Overview
In this guide, you can learn how to create a React web application that uses the MERN stack. The MERN stack is a web development framework that uses MongoDB, Express, React, and Node.js and consists of the following layers:
Database layer: MongoDB provides data storage and retrieval.
Application layer: Express and Node.js make up the middle tier for server-side logic.
Presentation layer: React implements the user interface and front-end interactions.
Why Use MongoDB in a React Application?
By storing your React application data in MongoDB, you can use the document data model to build complex query expressions. The document model's flexibility allows you to store nested data structures and iterate quickly on your application design. You can also grow your application easily by using MongoDB's horizontal scaling capabilities.
The MERN stack with MongoDB supports applications that require dynamic, evolving data structures. As a result, this framework is well-designed for real world applications such as real-time dashboards or one-page applications that update content continuously.
Quick Start Tutorial
This tutorial shows you how to build a web application by using the MERN stack. The application accesses sample restaurant data, queries the data, and displays the results on a locally hosted site. The tutorial also includes instructions for connecting to a MongoDB cluster hosted on MongoDB Atlas and accessing and displaying data from your database.
Tip
If you prefer to connect to MongoDB by using the Node.js driver without React, see the Get Started with the Node.js Driver guide.
Set Up Your Project
Follow the steps in this section to install the project dependencies, create an Atlas cluster, and set up the application directories.
Verify the prerequisites
To create the Quick Start application, you need the following software installed in your development environment:
Prerequisite | Notes |
|---|---|
Download either the Latest LTS or Latest Release version. | |
Code editor | This tutorial uses Visual Studio Code, but you can use the editor of your choice. |
Terminal app and shell | For MacOS users, use Terminal or a similar app. For Windows users, use PowerShell. |
Create a MongoDB Atlas cluster
MongoDB Atlas is a fully managed cloud database service that hosts your
MongoDB deployments. If you do not have a MongoDB deployment, you can create a MongoDB
cluster for free (no credit card required) by completing the
MongoDB Get Started
tutorial. The MongoDB Get Started tutorial also demonstrates how to load sample
datasets into your cluster, including the sample_restaurants database
that is used in this tutorial.
To connect to your MongoDB cluster, you must use a connection URI. To learn how to retrieve your connection URI, see the Add your connection string section of the MongoDB Get Started tutorial.
Important
Save your connection string in a secure location.
Create your project directories
Run the following command in your terminal to create a directory for
your project named react-quickstart:
mkdir react-quickstart cd react-quickstart
Then, run the following commands from the react-quickstart directory
to create a folder for the back end named server and initialize the
package.json file:
mkdir server cd server npm init -y
Modify your package.json file
Navigate to the package.json file in the react-quickstart/server
directory. To use ECMAScript modules,
the standard format for packaging JavaScript code for reuse, replace the
existing line that specifies the "type" field with the following line:
"type": "module",
Run the following command to install the mongodb, express, and cors
dependencies:
npm install mongodb express cors
This command installs MongoDB, the Express web framework, and the
cors Node.js package that enables cross-origin resource sharing.
Configure the Back End
After setting up the project structure and dependencies, follow the steps in this section to configure your web server and connect to MongoDB.
Configure your Express web server
Create a file named server.js in your react-quickstart/server directory
and paste the following code:
import express from "express"; import cors from "cors"; import restaurants from "./routes/restaurant.js"; const PORT = process.env.PORT || 5050; const app = express(); app.use(cors()); app.use(express.json()); app.use("/restaurant", restaurants); // start the Express server app.listen(PORT, () => { console.log(`Server listening on port ${PORT}`); });
Set environment variables
In the server directory, create a config.env file that stores the
following variables:
MONGODB_URI=<connection URI> PORT=5050
Replace the <connection URI> placeholder with the connection
URI that you saved in a previous step.
Create server API endpoints
In the server directory, create a subdirectory named routes.
Create a file named restaurant.js in the routes subdirectory and
paste the following code:
import express from "express"; import db from "../db/connection.js"; // Creates an instance of the Express router, used to define our routes const router = express.Router(); // Gets a list of all the restaurants router.get("/", async (req, res) => { let collection = await db.collection("restaurants"); let results = await collection.find({}).toArray(); res.send(results).status(200); }); // Lists restaurants that match the query filter router.get("/browse", async (req, res) => { try { let collection = await db.collection("restaurants"); let query = { borough: "Queens", name: { $regex: "Moon", $options: "i" }, }; let results = await collection.find(query).toArray(); res.send(results).status(200); } catch (err) { console.error(err); res.status(500).send("Error browsing restaurants"); } }); export default router;
This file accesses the restaurants collection in the
sample_restaurants database and defines the following GET
endpoints:
/: Retrieves all restaurants from the sample collection/browse: Retrieves restaurants that match the query criteria, which filters for restaurants in Queens that contain the word"Moon"in the name
Configure the Front End
After setting up the application's back end, follow the steps in this section to configure React and add the front end components.
Add the React template
In the react-quickstart directory, run the following commands
to add the React template files by using Vite:
npm create vite@latest client
This command prompts you to respond to a series of configuration questions. For each question, choose the following responses from the dropdown menu:
Select a framework: React
Select a variant: JavaScript
Use rolldown-vite (Experimental)?: No
Install with npm and start now?: No
After running the command, your project has a client directory
that contains front-end scaffolding.
Install Tailwind CSS
This sample application uses the Tailwind CSS framework
for UI formatting. To install it, navigate to the client
directory created in the previous step and run the following command:
npm install tailwindcss @tailwindcss/vite
After installing, navigate to your vite.config.js file. Add the
@tailwindcss/vite plugin by updating the import statements
and plugins array, as shown in the highlighted lines:
import { defineConfig } from 'vite' import react from '@vitejs/plugin-react' import tailwindcss from '@tailwindcss/vite' // https://vite.dev/config/ export default defineConfig({ plugins: [ react(), tailwindcss() ], })
Then, navigate to the client/src/index.css file and add the following
import statement:
@import "tailwindcss";
Set up the React router
Navigate to the client/src/main.jsx file and paste
the following code:
import * as React from "react"; import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom/client"; import { createBrowserRouter, RouterProvider } from "react-router-dom"; import App from "./App"; import RestaurantList from "./components/RestaurantList"; import "./index.css"; const router = createBrowserRouter([ { path: "/", element: <App />, children: [ { path: "/", element: <RestaurantList />, }, ], }, { path: "/browse", element: <App />, children: [ { path: "/browse", element: <RestaurantList />, }, ], }, ]); ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root")).render( <React.StrictMode> <RouterProvider router={router} /> </React.StrictMode>, );
This file configures client-side routing and defines the following routes:
/: Renders theRestaurantListcomponent, which calls the/restaurant/API endpoint to display all restaurants/browse: Renders theRestaurantListcomponent, which calls the/restaurant/browseAPI endpoint to display filtered restaurants
Create the components
Run the following commands from the client directory to create a new folder named
components that contains two files:
mkdir src/components cd src/components touch Navbar.jsx RestaurantList.jsx
The Navbar.jsx file configures a navigation bar that links
to the required components. Paste the following code into this file:
import { NavLink } from "react-router-dom"; export default function Navbar() { return ( <div> <nav className="flex justify-between items-center mb-6"> <NavLink to="/"> <img alt="MongoDB logo" className="h-10 inline" src="https://d3cy9zhslanhfa.cloudfront.net/media/3800C044-6298-4575-A05D5C6B7623EE37/4B45D0EC-3482-4759-82DA37D8EA07D229/webimage-8A27671A-8A53-45DC-89D7BF8537F15A0D.png" ></img> </NavLink> </nav> </div> ); }
The RestaurantList.jsx file is the viewing component for the restaurants,
and it retrieves and displays the restaurant information. Paste the following
code into this file:
import { useEffect, useState } from "react"; import { useLocation } from "react-router-dom"; const Restaurant = (props) => ( <tr className="border-b transition-colors hover:bg-muted/50 data-[state=selected]:bg-muted"> <td className="p-4 align-middle [&:has([role=checkbox])]:pr-0"> {props.restaurant.name} </td> <td className="p-4 align-middle [&:has([role=checkbox])]:pr-0"> {props.restaurant.borough} </td> <td className="p-4 align-middle [&:has([role=checkbox])]:pr-0"> {props.restaurant.cuisine} </td> </tr> ); export default function RestaurantList() { const [restaurants, setRestaurants] = useState([]); const location = useLocation(); // Fetches the restaurants from the database useEffect(() => { async function getRestaurants() { // Determines which endpoint to call based on current route const endpoint = location.pathname === "/browse" ? "http://localhost:5050/restaurant/browse" : "http://localhost:5050/restaurant/"; const response = await fetch(endpoint); if (!response.ok) { const message = `An error occurred: ${response.statusText}`; console.error(message); return; } const restaurants = await response.json(); setRestaurants(restaurants); } getRestaurants(); return; }, [location.pathname]); // Maps each restaurant on the table function restaurantList() { return restaurants.map((restaurant) => { return <Restaurant restaurant={restaurant} key={restaurant._id} />; }); } // Retrieves the dynamic title based on current route const getTitle = () => { return location.pathname === "/browse" ? 'Filtered Restaurants (Queens, containing "Moon")' : "All Restaurants"; }; // Displays the restaurants table return ( <> <h3 className="text-lg font-semibold p-4">{getTitle()}</h3> <div className="border rounded-lg overflow-hidden"> <div className="relative w-full overflow-auto"> <table className="w-full caption-bottom text-sm"> <thead className="[&_tr]:border-b"> <tr className="border-b transition-colors hover:bg-muted/50 data-[state=selected]:bg-muted"> <th className="h-12 px-4 text-left align-middle font-medium text-muted-foreground [&:has([role=checkbox])]:pr-0"> Name </th> <th className="h-12 px-4 text-left align-middle font-medium text-muted-foreground [&:has([role=checkbox])]:pr-0"> Borough </th> <th className="h-12 px-4 text-left align-middle font-medium text-muted-foreground [&:has([role=checkbox])]:pr-0"> Cuisine </th> </tr> </thead> <tbody className="[&_tr:last-child]:border-0"> {restaurantList()} </tbody> </table> </div> </div> </> ); }
Finally, navigate to the client/src/App.jsx file. This file is the main
layout component, and it ensures that the Navbar component renders at the top
of each page above the child component. Paste the following code
into this file:
import { Outlet } from "react-router-dom"; import Navbar from "./components/Navbar"; const App = () => { return ( <div className="w-full p-6"> <Navbar /> <Outlet /> </div> ); }; export default App;
Run Your Application
Finally, follow the steps in this section to run your application and view the rendered restaurant data.
Run the server application
Navigate to the react-quickstart/server directory and run
the following command to start the server:
node --env-file=config.env server
If successful, this command outputs the following information:
Pinged your deployment. You successfully connected to MongoDB! Server listening on port 5050
Run the client application
In a separate terminal window, navigate to the react-quickstart/client
directory. Run the following command to start the React front end:
npm run dev
If successful, this command outputs the following information:
VITE v7.2.4 ready in 298 ms ➜ Local: http://localhost:5173/ ➜ Network: use --host to expose ➜ press h + enter to show help
Open the application site
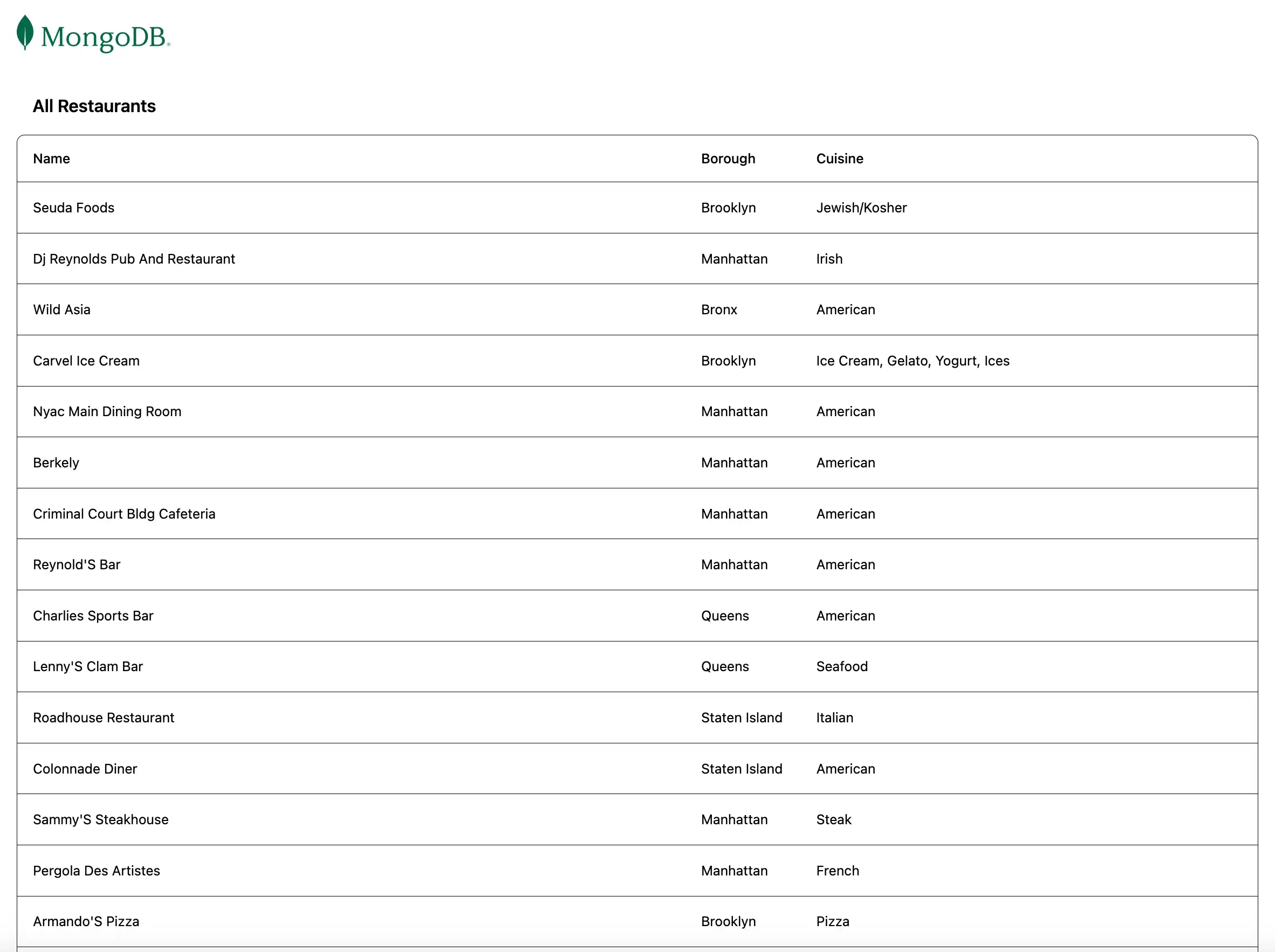
Open the http://localhost:5173/ URL, retrieved from the preceding step. The initial
landing page displays a list all restaurants in the sample_restaurants.restaurants
collection:
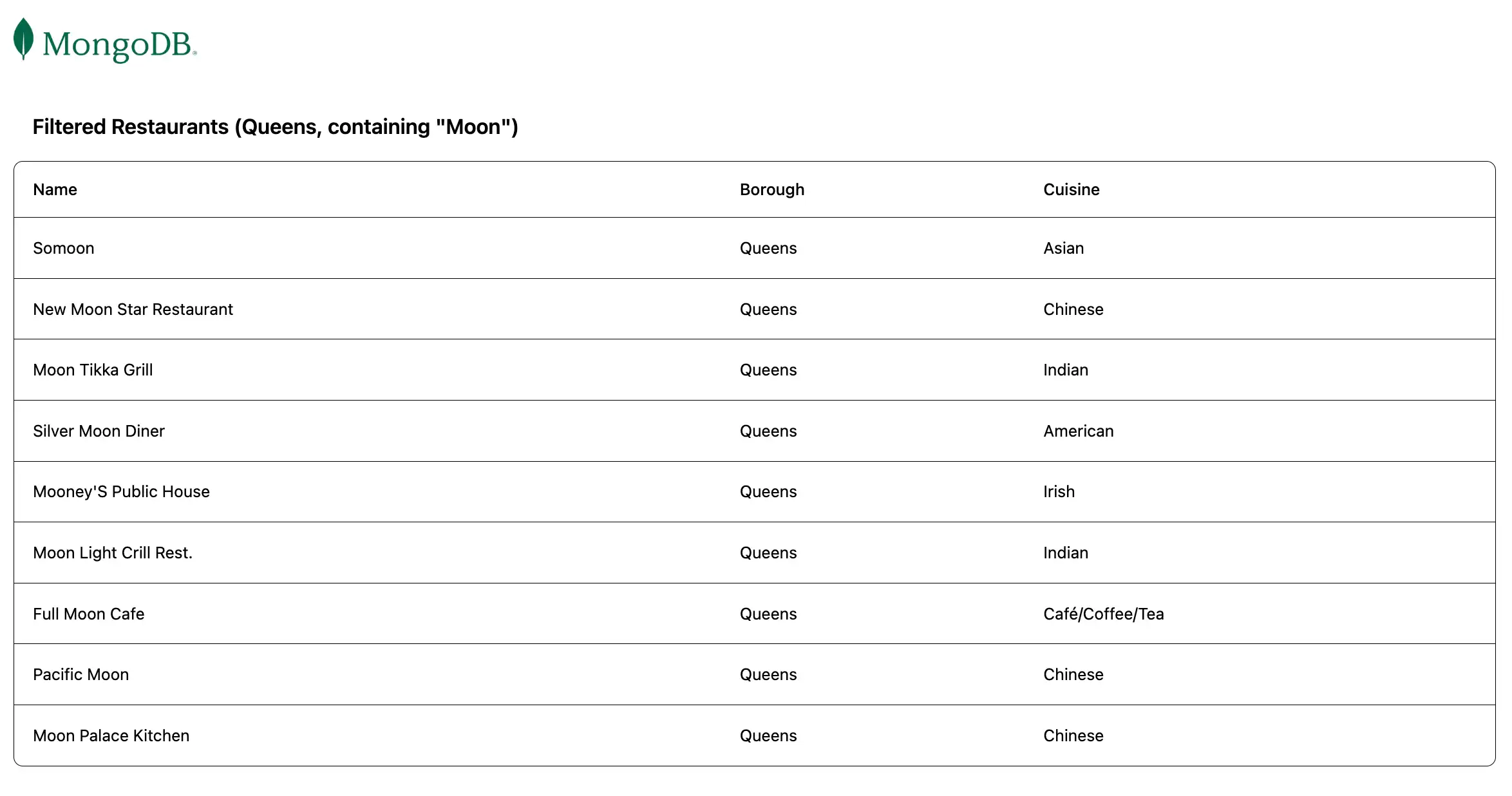
Then, navigate to the http://localhost:5173/browse URL to view
the restaurants that match the name and borough field query:
Congratulations on completing the Quick Start tutorial!
After you complete these steps, you have a React web application that connects to your MongoDB deployment, runs a query on sample restaurant data, and renders a retrieved result.
Additional Resources
To learn more about React, MongoDB, and the MERN stack, view the following resources:
React documentation
Express documentation
Node.js driver documentation