-model-api-key"
Run semantic search queries.
Expand each section to get code examples for each type of semantic search.
Create a file named
semantic_search_basic.pyin your project and paste the following code into it:
import voyageai import numpy as np # Initialize Voyage AI client vo = voyageai.Client() # Sample documents documents = [ "The Mediterranean diet emphasizes fish, olive oil, and vegetables, believed to reduce chronic diseases.", "Photosynthesis in plants converts light energy into glucose and produces essential oxygen.", "20th-century innovations, from radios to smartphones, centered on electronic advancements.", "Rivers provide water, irrigation, and habitat for aquatic species, vital for ecosystems.", "Apple's conference call to discuss fourth fiscal quarter results and business updates is scheduled for Thursday, November 2, 2023 at 2:00 p.m. PT / 5:00 p.m. ET.", "Shakespeare's works, like 'Hamlet' and 'A Midsummer Night's Dream,' endure in literature." ] # Search query query = "When is Apple's conference call scheduled?" # Generate embeddings for documents doc_embeddings = vo.embed( texts=documents, model="voyage-4-large", input_type="document" ).embeddings # Generate embedding for query query_embedding = vo.embed( texts=[query], model="voyage-4-large", input_type="query" ).embeddings[0] # Calculate similarity scores using dot product similarities = np.dot(doc_embeddings, query_embedding) # Sort documents by similarity (highest to lowest) ranked_indices = np.argsort(-similarities) # Display results print(f"Query: '{query}'\n") for rank, idx in enumerate(ranked_indices, 1): print(f"{rank}. {documents[idx]}") print(f" Similarity: {similarities[idx]:.4f}\n")
Run the following command in your terminal:
python semantic_search_basic.py
Query: 'When is Apple's conference call scheduled?' 1. Apple's conference call to discuss fourth fiscal quarter results and business updates is scheduled for Thursday, November 2, 2023 at 2:00 p.m. PT / 5:00 p.m. ET. Similarity: 0.6691 2. 20th-century innovations, from radios to smartphones, centered on electronic advancements. Similarity: 0.2751 3. Shakespeare's works, like 'Hamlet' and 'A Midsummer Night's Dream,' endure in literature. Similarity: 0.2335 4. The Mediterranean diet emphasizes fish, olive oil, and vegetables, believed to reduce chronic diseases. Similarity: 0.1955 5. Photosynthesis in plants converts light energy into glucose and produces essential oxygen. Similarity: 0.1881 6. Rivers provide water, irrigation, and habitat for aquatic species, vital for ecosystems. Similarity: 0.1601
Create a file named
semantic_search_reranker.pyin your project and paste the following code into it:
import voyageai import numpy as np # Initialize Voyage AI client vo = voyageai.Client() # Sample documents documents = [ "The Mediterranean diet emphasizes fish, olive oil, and vegetables, believed to reduce chronic diseases.", "Photosynthesis in plants converts light energy into glucose and produces essential oxygen.", "20th-century innovations, from radios to smartphones, centered on electronic advancements.", "Rivers provide water, irrigation, and habitat for aquatic species, vital for ecosystems.", "Apple's conference call to discuss fourth fiscal quarter results and business updates is scheduled for Thursday, November 2, 2023 at 2:00 p.m. PT / 5:00 p.m. ET.", "Shakespeare's works, like 'Hamlet' and 'A Midsummer Night's Dream,' endure in literature." ] # Search query query = "When is Apple's conference call scheduled?" # Generate embeddings for documents doc_embeddings = vo.embed( texts=documents, model="voyage-4-large", input_type="document" ).embeddings # Generate embedding for query query_embedding = vo.embed( texts=[query], model="voyage-4-large", input_type="query" ).embeddings[0] # Calculate similarity scores using dot product similarities = np.dot(doc_embeddings, query_embedding) # Sort by similarity (highest to lowest) ranked_indices = np.argsort(-similarities) # Display results before reranking print(f"Query: '{query}'\n") print("Before reranker (embedding similarity only):") for rank, idx in enumerate(ranked_indices[:3], 1): print(f"{rank}. {documents[idx]}") print(f" Similarity Score: {similarities[idx]:.4f}\n") # Rerank documents for improved accuracy rerank_results = vo.rerank( query=query, documents=documents, model="rerank-2.5" ) # Display results after reranking print("\nAfter reranker:") for rank, result in enumerate(rerank_results.results[:3], 1): print(f"{rank}. {documents[result.index]}") print(f" Relevance Score: {result.relevance_score:.4f}\n")
Run the following command in your terminal:
python semantic_search_reranker.py
Query: 'When is Apple's conference call scheduled?' Before reranker (embedding similarity only): 1. Apple's conference call to discuss fourth fiscal quarter results and business updates is scheduled for Thursday, November 2, 2023 at 2:00 p.m. PT / 5:00 p.m. ET. Similarity Score: 0.6691 2. 20th-century innovations, from radios to smartphones, centered on electronic advancements. Similarity Score: 0.2751 3. Shakespeare's works, like 'Hamlet' and 'A Midsummer Night's Dream,' endure in literature. Similarity Score: 0.2335 After reranker: 1. Apple's conference call to discuss fourth fiscal quarter results and business updates is scheduled for Thursday, November 2, 2023 at 2:00 p.m. PT / 5:00 p.m. ET. Relevance Score: 0.9453 2. 20th-century innovations, from radios to smartphones, centered on electronic advancements. Relevance Score: 0.2832 3. The Mediterranean diet emphasizes fish, olive oil, and vegetables, believed to reduce chronic diseases. Relevance Score: 0.2637
Create a file named
semantic_search_multilingual.pyin your project and paste the following code into it:
import voyageai import numpy as np # Initialize Voyage AI client vo = voyageai.Client() # English documents about technology companies english_docs = [ "Apple announced record-breaking revenue in its latest quarterly earnings report.", "The Mediterranean diet emphasizes fish, olive oil, and vegetables.", "Microsoft is investing heavily in artificial intelligence and cloud computing.", "Shakespeare's plays continue to influence modern literature and theater." ] # Spanish documents about technology companies spanish_docs = [ "Apple anunció ingresos récord en su último informe trimestral de ganancias.", "La dieta mediterránea enfatiza el pescado, el aceite de oliva y las verduras.", "Microsoft está invirtiendo fuertemente en inteligencia artificial y computación en la nube.", "Las obras de Shakespeare continúan influenciando la literatura y el teatro modernos." ] # Chinese documents about technology companies chinese_docs = [ "苹果公司在最新季度财报中宣布创纪录的收入。", "地中海饮食强调鱼类、橄榄油和蔬菜。", "微软正在大力投资人工智能和云计算。", "莎士比亚的作品继续影响现代文学和戏剧。" ] # Perform semantic search in English english_query = "tech company earnings" # Generate embeddings for English documents english_embeddings = vo.embed( texts=english_docs, model="voyage-4-large", input_type="document" ).embeddings # Generate embedding for English query english_query_embedding = vo.embed( texts=[english_query], model="voyage-4-large", input_type="query" ).embeddings[0] # Calculate similarity scores using dot product english_similarities = np.dot(english_embeddings, english_query_embedding) # Sort by similarity (highest to lowest) english_ranked = np.argsort(-english_similarities) print(f"English Query: '{english_query}'\n") for rank, idx in enumerate(english_ranked[:2], 1): print(f"{rank}. {english_docs[idx]}") print(f" Similarity: {english_similarities[idx]:.4f}\n") # Perform semantic search in Spanish spanish_query = "ganancias de empresas tecnológicas" # Generate embeddings for Spanish documents spanish_embeddings = vo.embed( texts=spanish_docs, model="voyage-4-large", input_type="document" ).embeddings # Generate embedding for Spanish query spanish_query_embedding = vo.embed( texts=[spanish_query], model="voyage-4-large", input_type="query" ).embeddings[0] # Calculate similarity scores using dot product spanish_similarities = np.dot(spanish_embeddings, spanish_query_embedding) # Sort by similarity (highest to lowest) spanish_ranked = np.argsort(-spanish_similarities) print(f"Spanish Query: '{spanish_query}'\n") for rank, idx in enumerate(spanish_ranked[:2], 1): print(f"{rank}. {spanish_docs[idx]}") print(f" Similarity: {spanish_similarities[idx]:.4f}\n") # Perform semantic search in Chinese chinese_query = "科技公司收益" # Generate embeddings for Chinese documents chinese_embeddings = vo.embed( texts=chinese_docs, model="voyage-4-large", input_type="document" ).embeddings # Generate embedding for Chinese query chinese_query_embedding = vo.embed( texts=[chinese_query], model="voyage-4-large", input_type="query" ).embeddings[0] # Calculate similarity scores using dot product chinese_similarities = np.dot(chinese_embeddings, chinese_query_embedding) # Sort by similarity (highest to lowest) chinese_ranked = np.argsort(-chinese_similarities) print(f"Chinese Query: '{chinese_query}'\n") for rank, idx in enumerate(chinese_ranked[:2], 1): print(f"{rank}. {chinese_docs[idx]}") print(f" Similarity: {chinese_similarities[idx]:.4f}\n")
Run the following command in your terminal:
python semantic_search_multilingual.py
English Query: 'tech company earnings' 1. Apple announced record-breaking revenue in its latest quarterly earnings report. Similarity: 0.5172 2. Microsoft is investing heavily in artificial intelligence and cloud computing. Similarity: 0.4745 Spanish Query: 'ganancias de empresas tecnológicas' 1. Apple anunció ingresos récord en su último informe trimestral de ganancias. Similarity: 0.5232 2. Microsoft está invirtiendo fuertemente en inteligencia artificial y computación en la nube. Similarity: 0.4871 Chinese Query: '科技公司收益' 1. 苹果公司在最新季度财报中宣布创纪录的收入。 Similarity: 0.4725 2. 微软正在大力投资人工智能和云计算。 Similarity: 0.4426
Search for sample images and save them in your project directory. The following code example assumes you have images of a cat, dog, and banana.
Create a file named
semantic_search_multimodal.pyin your project and paste the following code into it:
import voyageai import numpy as np from PIL import Image # Initialize Voyage AI client vo = voyageai.Client() # Prepare interleaved text + image inputs interleaved_inputs = [ ["An orange cat", Image.open('cat.jpg')], ["A golden retriever", Image.open('dog.jpg')], ["A banana", Image.open('banana.jpg')], ] # Prepare image-only inputs image_only_inputs = [ [Image.open('cat.jpg')], [Image.open('dog.jpg')], [Image.open('banana.jpg')], ] # Labels for display labels = ["cat.jpg", "dog.jpg", "banana.jpg"] # Search query query = "a cute pet" # Generate embeddings for interleaved text + image inputs interleaved_embeddings = vo.multimodal_embed( inputs=interleaved_inputs, model="voyage-multimodal-3.5" ).embeddings # Generate embedding for query query_embedding = vo.multimodal_embed( inputs=[[query]], model="voyage-multimodal-3.5" ).embeddings[0] # Calculate similarity scores using dot product interleaved_similarities = np.dot(interleaved_embeddings, query_embedding) # Sort by similarity (highest to lowest) interleaved_ranked = np.argsort(-interleaved_similarities) print(f"Query: '{query}'\n") print("Search with interleaved text + image:") for rank, idx in enumerate(interleaved_ranked, 1): print(f"{rank}. {interleaved_inputs[idx][0]}") print(f" Similarity: {interleaved_similarities[idx]:.4f}\n") # Generate embeddings for image-only inputs image_only_embeddings = vo.multimodal_embed( inputs=image_only_inputs, model="voyage-multimodal-3.5" ).embeddings # Calculate similarity scores using dot product image_only_similarities = np.dot(image_only_embeddings, query_embedding) # Sort by similarity (highest to lowest) image_only_ranked = np.argsort(-image_only_similarities) print("\nSearch with image-only:") for rank, idx in enumerate(image_only_ranked, 1): print(f"{rank}. {labels[idx]}") print(f" Similarity: {image_only_similarities[idx]:.4f}\n")
Run the following command in your terminal:
python semantic_search_multimodal.py
Query: 'a cute pet' Search with interleaved text + image: 1. An orange cat Similarity: 0.2685 2. A golden retriever Similarity: 0.2325 3. A banana Similarity: 0.1564 Search with image-only: 1. dog.jpg Similarity: 0.2485 2. cat.jpg Similarity: 0.2438 3. banana.jpg Similarity: 0.1210
Create a file named
semantic_search_contextualized.pyin your project and paste the following code into it:
import voyageai import numpy as np # Initialize Voyage AI client vo = voyageai.Client() # Sample documents (each document is a list of chunks that share context) documents = [ [ "This is the SEC filing on Greenery Corp.'s Q2 2024 performance.", "The company's revenue increased by 7% compared to the previous quarter." ], [ "This is the SEC filing on Leafy Inc.'s Q2 2024 performance.", "The company's revenue increased by 15% compared to the previous quarter." ], [ "This is the SEC filing on Elephant Ltd.'s Q2 2024 performance.", "The company's revenue decreased by 2% compared to the previous quarter." ] ] # Search query query = "What was the revenue growth for Leafy Inc. in Q2 2024?" # Generate contextualized embeddings (preserves relationships between chunks) contextualized_result = vo.contextualized_embed( inputs=documents, model="voyage-context-3", input_type="document" ) # Flatten the embeddings and chunks for semantic search contextualized_embeddings = [] all_chunks = [] chunk_to_doc = [] # Maps chunk index to document index for doc_idx, result in enumerate(contextualized_result.results): for emb, chunk in zip(result.embeddings, documents[doc_idx]): contextualized_embeddings.append(emb) all_chunks.append(chunk) chunk_to_doc.append(doc_idx) # Generate contextualized query embedding query_embedding_ctx = vo.contextualized_embed( inputs=[[query]], model="voyage-context-3", input_type="query" ).results[0].embeddings[0] # Calculate similarity scores using dot product similarities_ctx = np.dot(contextualized_embeddings, query_embedding_ctx) # Sort by similarity (highest to lowest) ranked_indices_ctx = np.argsort(-similarities_ctx) # Display top 3 results print(f"Query: '{query}'\n") for rank, idx in enumerate(ranked_indices_ctx[:3], 1): doc_idx = chunk_to_doc[idx] print(f"{rank}. {all_chunks[idx]}") print(f" (From document: {documents[doc_idx][0]})") print(f" Similarity: {similarities_ctx[idx]:.4f}\n")
Run the following command in your terminal:
python semantic_search_contextualized.py
Query: 'What was the revenue growth for Leafy Inc. in Q2 2024?' 1. The company's revenue increased by 15% compared to the previous quarter. (From document: This is the SEC filing on Leafy Inc.'s Q2 2024 performance.) Similarity: 0.7138 2. This is the SEC filing on Leafy Inc.'s Q2 2024 performance. (From document: This is the SEC filing on Leafy Inc.'s Q2 2024 performance.) Similarity: 0.6630 3. The company's revenue increased by 7% compared to the previous quarter. (From document: This is the SEC filing on Greenery Corp.'s Q2 2024 performance.) Similarity: 0.5531
Create a file named
semantic_search_large_corpus.pyin your project and paste the following code into it:
import voyageai import numpy as np from datasets import load_dataset from collections import defaultdict # Initialize Voyage AI client vo = voyageai.Client() # Load legal benchmark dataset corpus_ds = load_dataset("mteb/legalbench_consumer_contracts_qa", "corpus")["corpus"] queries_ds = load_dataset("mteb/legalbench_consumer_contracts_qa", "queries")["queries"] qrels_ds = load_dataset("mteb/legalbench_consumer_contracts_qa")["test"] # Extract corpus and query data corpus_ids = [row["_id"] for row in corpus_ds] corpus_texts = [row["text"] for row in corpus_ds] query_ids = [row["_id"] for row in queries_ds] query_texts = [row["text"] for row in queries_ds] # Build relevance mapping (defaultdict creates sets for missing keys) qrels = defaultdict(set) for row in qrels_ds: if row["score"] > 0: qrels[row["query-id"]].add(row["corpus-id"]) # Generate embeddings for the entire corpus print(f"Generating embeddings for {len(corpus_texts)} documents...") corpus_embeddings = vo.embed( texts=corpus_texts, model="voyage-4-large", input_type="document" ).embeddings # Select a sample query query_idx = 1 query = query_texts[query_idx] query_id = query_ids[query_idx] # Generate embedding for the query query_embedding = vo.embed( texts=[query], model="voyage-4-large", input_type="query" ).embeddings[0] # Calculate similarity scores using dot product similarities = np.dot(corpus_embeddings, query_embedding) # Sort by similarity (highest to lowest) ranked_indices = np.argsort(-similarities) # Display top 5 results print(f"Query: {query}\n") print("Top 5 Results:") for rank, idx in enumerate(ranked_indices[:5], 1): doc_id = corpus_ids[idx] is_relevant = "✓" if doc_id in qrels[query_id] else "✗" print(f"{rank}. [{is_relevant}] Document ID: {doc_id}") print(f" Similarity: {similarities[idx]:.4f}") print(f" Text: {corpus_texts[idx][:100]}...\n") # Show the ground truth most relevant document most_relevant_id = list(qrels[query_id])[0] most_relevant_idx = corpus_ids.index(most_relevant_id) print(f"Ground truth most relevant document:") print(f"Document ID: {most_relevant_id}") print(f"Rank in results: {np.where(ranked_indices == most_relevant_idx)[0][0] + 1}") print(f"Similarity: {similarities[most_relevant_idx]:.4f}")
Run the following command in your terminal:
python semantic_search_large_corpus.py
Generating embeddings for 154 documents... Query: Will Google come to a users assistance in the event of an alleged violation of such users IP rights? Top 5 Results: 1. [✓] Document ID: 9NIQ0Wobtq Similarity: 0.6047 Text: Your content Some of our services give you the opportunity to make your content publicly available ... 2. [✗] Document ID: gAk7Gdp0CX Similarity: 0.5515 Text: Taking action in case of problems Before taking action as described below, well provide you with adv... 3. [✗] Document ID: S87XwXaHCP Similarity: 0.5178 Text: Privacy and Data Protection Our Privacy Center explains how we treat your personal data. By using th... 4. [✗] Document ID: 8IRh1E2JDB Similarity: 0.5134 Text: OUR PROPERTY The Service is protected by copyright, trademark, and other US and foreign laws. These ... 5. [✗] Document ID: 50OXirZRiR Similarity: 0.5098 Text: Uploading Content If you have a YouTube channel, you may be able to upload Content to the Service. Y... Ground truth most relevant document: Document ID: 9NIQ0Wobtq Rank in results: 1 Similarity: 0.6047
About The Examples
The following table summarizes the examples on this page:
Example | Model Used | Understanding Results |
|---|---|---|
Basic Semantic Search |
| The Apple conference call document ranks first, significantly higher than unrelated documents, demonstrating accurate semantic matching. |
Semantic Search with Reranker |
| Reranking improves search accuracy by analyzing the full query-document relationship. While embedding similarity alone ranks the correct document first with a moderate score, the reranker significantly boosts its relevance score which better separates it from irrelevant results. |
Multilingual Semantic Search |
| Voyage models perform semantic search effectively across different languages. The example demonstrates three separate searches in English, Spanish, and Chinese, each correctly identifying the most relevant documents about tech company earnings within their respective languages. |
Multimodal Semantic Search |
| The model supports interleaved text, image, and video, as well as image-only and video-only search. In both cases, pet images (cat and dog) rank significantly higher than the unrelated banana image, demonstrating accurate visual content retrieval. Interleaved inputs with descriptive text produce slightly higher similarity scores than image-only inputs. |
Contextualized Chunk Embeddings |
| The 15% revenue growth chunk ranks first because it's linked to the Leafy Inc. document. The similar 7% growth chunk from Greenery Corp. scores lower, showing how the model accurately considers document context to distinguish between otherwise similar chunks. |
Semantic Search with Large Corpus |
| The ground truth document about user content ranks first among 154 documents, demonstrating effective retrieval at scale despite semantic complexity. |
- Accessing Embeddings
The examples use the Python Client,
voyageai.Client(), which automatically reads your API key from theVOYAGE_API_KEYenvironment variable. The API returns a response object. Use the.embeddingsattribute to access the actual embedding vectors:result = vo.embed(texts=["example"], model="voyage-4-large", input_type="document") embeddings = result.embeddings # List of embedding vectors - Calculating Similarity
The examples calculate similarity scores between query and document embeddings using Numpy's dot product function:
np.dot(). Since Voyage AI embeddings are normalized to length 1, the dot product is mathematically equivalent to cosine similarity.To rank results by similarity, the examples use Numpy's
argsort()function to display the top N results. The negative sign sorts in descending order, so the highest similarity scores appear first.- Input Type Parameter
- The
input_typeparameter is set toqueryordocumentto optimize how Voyage AI models create the vectors. Do not omit this parameter. To learn more, see Specifying Input Type.
To learn more, see Accessing Voyage AI Models or explore the full API specification.
What is Semantic Search?
Semantic search is a search method that returns results based on your data's semantic, or underlying, meaning. Unlike traditional full-text search which finds text matches, semantic search finds vectors that are close to your search query in multi-dimensional space. The closer the vectors are to your query, the more similar they are in meaning.
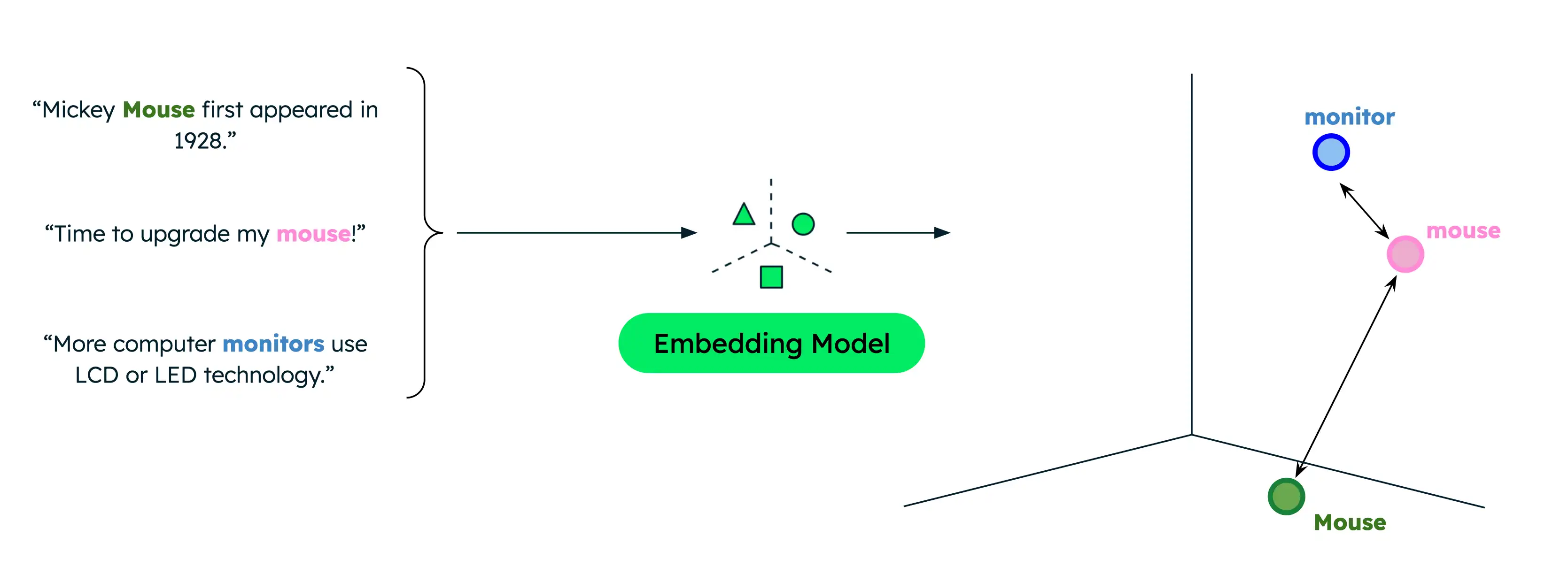
Example
Traditional text search returns only exact matches, limiting results when users search with different terms than those in your data. For example, if your data contains documents about computer mice and animal mice, searching for "mouse" when you intend to find information about computer mice results in incorrect matches.
Semantic search, however, captures the underlying relationship between words or phrases even when there is no lexical overlap. Searching for "mouse" when indicating that you are looking for computer products results in more relevant results. This is because semantic search compares the semantic meaning of the search query against your data to return only the most relevant results, regardless of the exact search terms.
Similarity functions measure how close two vectors are to each other, and therefore how similar they are. Common functions include dot product, cosine similarity, and Euclidean distance. Voyage AI embeddings are normalized to length 1, which means that:
Cosine similarity is equivalent to dot product similarity, while the latter can be computed more quickly.
Cosine similarity and Euclidean distance result in identical rankings.
Semantic Search in Production
While storing your vectors in memory and implementing your own search pipelines is suitable for prototyping and experimentation, use a vector database and enterprise search solution for production applications so you can perform efficient retrieval from a larger corpus.
MongoDB has native support for vector storage and retrieval, making it a convenient choice for storing and searching vector embeddings alongside your other data. To complete a tutorial on performing semantic search with MongoDB Vector Search, see How to Perform Semantic Search Against Data in Your Atlas Cluster.
Next Steps
Combine semantic search with an LLM to implement a RAG application.