Modern organizations operate in increasingly complex environments. Teams are often distributed across cities, countries, or even continents, and many work in situations where connectivity is intermittent or completely unavailable. Construction crews in remote locations, healthcare workers in rural clinics, field engineers on offshore sites, and logistics operators managing warehouses all rely on digital tools to capture, share, and analyze data. Any interruption in access or performance can create inefficiencies, data inconsistencies, and even operational risks.
The integration of RxDB with MongoDB Atlas addresses these challenges by enabling applications to adopt a local-first architecture. This approach ensures that users can continue their work seamlessly, regardless of network availability, while keeping enterprise-grade cloud infrastructure synchronized and up to date. By storing data directly on the client device and automatically synchronizing with MongoDB Atlas when connectivity is restored, organizations can achieve both resilience and consistency across distributed teams and systems.
Seamless local-first with RxDB and MongoDB Atlas
The combination of RxDB and MongoDB Atlas delivers an offline-capable architecture that feels instantaneous to end-users. Actions such as creating, editing, or completing tasks occur directly on the user’s device, eliminating delays caused by network latency. Once the device reconnects, all changes are synchronized with MongoDB Atlas, ensuring the central database remains accurate and reliable. This seamless synchronization is particularly valuable for employees operating in remote or low-connectivity environments, where delays or data loss can directly impact operational effectiveness.
Beyond immediate performance improvements for end-users, this architecture provides IT teams and business leaders with confidence that data integrity is maintained across the organization. By leveraging MongoDB Atlas as the central persistence layer, organizations benefit from built-in security, automated backups, and a globally distributed cloud platform capable of scaling to meet enterprise demands. Local-first applications powered by RxDB allow businesses to deliver a responsive, real-time experience without compromising control, governance, or oversight.
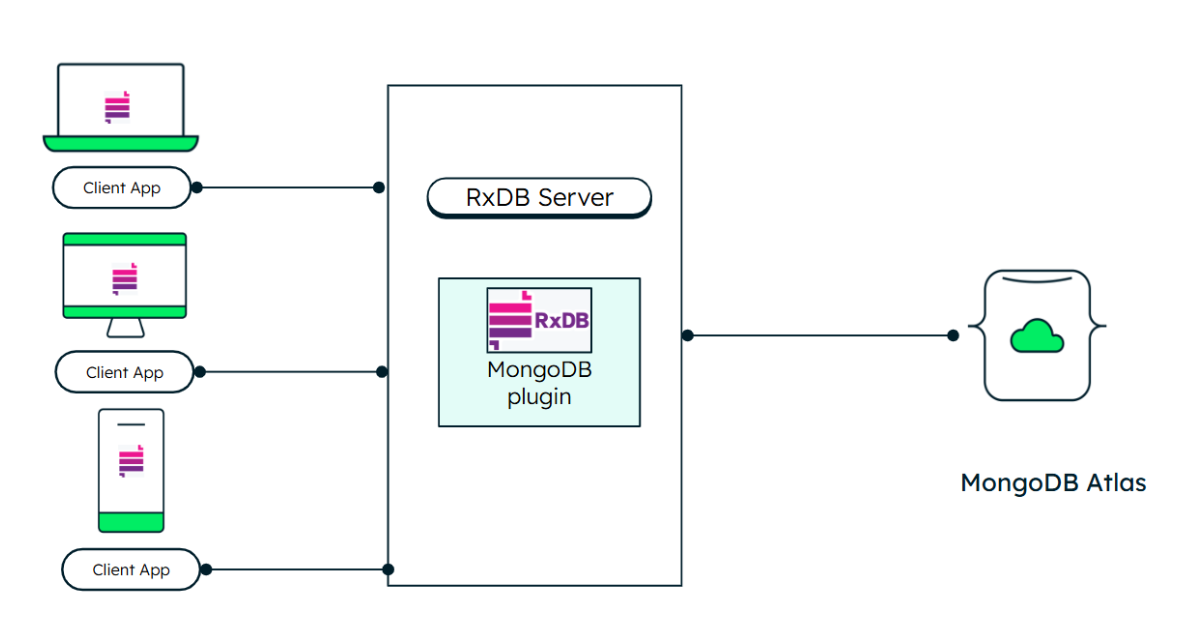
The heart of RxDB’s local-first approach is that the database actually lives inside the client application itself. Each client app (whether it’s a web app, mobile app, or desktop app) runs its own local RxDB instance, storing data directly on the device using technologies like IndexedDB, SQLite, or LokiJS. This makes every read and write operation instant and allows the app to keep working even without a network connection.
While each client app runs its own embedded RxDB instance to deliver local-first functionality, synchronization with MongoDB Atlas is handled by an RxDB Server. This server runs as a Node.js service and uses the MongoDB plugin to connect directly to an Atlas cluster. The plugin defines how data is replicated—whether inserts are handled one by one or in bulk, how collections are mapped, and how conflicts are resolved. This architecture keeps the local database on the device for speed and resilience, while MongoDB Atlas serves as the secure, centralized backbone for persistence and global access.
Experience the perfect blend: Real use cases
RxDB, when combined with MongoDB Atlass, offers a local-first, real-time synchronized, cloud-persistent solution that ensures uninterrupted data capture and reliable cloud storage.
In the field service & maintenance sector, technicians often work in remote locations with intermittent or no network connectivity. By using RxDB, their devices function as local databases, enabling offline-first operation.
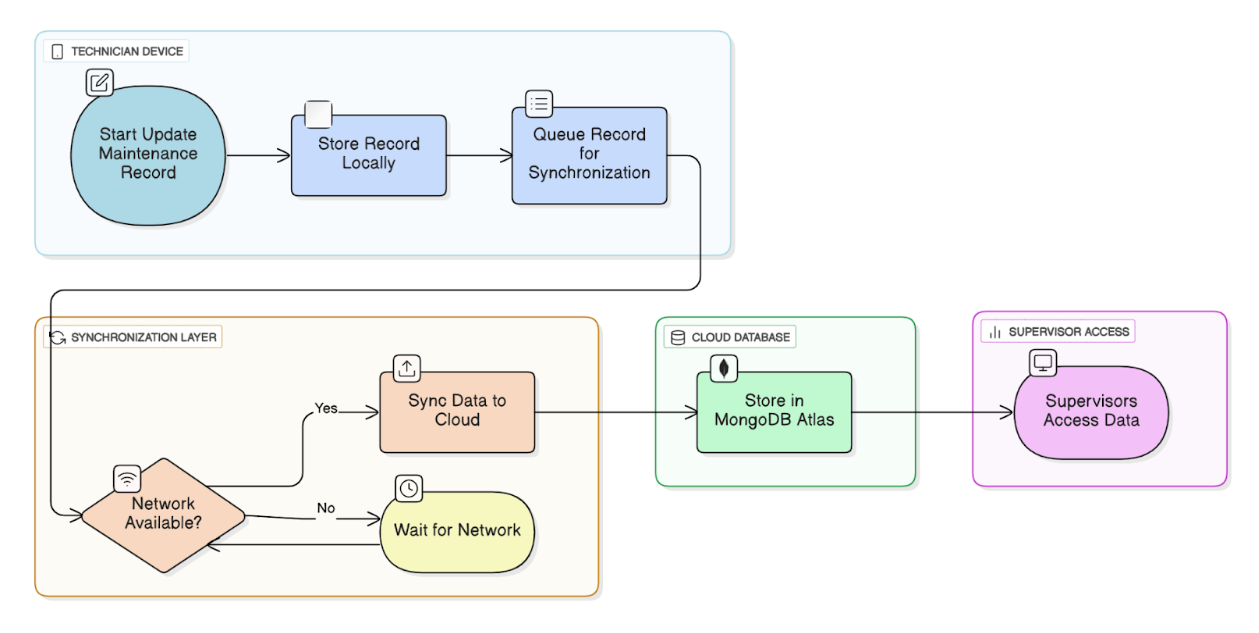
For example, when a technician updates an equipment maintenance record on a mobile app, the record is immediately stored locally. Once network connectivity is restored, RxDB automatically synchronizes the record with MongoDB Atlas, ensuring a single source of truth. Supervisors can then access the updated maintenance data in real time via dashboards or operational tools connected to MongoDB Atlas.
This approach eliminates gaps in service logs, prevents duplicate or conflicting entries, and enables operational continuity and timely reporting without manual intervention. Conceptually, the sequence follows this flow: the technician’s device updates a local record, RxDB queues it for synchronization, connectivity is checked, the data is synced to MongoDB Atlas, and supervisors access the updated information through dashboards or analytics tools.
In the retail & inventory management sector, employees in warehouses, stores, or logistics hubs may also face intermittent connectivity. By leveraging RxDB on mobile scanners or POS devices, immediate data capture is possible for transactions, stock adjustments, and inventory checks.
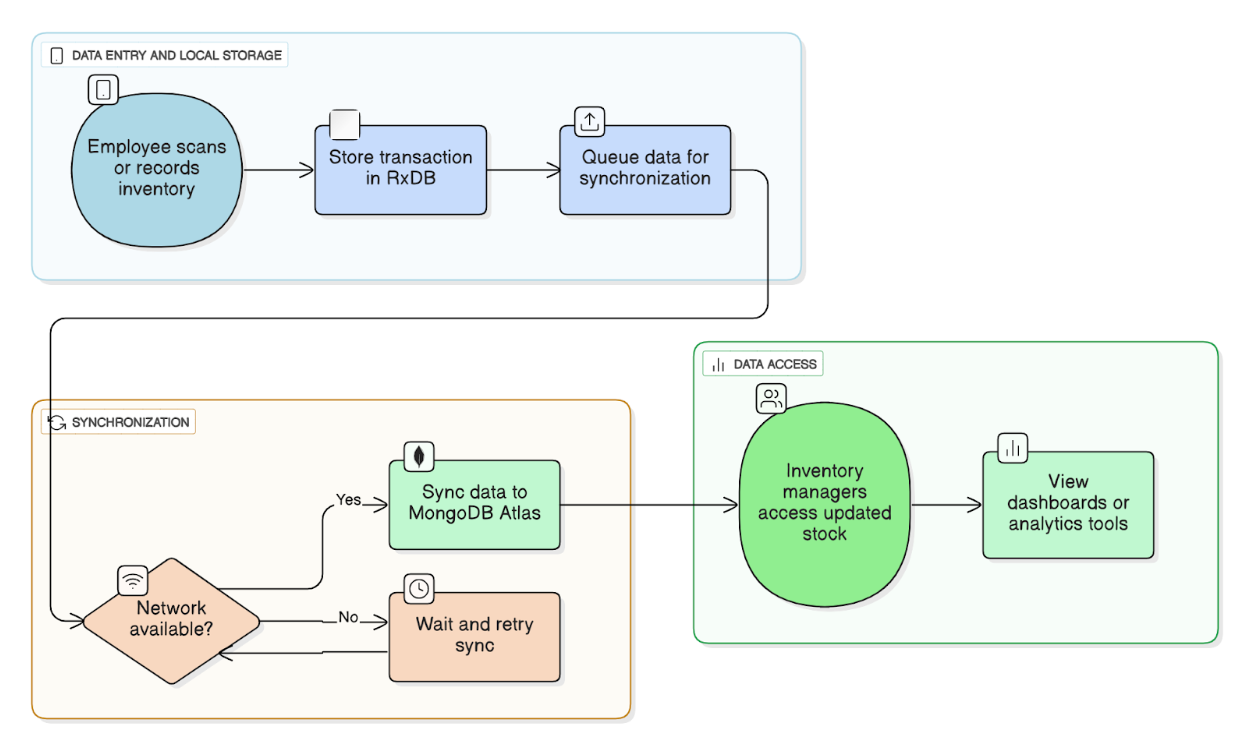
For instance, when a warehouse employee scans items for stock intake or shipment, each transaction is stored locally until the device reconnects. RxDB then synchronizes all changes with MongoDB Atlas, consolidating data across multiple locations. Inventory managers can monitor up-to-date stock levels in real time, enabling accurate demand planning and order fulfillment.
This method maintains accurate inventory, reduces errors caused by offline periods, and supports real-time decision-making. The flow mirrors that of field service: the device records the transaction locally, RxDB queues it, connectivity is checked, the data is synced to MongoDB Atlas, and inventory managers view the results through dashboards.
While this post focuses on the field service and retail sectors, the RxDB + MongoDB Atlas solution is equally valuable across other sectors such as healthcare, remote patient monitoring, IoT, and smart devices, supporting offline-first operations, real-time analytics, and cloud-backed persistence.
Next steps
Take the next step—explore our implementation guides, start a pilot, and see how your organization can deliver reliable, always-on experiences to users worldwide.
Visit our solutions library to learn more about how MongoDB can power your applications.