When designing MongoDB systems that utilize MongoDB Search and MongoDB Vector Search, there are two common deployment types:
A co-located architecture where
mongodandmongotprocesses share the same host. This architecture is suitable for development and small search or vector search workloads.A dedicated infrastructure model where
mongodandmongotprocesses run on separate machines, each sized according to the needs of each workload. This infrastructure is recommended for applications that demand high availability, sharding, or substantial search or vector workloads with heavy search queries and indexing.
This section describes both deployment types. It also describes the
implications of deploying mongot in sharded MongoDB clusters.
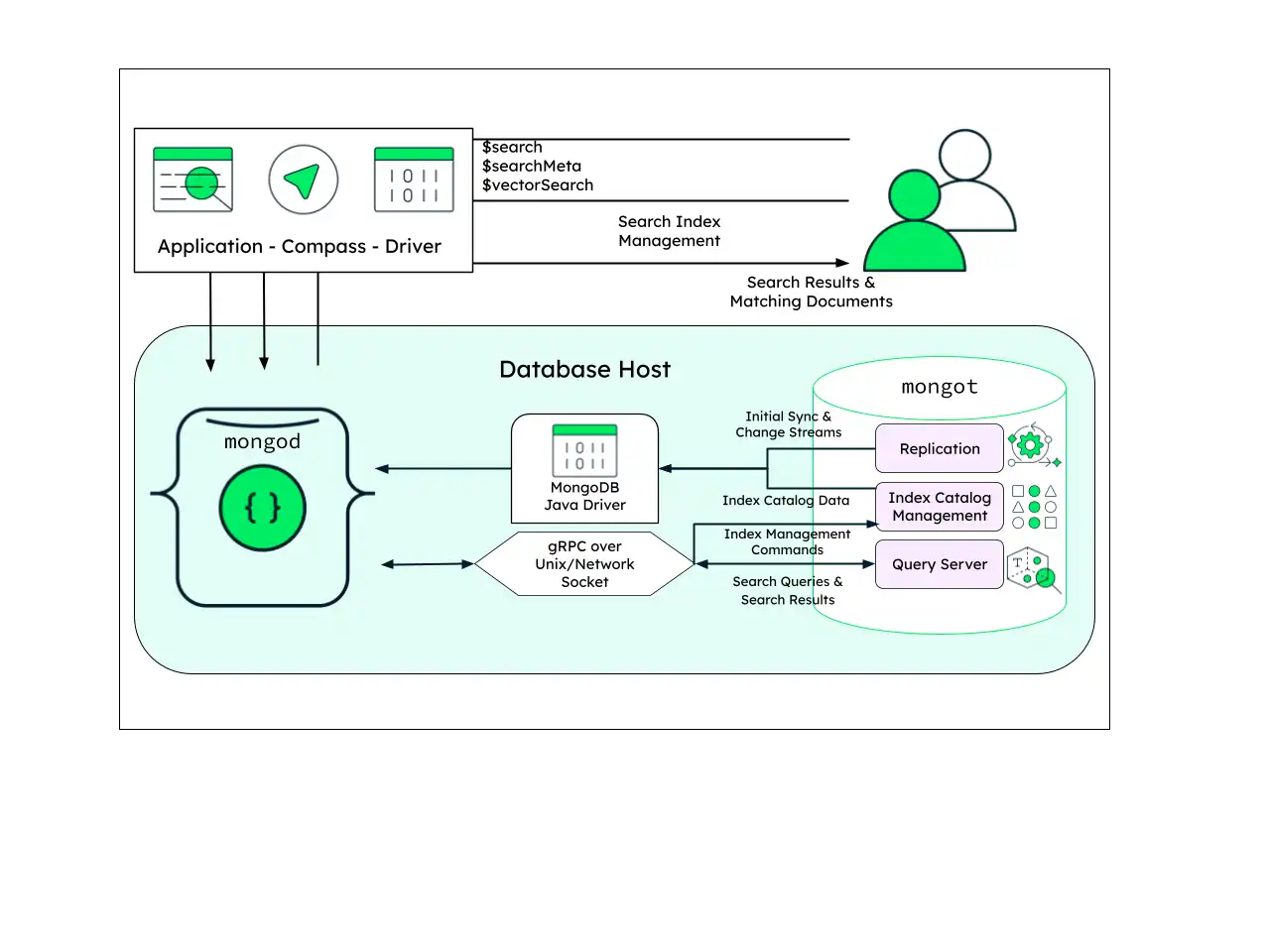
Co-Located Architecture
This is the simplest architecture, recommended for development environments or any situation that requires quick iteration. It excels in rapid prototyping and requires the least amount of configuration.
The deployment consists of a single machine running both
mongod and mongot processes. All communication can take
place over localhost addresses, and all authentication and
security features can be disabled or made more permissive.
For most small search workloads, you can expand this architecture to a multi-node replica set. Use caution when implementing a co-located architecture, and monitor for signs of resource contention.
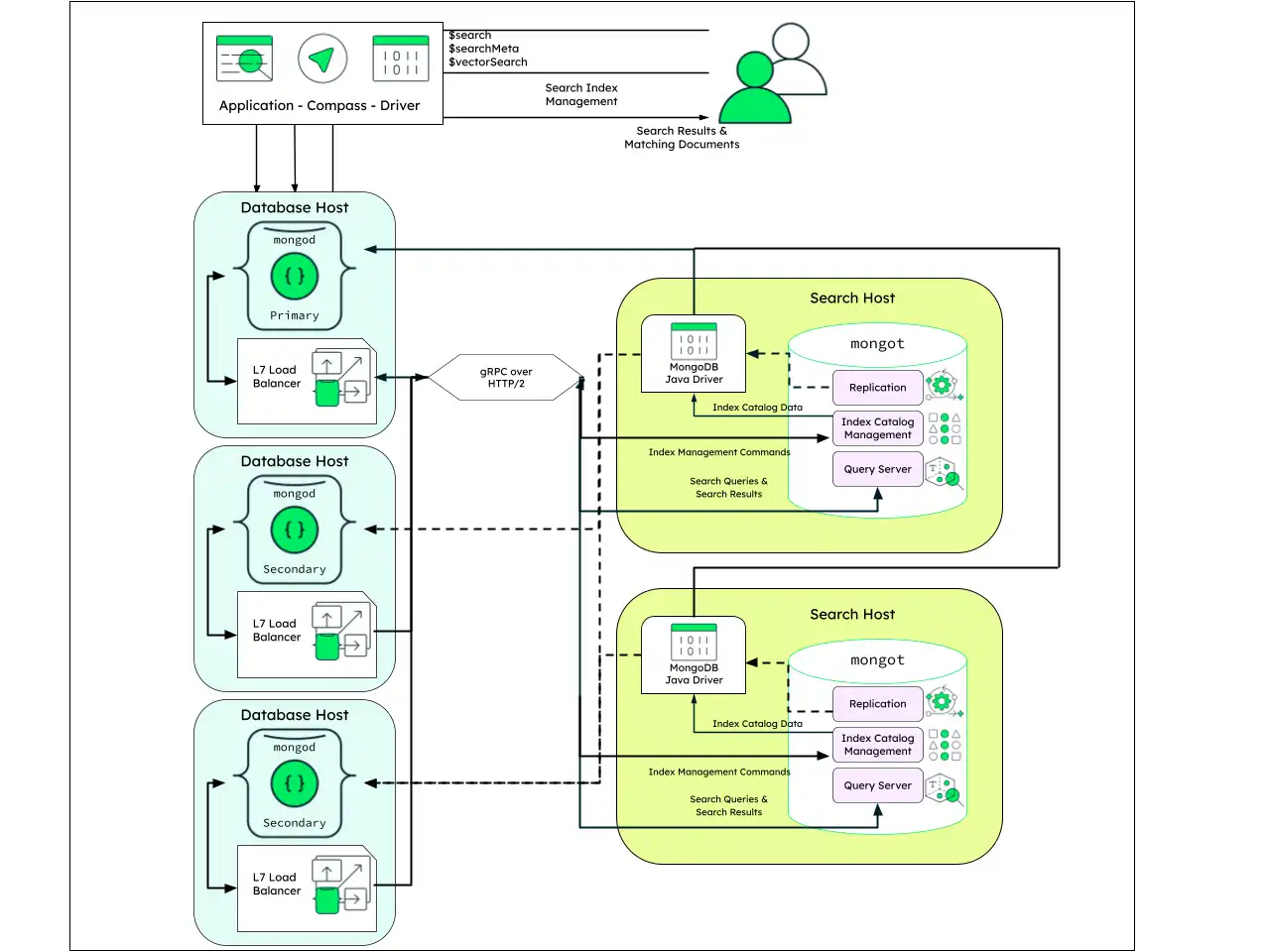
Dedicated Infrastructure
This is a general-purpose architecture, recommended for production environments. Dedicated infrastructure accommodates both horizontal and vertical scalability for both the database nodes and search nodes.
The deployment consists of at least three machines running mongod in
a replica set configuration, and at least two machines running
mongot. To provide high availability when querying Search, the
mongod nodes require an application-level load balancer. Consider a
load balancer like Envoy, and use a load balancing strategy such as
per-request round-robin.
No load balancing is required in the opposite direction.
mongot automatically chooses a mongod node to communicate
with for data replication and the index catalog data based on its
configuration.
Note
Search Index Storage
Each mongot maintains indexes that are built from the data
continuously sourced from the database. The index definitions
(metadata) are stored in the database itself.
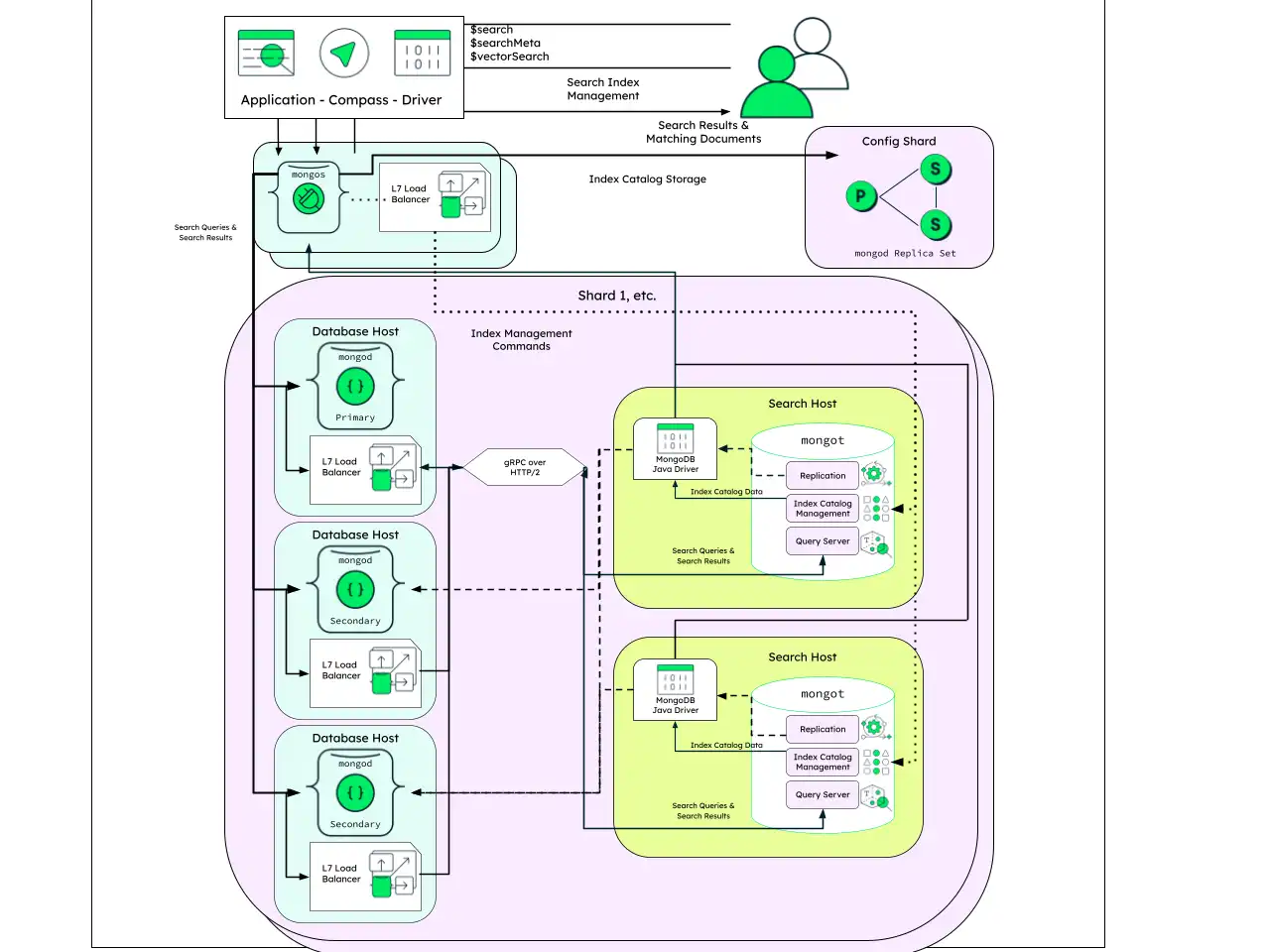
Sharded Topology
This architecture is similar to the dedicated infrastructure architecture, but the replica set configuration is duplicated to each individual shard.
Note
Even though you should only configure mongot to replicate
from one shard, mongot still requires the router address
to be configured in order to access the index catalog.
With the sharded topology architecture, mongot only belongs to
a single shard at a time. As a result, load balancers within each
shard should only be configured to direct traffic to that individual shard.
If you add shards to a collection with an existing MongoDB Search index, an initial sync occurs on the newly added shards for that MongoDB Search index. Each shard's MongoDB Search index contains only the documents from the collection that exist on that shard.
Important
Search Index Storage in Sharded Clusters
In a sharded cluster, search indexes are distributed across the
mongot processes associated with each shard. Consider this when
planning your backup and recovery policies, as you will need to
account for both the database data and the search index data stored
on each shard's mongot nodes.
To learn more, see Shard a Global Collection.
Warning
If you shard a collection that already has a MongoDB Search index, you might experience a brief period of incomplete search results while the index is building on a shard.
Also, if you add a shard for an already sharded collection that contains a MongoDB Search index, your search queries against that collection might return incomplete results until the initial sync process completes on the added shards. To learn more, see troubleshoot-initial-sync.