MongoDB powers open finance with flexible data integration, built-in security, and scalable financial services.
Use cases: App Driven-Analytics
Industries: Financial Services
Products and tools: Aggregation Pipeline, MongoDB Atlas
Solution Overview
Open finance is transforming the financial industry, enabling seamless data sharing across banks, fintech companies, and third-party providers. However, the integration of diverse financial data while ensuring security, compliance, and scalability remains a major challenge. MongoDB provides a foundation for open finance through its:
Flexible document model
Native JSON support
Powerful aggregation framework
These features allow institutions to unify data from multiple sources and ensure secure and compliant data management without the complexity of traditional relational databases.
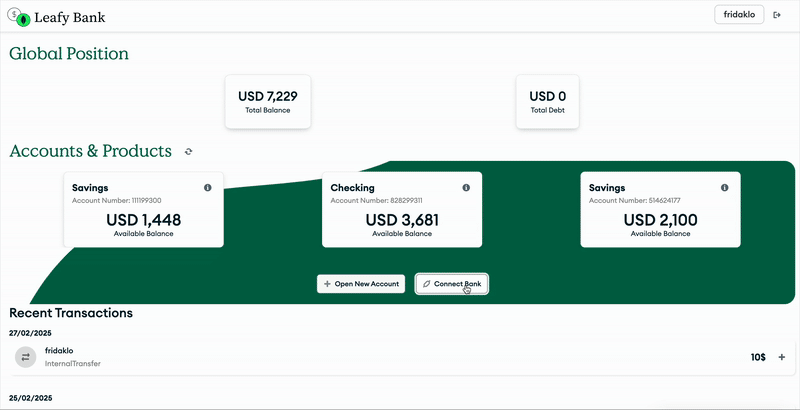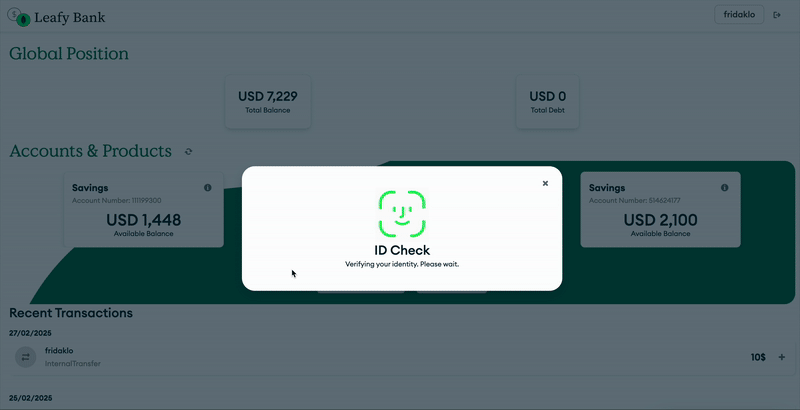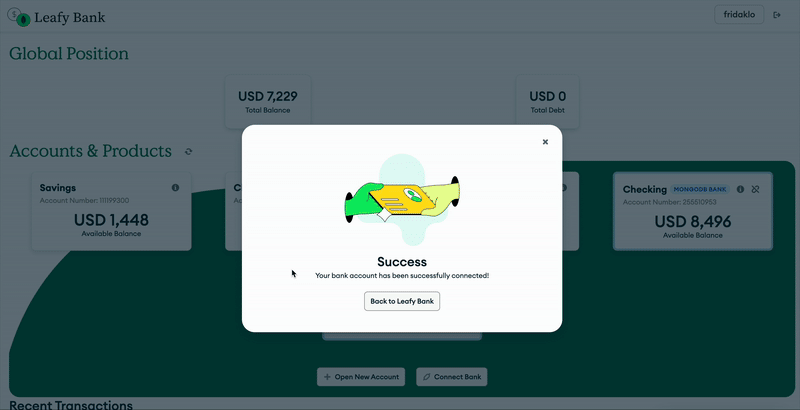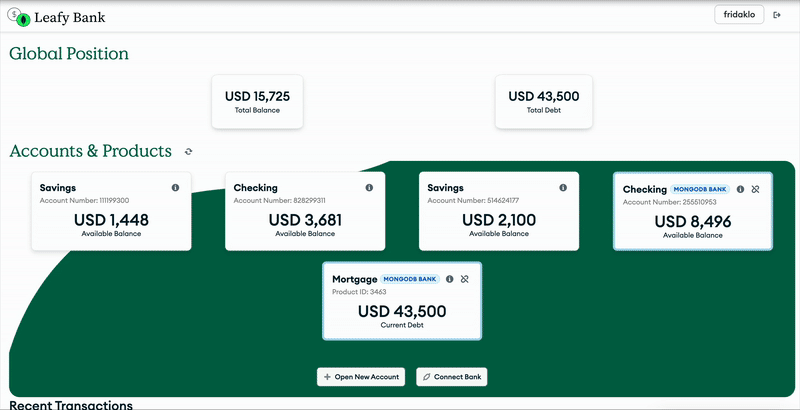
Figure 1. Open finance application with MongoDB
Reference Architectures
This solution demonstrates a banking application that allows users to securely connect external bank accounts.
The user initiates requests to connect their external bank accounts. This operation requires explicit user consent, ensuring security and compliance with regulations like PSD2. To authenticate, the application emulates OAuth 2.0 and generates tokens to enable secure communication between institutions.
When authorized, the application uses APIs to communicate with external banks. These banks expose financial data such as accounts, transactions, and balances through their microservices. The responses are in JSON format, which ensures compatibility and seamless data exchange.
The application then pushes the financial data into MongoDB Atlas. With the document model, MongoDB lets you handle diverse data structures from different banks. The application can then use aggregation pipelines to analyze and enrich the data, giving users a holistic financial view while enabling the bank to offer personalized financial insights.

Figure 2. Open finance architecture diagram
Data Model Approach
In this solution, the data model emulates real-world financial data integration. This approach leverages the flexibility of the document model to handle diverse data structures from different financial entities.
Components
Collection | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stores Bearer tokens, which the application uses for authenticating and authorizing API requests with external banks. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Stores information on external bank accounts linked by users. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Stores information on financial products (such as loans and mortgages) associated with users. |
In real-world applications, these collections would involve more complex security mechanisms and detailed information. Each financial entity has its own data model definitions.
- Data mapping and relationships
- The application needs a robust data mapping and relationship later to translate diverse data models from different financial entities to a unified format.
- Security and compliance
- The application must ensure data security and compliance with regulations, such as GDPR, PSD2, and other local financial regulations. This includes encryption, access controls, and audit trails.
- Scalability and performance
- The application requires a data model that can handle large volumes of data efficiently with considerations for indexing, sharding, and performance optimization.
- Integration and interoperability
- The application implements APIs and microservices that can integrate with various external systems, ensuring interoperability and real-time data exchange.
With the flexibility of the document model, this solution demonstrates how financial institutions can unify and manage diverse data sources. A production-grade implementation needs to address the complexities and nuances of real-world financial data integration.
Build the Solution
This solution is available through two GitHub repositories:
Solution Backend: The Backend repository provides the open finance demo service. It shows how to integrate with third party banks and secure data exchange.
Solution Frontend: The Frontend repository provides the open finance user interface. The UI acts as the main hub and provides an overview of all integrated services.
Solution Backend
For details of the solution backend, see the Backend GitHub repository. This repository provides the open finance demo service. It shows how to integrate with third-party banks and secure data exchange. MongoDB serves as the central data store.
To build the solution, complete the following steps:
Solution Frontend
The user interface of this solution is available in the Frontend repository on GitHub. The components are designed as microservices. The UI repository acts as the main hub and provides an overview of all integrated services.
Key Learnings
Implement a central data store: Use MongoDB as a central data store to support open finance ecosystems.
Secure data management: MongoDB provides secure data management with built-in encryption, granular access controls, and high availability. This helps organizations protect sensitive information and comply with regulatory requirements.
Offer personalized insights: Use MongoDB’s aggregation pipeline to analyze customer data and deliver customized financial insights to your users.
Authors
Luis Pazmino Diaz, MongoDB
Ainhoa Mugica, MongoDB
Julian Boronat, MongoDB
Andrea Alaman Calderon, MongoDB