O assistente inteligente é uma ferramenta alimentada por IA projetada para suporte ao desenvolvimento integrado do MongoDB no MongoDB Compass. Ele fornece respostas a perguntas de linguagem natural, ajuda na depuração de erros e fornece orientação para otimização do desempenho.
Habilitar recursos de IA
Para usar o assistente inteligente no MongoDB Compass, primeiro ative os recursos de IA nas configurações.
Para obter mais informações sobre como alternar as funcionalidades de IA no MongoDB Compass, consulte Habilitar query de linguagem natural.
Acesse o assistente inteligente
Para acessar o assistente inteligente no MongoDB Compass, clique no painel da barra lateral com o . Isso abre o assistente, onde você pode fazer uma variedade de perguntas relacionadas aos erros de conexão do MongoDB Compass, saídas de query, explicar estatísticas do plano e muito mais.
figura 1. A página inicial do MongoDB Compass com o assistente recolhida.
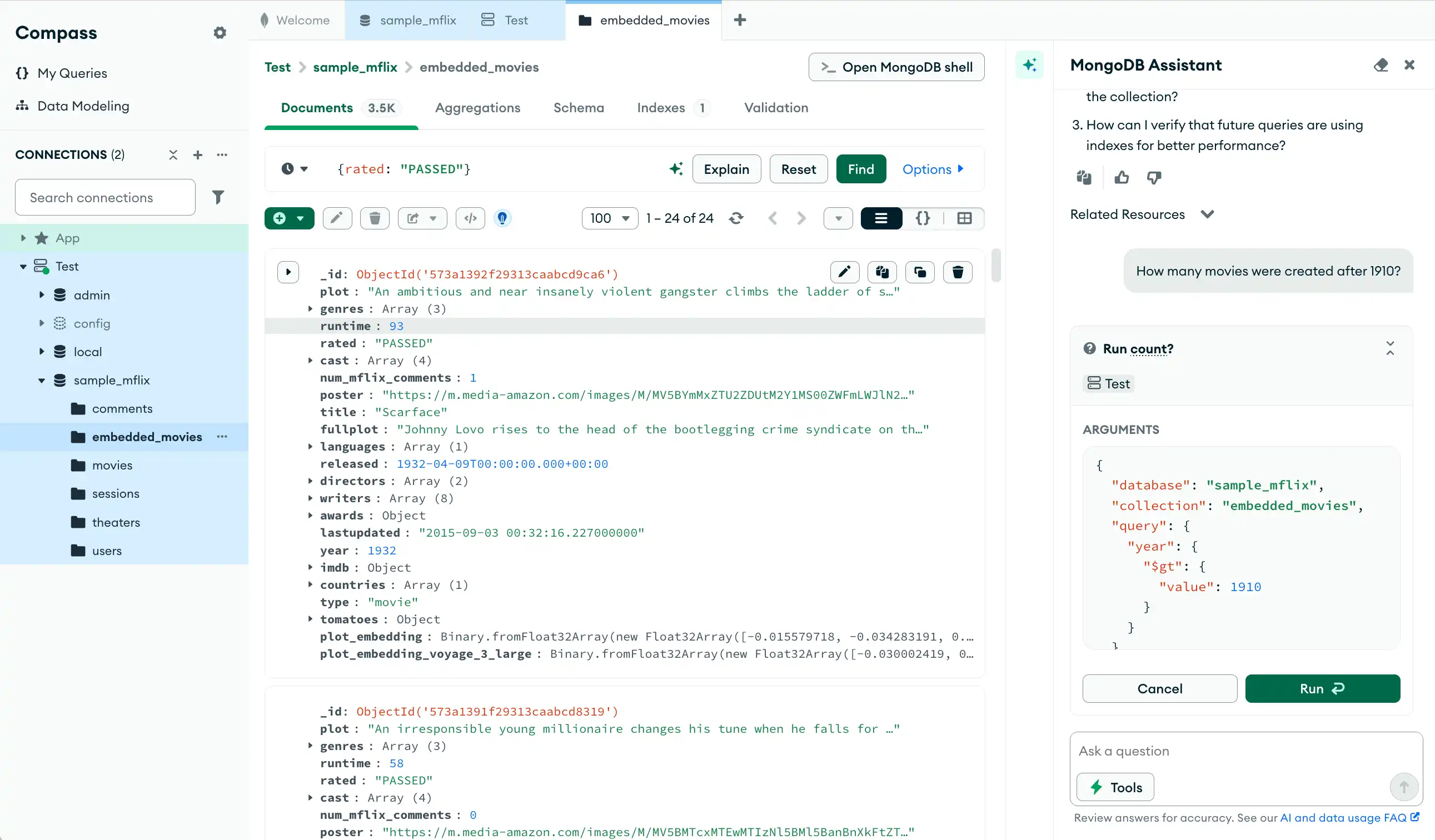
figura 2. A página inicial do MongoDB Compass com o assistente expandido.
Ferramentas somente leitura
As FERRAMENTAS somente para leitura no assistente do MongoDB Compass obtêm contexto de sua tarefa atual ou executam operações de banco de dados em sua implantação conectada do MongoDB com aprovação humana. Ao contrário das respostas de conversação, essas FERRAMENTAS podem realizar queries de banco de dados reais e retornar dados ativos do seu banco de dados.
As ferramentas assistentes exibem as seguintes características principais:
Somente leitura: as ferramentas não podem modificar, inserir, atualizar ou excluir dados.
Aprovado pelo usuário: a execução de cada ferramenta requer a confirmação explícita do usuário.
Contextual: o assistente leva em conta seu banco de dados, coleção e conexão atuais ao decidir chamar ferramentas.
Dados em tempo real: os resultados vêm da sua implementação conectada do MongoDB em tempo real.
FERRAMENTAS do Compass
As ferramentas a seguir buscam conteúdo sensível para os usuários e exigem confirmação. Essas FERRAMENTAS não interagem com o banco de dados, mas exigem a confirmação do usuário antes do uso:
Nome da Ferramenta Compass | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Extrai parâmetros de query ativos do MongoDB da barra de query |
| Extrai o pipeline de agregação ativo do construtor de agregação |
Ferramentas de banco de dados
Nome da Ferramenta de Banco de Dados | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Exibe todos os bancos de dados disponíveis em sua implantação do MongoDB com seus tamanhos de armazenamento. |
| Mostra todas as coleções em um banco de dados específico. |
| Recupera documentos reais de uma coleção que correspondam a critérios de pesquisa específicos. |
| Retorna rapidamente o número total de documentos em uma coleção sem recuperar os próprios documentos. |
| Executa operações complexas de processamento de dados, como agrupamento, filtragem, transformação e cálculo de estatísticas em documentos. |
| Lista todos os índices definidos em uma coleção. |
| Analisa uma coleção para revelar a estrutura de documentos, incluindo nomes de campo e tipos de dados. |
| Relata o espaço em disco físico ocupado por uma collection, incluindo dados e índices. |
| Fornece uma visão geral abrangente da integridade do banco de dados, incluindo contagens de coleções, totais de documento, uso de armazenamento e estatísticas de índice. |
| Recupera logs recentes do servidor para solução de problemas, monitoramento do desempenho e auditoria de segurança. |
| Mostra o plano de execução da query detalhado e as estatísticas de desempenho, revelando como o MongoDB processa uma query e se ela usa índices. |
Observação
As fases do pipeline de agregação $out e $merge não são suportadas na chamada de ferramentas porque executam operações de gravação. O assistente oferece suporte apenas a ferramentas somente leitura.
Fluxo de exemplo
Revise o cartão de ferramentas
O assistente detecta sua intenção e exibe um cartão de ferramenta em um estado pendente. Esta lista enumera os possíveis elementos que o cartão de ferramentas pode mostrar:
Operação do nome da ferramenta
Implantação (hospedar/ponto de extremidade)
Banco de dados e coleção sendo consultados
Quaisquer parâmetros ou filtros
Run e Cancel botões
Para o exemplo acima, o cartão de ferramenta mostra para "bancos de dados de lista".
Exemplos
Os cenários a seguir mostram vários usos do assistente inteligente no MongoDB Compass.
Erro de conexão
Se você receber uma mensagem de erro de conexão, será exibida uma janela pop-up orientando você a usar o Assistente do MongoDB para depurar o erro. Clicar em Debug solicita que o assistente gere automaticamente um prompt para diagnosticar o erro.
Diagnose why my Compass connection is failing and help me debug it. Connection string (password redacted): mongodb+srv://user:****@cluster0.pndqllj.mongodb.net/ Error message: querySrv ECONNREFUSED
The error message querySrv ECONNREFUSED in MongoDB Compass typically points to a network issue when Compass is trying to discover your Atlas cluster using DNS SRV records in your connection string. Here are the most common causes and solutions for this issue: 1. Incorrect Hostname or Cluster Name - Ensure that the cluster hostname (cluster0.hrdfe.mongodb.net) in your connection string matches what is shown in your Atlas dashboard. - Typos or a deleted/renamed cluster will cause connection refusal. 2. Network Restrictions or Firewall Blocking - Atlas clusters operate on port 27017. Compass must be able to reach that port through your network. - Firewalls, VPNs, or proxies might block outbound connections to MongoDB Atlas. - Try connecting from a different network/location to rule out local filtering. - You can test if your network allows access to this port using http://portquiz.net:27017/. 3. DNS Issues - Compass uses DNS to resolve the SRV record in the connect string. If your DNS settings are incorrect or your network blocks DNS SRV lookups, connection will fail. Try restarting your computer or flushing your DNS cache. 4. Cluster Status - Verify that your MongoDB Atlas cluster is running and not paused or shut down. 5. Compass Version - Make sure you’re using an up-to-date version of MongoDB Compass. Atlas typically requires recent client versions. Recommended Steps to Debug: - Double-check your Atlas cluster name and hostname. - Ensure your local firewall allows outbound connections to “*.mongodb.net” over port 27017. - Check that the Atlas cluster is running (not paused). - Make sure your connection string is correct. - Use another network or device to see if the issue persists. If you’re still having trouble after these checks, please provide more details about your environment (e.g., Compass version, operating system, network setup), and I’ll be happy to help you further! For further reading, I recommend checking the Compass troubleshooting documentation, which covers these scenarios in detail before making any major changes to your environment.
Explicar plano
peça ao assistente inteligente para analisar a saída de sua consulta do MongoDB Compass :
Interpret this explain plan for me.
## Summary - **Query Logic:** This pipeline counts the number of Italian restaurants in Manhattan by first filtering documents and then aggregating the count. - **Performance:** Fair - **Recommendations:** Create a compound index on `{ borough: 1, cuisine: 1 }` to optimize document retrieval. ## Details ### Query Logic 1. `$match`: Filters documents where `borough` is "Manhattan" and `cuisine` is "Italian". 2. `$count`: Counts the number of documents matching the filter and outputs the total. ### Performance Analysis - The winning plan uses an index scan on the `cuisine` field (`cuisine_1`) and applies an in-memory filter for `borough` ("Manhattan"). - Both `totalKeysExamined` and `totalDocsExamined` are high (43,207), which implies that every document with `cuisine: "Italian"` is examined and then filtered by `borough`. - No compound index exists, meaning MongoDB cannot efficiently combine both filter criteria in a single index lookup. - The pipeline does properly filter before counting, but index usage is only partial, causing increased resource usage. ### Recommendations - Create a compound index on `{ borough: 1, cuisine: 1 }` to allow MongoDB to retrieve documents matching both criteria directly from the index, minimizing documents examined. - This optimization will reduce execution time and system load without changing the output of your aggregation pipeline. Below is the recommended Aggregation Pipeline. This optimized Aggregation Pipeline will leverage the compound index to scan fewer documents, as both filter criteria are present in the index. ```json [ { "$match": { "borough": "Manhattan", "cuisine": "Italian" } }, { "$count": "totalItalianRestaurants" } ] ``` ### Follow-Up Questions 1. How do I create a compound index in MongoDB Compass or via a shell command? 2. What other fields should I consider adding to my indexes for restaurant lookups? 3. How can I further optimize aggregations when working with larger datasets?
Perguntas do usuário
Os exemplos a seguir demonstram perguntas que você pode fazer ao assistente inteligente sobre as funções e consultas do MongoDB Compass .
How is MongoDB data modeling different from data modeling with a relational database?
MongoDB data modeling differs from relational database (RDBMS) data modeling in some important ways: 1. Document-Oriented vs. Table-Oriented - MongoDB stores data as flexible, hierarchical JSON-like documents. - Relational databases use tables with fixed schemas and columns. 2. Schema Flexibility - In MongoDB, collections can contain documents with different structures. Schema enforcement is optional. - RDBMS tables have a strict schema that enforces data types and relationships. 3. Embedding vs. Normalization - MongoDB encourages embedding related data inside documents when appropriate (denormalization). Example: An order document may include an array of items directly inside it. - Relational databases emphasize normalization—splitting data across tables connected by foreign keys. 4. Relationships - MongoDB does support references between documents (similar to foreign keys), but joins are less central and not as efficient as in RDBMS. - RDBMSs use normalized data and JOIN operations to relate tables efficiently. 5. Performance & Scaling - MongoDB’s data model enables horizontal scaling (sharding), making it well-suited for large, distributed datasets. - RDBMS scaling typically relies on vertical scaling or complex clustering; JOINs can become expensive as data grows. 6. Use Cases and Design Philosophy - MongoDB models are often designed to optimize common query patterns, reducing the need for joins and complex queries. - RDBMS models are designed for transactional consistency and for representing organized, well-structured relationships. In summary, MongoDB encourages a more flexible, application-driven approach to modeling, while relational databases rely on rigid schemas and normalized relationships. Compass provides tools to visually explore your document structures and relationships, which can be especially helpful as your model evolves.
How can I combine multiple conditions in a single $search query?
To combine multiple conditions in a single $search query in MongoDB Atlas Search (including Compass), you should use the compound operator. The compound operator allows you to specify multiple criteria using must, mustNot, filter, and should clauses. Example: Combine Multiple Conditions Suppose you want to: - Match documents where the plot field contains "baseball" - Exclude documents where the genres field contains "Comedy" or "Romance" Your $search stage would look like this: { "$search": { "compound": { "must": [ { "text": { "query": "baseball", "path": "plot" } } ], "mustNot": [ { "text": { "query": ["Comedy", "Romance"], "path": "genres" } } ] } } }