Use cases: Gen AI, Fraud Prevention
Industries: Financial Services, Insurance, Retail
Products and tools: MongoDB Atlas, MongoDB Atlas Clusters, MongoDB Change Streams, MongoDB Atlas Triggers, MongoDB Spark Streaming Connector
Partners: Databricks
Solutions Overview
This solution shows how to build an ML-based fraud solution using MongoDB and Databricks. The solution's key features include data completeness through integration with external sources, real-time processing for timely fraud detection, AI/ML modeling to identify potential fraud patterns, real-time monitoring for instant analysis, and robust security measures.
The system facilitates ease of operation and fosters collaboration between application development and data science teams. It also supports end-to-end CI/CD pipelines to ensure up-to-date and secure systems.
Existing Challenges
Fraud solutions face the following challenges:
Incomplete data visibility from legacy systems: Lack of access to relevant data sources hampers fraud pattern detection.
Latency issues in fraud prevention systems: Legacy systems lack real-time processing, causing delays in fraud detection.
Difficulty in adapting legacy systems: Inflexibility hinders the adoption of advanced fraud prevention technologies.
Weak security protocols in legacy systems: Outdated security exposes vulnerabilities to cyber attacks.
Operational challenges due to technical sprawl: Diverse technologies complicate maintenance and updates.
High operation costs of legacy systems: Costly maintenance limits budget for fraud prevention.
Lack of collaboration between teams: Siloed approach leads to delayed solutions and higher overhead.
The following video gives an overview of the existing challenges and the reference architecture of the solution:
Reference Architectures
The ML-based fraud solution is suitable for industries where real-time processing, AI/ML modeling, flexibility, and collaboration between teams are essential. The system ensures up-to-date and secure operations through end-to-end CI/CD pipelines. This system can be applied to several industries, including:
Financial services: Fraud detection in transactions
E-commerce: Fraud detection in orders
Healthcare and insurance: Fraud detection in claims
The following diagram demonstrates how MongoDB, AWS, and Databricks interact to build the card fraud solution architecture:
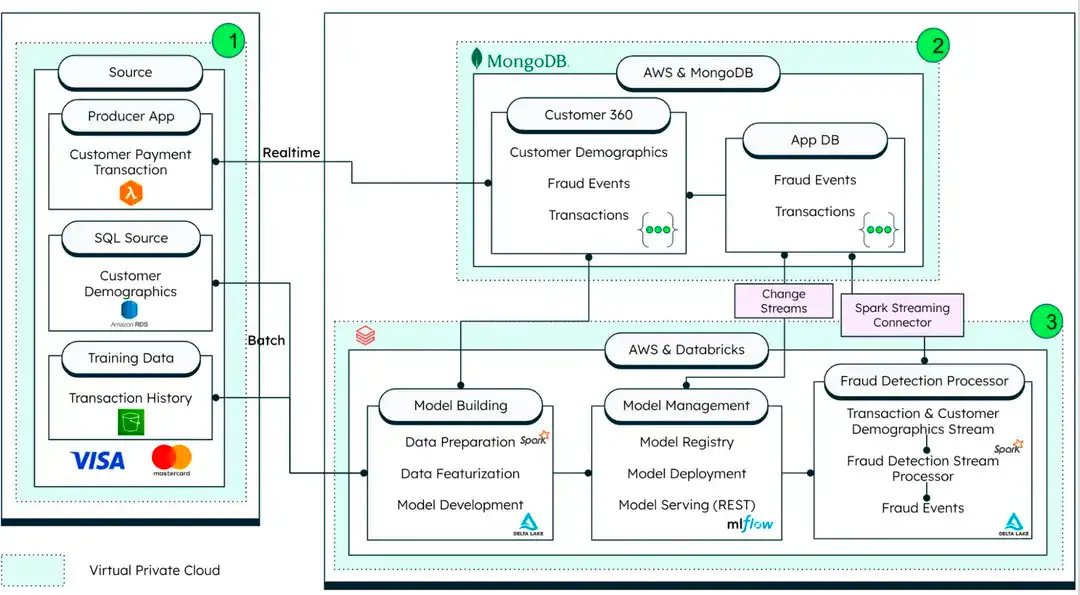
Figure 1. Card fraud solution architecture
Data Model Approach
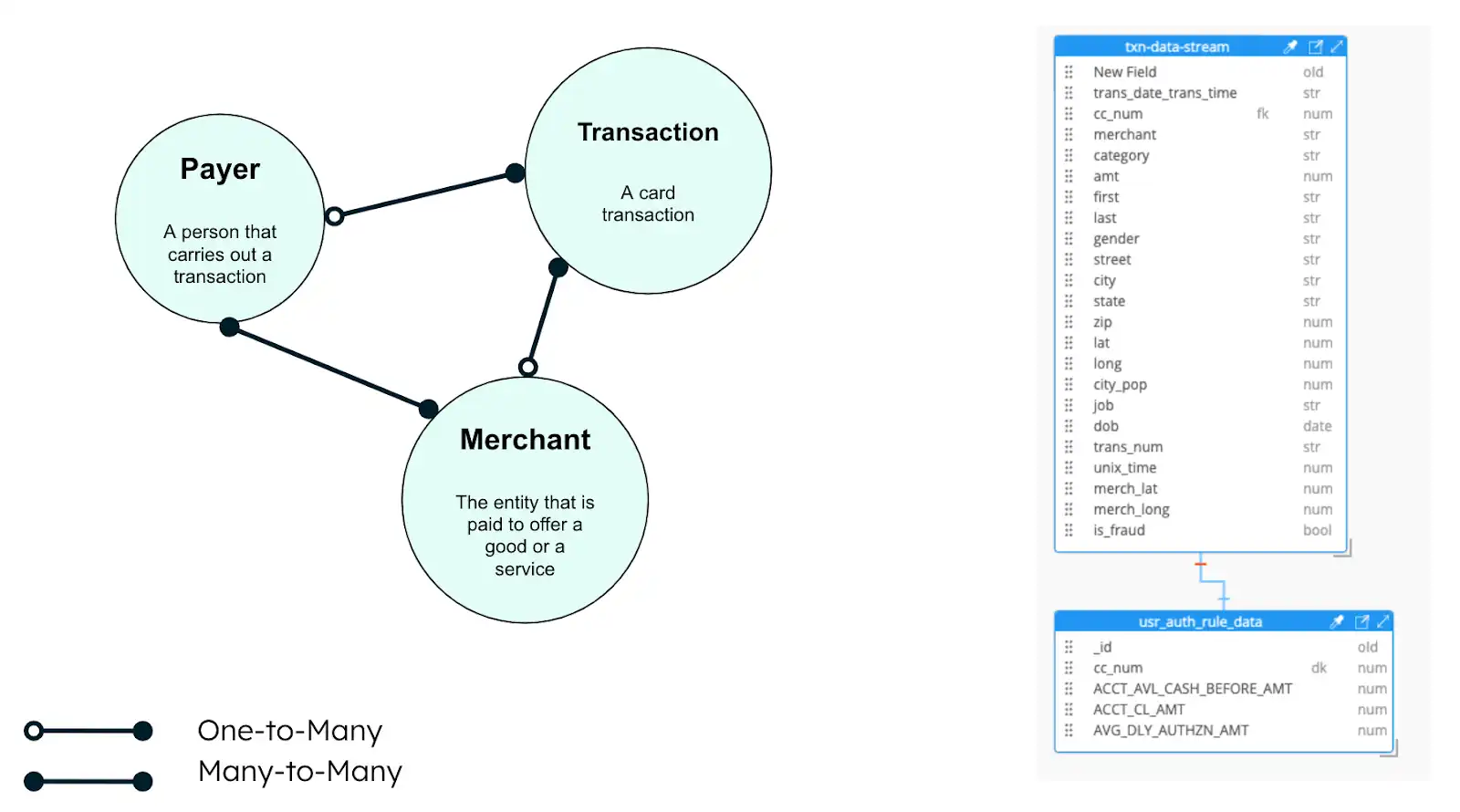
Figure 2. Card fraud solution data model
The diagram shows three entities for credit card transactions:
The transaction
The merchant
The payer
The three entities use the extended reference pattern, which embeds together relevant data fields that are frequently accessed. The fraud detection application includes fields from these entities in a single document.
Build the Solution
The solution uses these components:
Data sourcing
Producer apps: The producer mobile app simulates the generation of live transactions.
Legacy data source: The SQL external data source is used for customer demographics.
Training data: Historical transaction data needed for model training is sourced from cloud object storage - Amazon S3 or Microsoft Azure Blob Storage.
MongoDB Atlas: Serves as the Operational Data Store (ODS) for card transactions and processes transactions in real-time. The solution leverages the MongoDB aggregation framework to perform in-app analytics and to process transactions based on pre-configured rules. It also communicates with Databricks for advanced AI/ML-based fraud detection via a native Spark connector.
Databricks: Hosts the AI/ML platform to complement MongoDB Atlas in-app analytics. The fraud detection algorithm uses a notebook inspired by Databricks' fraud framework MLFlow, and it manages the MLOps for managing this model. The trained model is a REST endpoint.
Data Sourcing
First, aggregate data from all relevant sources, as shown in the architecture diagram above. The diagram uses an event-driven architecture to process data from real-time sources, such as producer apps, SQL databases, and historical training datasets.
This approach enables data sourcing from facets such as transaction summary, customer demography, and merchant information.
Additionally, this proposed event-driven architecture provides the following benefits:
Unified real-time transactions, which allow to collect in real-time card data events, such as amount, location, and payment device.
Helps re-train monitoring models to combat fraud in real time.
The producer application is a Python script that generates live transaction information at a predefined rate.
MongoDB for Event-driven, Shift-left Analytics Architecture
MongoDB Atlas is an effective multi-cloud database platform for card fraud transaction classification. It offers several useful features, such as:
Flexible data model to store various data types.
High scalability to meet transactions demand.
Advanced security features to support compliance with regulatory requirements.
Real-time data processing for fast and accurate fraud detection.
Cloud-based deployment to store data closer to customers and comply with local data privacy regulations.
The MongoDB Spark Streaming Connector integrates Apache Spark and MongoDB. Apache Spark, hosted by Databricks, allows the real-time processing and analysis of large amounts of data.
Change Streams and Atlas Triggers also provode real-time data processing capabilities. You can use Atlas Trigger to invoke a REST service call to an AI/ML model hosted in the Databricks MLFlow framework.
The example solution manages rule-based fraud prevention by storing user-defined payment limits and user settings data. By filtering transactions with these rules before invoking AI/ML models, you can reduce fraud prevention cost.
Databricks as an AI/ML Ops Platform
Databricks is an AI/ML platform that develops models to identify fraudulent transactions. One of the key features of Databricks is the support of real-time analytics for modern fraud detection systems.
Databricks includes MLFlow, a tool for managing the end-to-end machine learning lifecycle. MLFlow allows users to track experiments, reproduce results, and deploy models at scale, making it easier to manage complex machine learning workflows.
MLFlow also offers model observability for performance and debugging. This includes access to model metrics and logs to improve model accuracy over time. These features also support the design of modern AI/ML-based fraud detection systems.
Key Learnings
A ML-based fraud solution with MongoDB and Databricks provides you the following capabilities:
Data completeness: Integrated with external sources for accurate data analysis.
Real-time processing: Enables timely detection of fraudulent activities.
AI/ML modeling: Identifies potential fraud patterns and behaviors.
Real-time monitoring: Allows instant data processing and analysis.
Model observability: Ensures full visibility into fraud patterns.
Flexibility and scalability: Accommodates changing business needs.
Robust security measures: Protects against potential breaches.
Ease of operation: Reduces operational complexities.
Application and data science team collaboration: Aligns goals and cooperation.
End-to-end CI/CD pipeline support: Ensures up-to-date and secure systems.
Authors
Shiv Pullepu, MongoDB
Luca Napoli, MongoDB
Ashwin Gangadhar, MongoDB
Rajesh Vinayagam, MongoDB