Frontier AI models are driving the widespread adoption of generative AI by demonstrating unprecedented capabilities. However, their deployment often entails significant costs. The strategic partnership between MongoDB and Fireworks.AI addresses these cost implications by offering solutions that optimize performance and resource utilization. This collaboration leverages MongoDB's efficient data management alongside Fireworks.AI's model optimization tools to enhance speed and efficiency while minimizing operational expenses.
In the current AI environment, achieving high performance is crucial, but equally important is optimizing the total cost of ownership (TCO). Businesses must focus on the price-performance ratio, ensuring that improvements in speed and efficiency lead to real cost savings.
This article will address the following topics:
How to build an agentic RAG using a Fireworks AI hosted LLM and MongoDB Atlas for retrieval.
Strategies for optimizing retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) applications using MongoDB Atlas and large language models (LLMs) through effective query and response caching.
Techniques using the Fireworks AI platform focus on fine-tuning models, accelerating LLM inference, and reducing hardware needs.
Steps to fine-tune a pretrained SLM with PEFT techniques using the Fireworks Platform.
Readers will gain a practical, in-depth strategy to improve AI performance while lowering costs. This will be demonstrated with examples and performance data.
Unlocking efficiency and performance with MongoDB and Fireworks AI
MongoDB Atlas is renowned for its flexible schema, efficient indexing, and distributed architecture, allowing organizations to scale their data infrastructure on demand. MongoDB Atlas is a general-purpose database that focuses on highlighting flexibility, AI suitability, and ACID transactions. Users have the flexibility to run their application anywhere but making sure that there are no compromises made in the security aspects of working with it. MongoDB offers a comprehensive, secure, and efficient database solution for modern applications, catering to various technical and strategic needs.
Fireworks AI is recognized for its suite of technologies focused on optimizing the performance and efficiency of large language models (LLMs). Their offerings span model optimization tools, a specialized FireOptimizer framework, and innovative attention mechanisms like FireAttention. These solutions aim to enhance inference speeds, reduce operational costs, and improve resource utilization. Furthermore, Fireworks AI provides parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods and adaptive speculative execution to tailor models for specific applications. Their advancements also include optimized processing for long-context tasks and techniques to maximize throughput and cost-effectiveness in model serving. Fireworks also provides model serving functionality for select models that are readily available, also they do provide a platform to host and serve custom implementations of LLM models for customers.
Core capabilities: FireOptimizer and FireAttention
The FireOptimizer is Fireworks.ai’s adaptation engine for customizing AI model performance in production environments. It automates latency and quality optimization for unique inference workloads. It tailors performance across hardware, model, and software layers using techniques like customizable quantization, fine-tuning, and adaptive caching. Its hallmark feature, adaptive speculative execution, automatically trains workload-specific draft models to parallelize token generation, achieving up to 3x latency improvements compared to generic speculative decoding. This method significantly boosts responsiveness without compromising accuracy by increasing the hit rate.
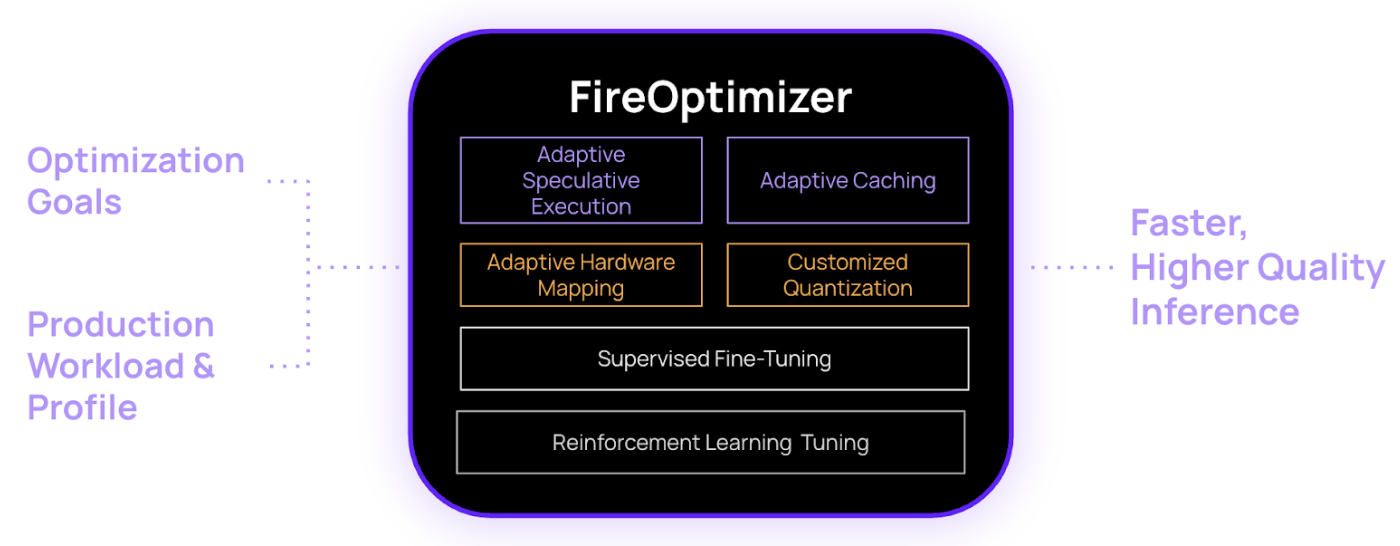
FireAttention, Fireworks AI's custom-built inference engine, significantly enhances LLM inference speed on GPUs. It achieves this by utilizing a novel micro-precision data format and rewriting key GPU kernels (such as attention and matrix multiplication) from scratch, aligning them with underlying hardware instructions. While FireAttention prioritizes speed, potentially at the cost of initial accuracy, this is mitigated through Quantization-Aware Training (QAT). This approach allows finetuned models to maintain high precision while reducing their memory footprint. Benchmarks demonstrate FireAttention V4's superior performance over SGLang on H200 and TRT-LLM on B200, particularly in MMLU Pro tests. Overall, FireAttention V4 represents a breakthrough in achieving low-latency, high-efficiency LLM inference, especially beneficial for frontier models like DeepSeek R1.
Key benefits:
Faster inference: FireOptimizer's adaptive speculative execution has demonstrated up to 3x latency improvements in production workloads across various models, ensuring highly responsive applications.
Hassle-free optimization: FireOptimizer automates the complexities of optimization, allowing users to concentrate on application development.
FireOptimizer
FireOptimizer improves batch inference by integrating with MongoDB for efficient model fine-tuning and streamlined deployment. This multi-layered customization is vital for compound AI systems, ensuring consistent model alignment. Available for enterprise on-premise and own-cloud, FireOptimizer enhances traditional inference performance through techniques like adaptive speculative execution, caching, customizable quantization, personalized fine-tuning at scale, and customizable hardware mapping.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the benefits of FireOptimizer to perform Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) so we can use a small language model(SLM) model to carry out personalized tasks such as RAG for a private dataset. This activity will demonstrate how generative AI can be adopted for general use at scale and critical domains effectively.
Survey of fine-tuning strategies for smaller, efficient models
Smaller language models present significant opportunities for tailored adaptation while using fewer resources. The ongoing evolution in this field is fueled by increasing demand for deploying optimized LLMs across diverse environments, including cloud platforms, edge devices, and specialized hardware. These fine-tuning approaches can be categorized as follows:
- Additive parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT): This class of methods augments pre-trained models with new trainable parameters without altering the original weights.
- Adapters: These involve inserting small, trainable modules, known as adapters, within the pre-trained model's layers. These adapters learn task-specific adjustments, enabling adaptation to new tasks without changing the pre-existing parameters.
- Soft prompts: These are trainable vector embeddings appended to the input sequence, acting as guiding signals to influence the model's output for a specific task.
- Prefix tuning: This technique adds a trainable prefix to the input sequence. This prefix learns task-specific information without requiring modifications to the core model architecture.
- Reparametrization PEFT: This approach reduces the number of trainable parameters by reparameterizing existing model weights using low-rank approximations.
- Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA): LoRA approximates weight updates in the attention layers of a pre-trained model using low-rank matrices, significantly decreasing the number of trainable parameters.
- Quantized LoRA (QLoRA): QLoRA builds upon LoRA by integrating quantization methods, further decreasing memory footprint and computational expenses.
- Selective fine-tuning: This category focuses on fine-tuning only specific parameters of the pre-trained model, leading to improved computational efficiency.
- BitFit: This method fine-tunes only the bias terms, or other designated parameters, of the pre-trained model, enhancing computational efficiency.
- DiffPruning: This technique identifies and removes parameters that have minimal impact on the model's performance, thus reducing the number of trainable parameters.
- Layer freezing strategies: These strategies involve selectively freezing certain layers of the pre-trained model while fine-tuning others to optimize the adaptation process.
- Freeze and reconfigure (FAR): FAR involves freezing specific layers of the pre-trained model and fine-tuning the remaining layers to optimize model adaptation.
- FishMask: This technique uses a mask to selectively freeze or fine-tune layers, optimizing adaptation for specific tasks.
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) is a popular technique for adapting small pre-trained models to niche tasks. By adjusting only a small portion of the model's parameters, PEFT prevents overfitting, especially on smaller datasets, and greatly reduces computational and memory demands compared to full fine-tuning. Additionally, PEFT helps mitigate catastrophic forgetting in LLMs. This approach allows for efficient model customization in resource-constrained environments without the need for complete retraining.
Leveraging PEFT LoRA techniques in Fireworks AI, combined with the availability of trace data and labeled data, allows for efficient fine-tuning of smaller models.
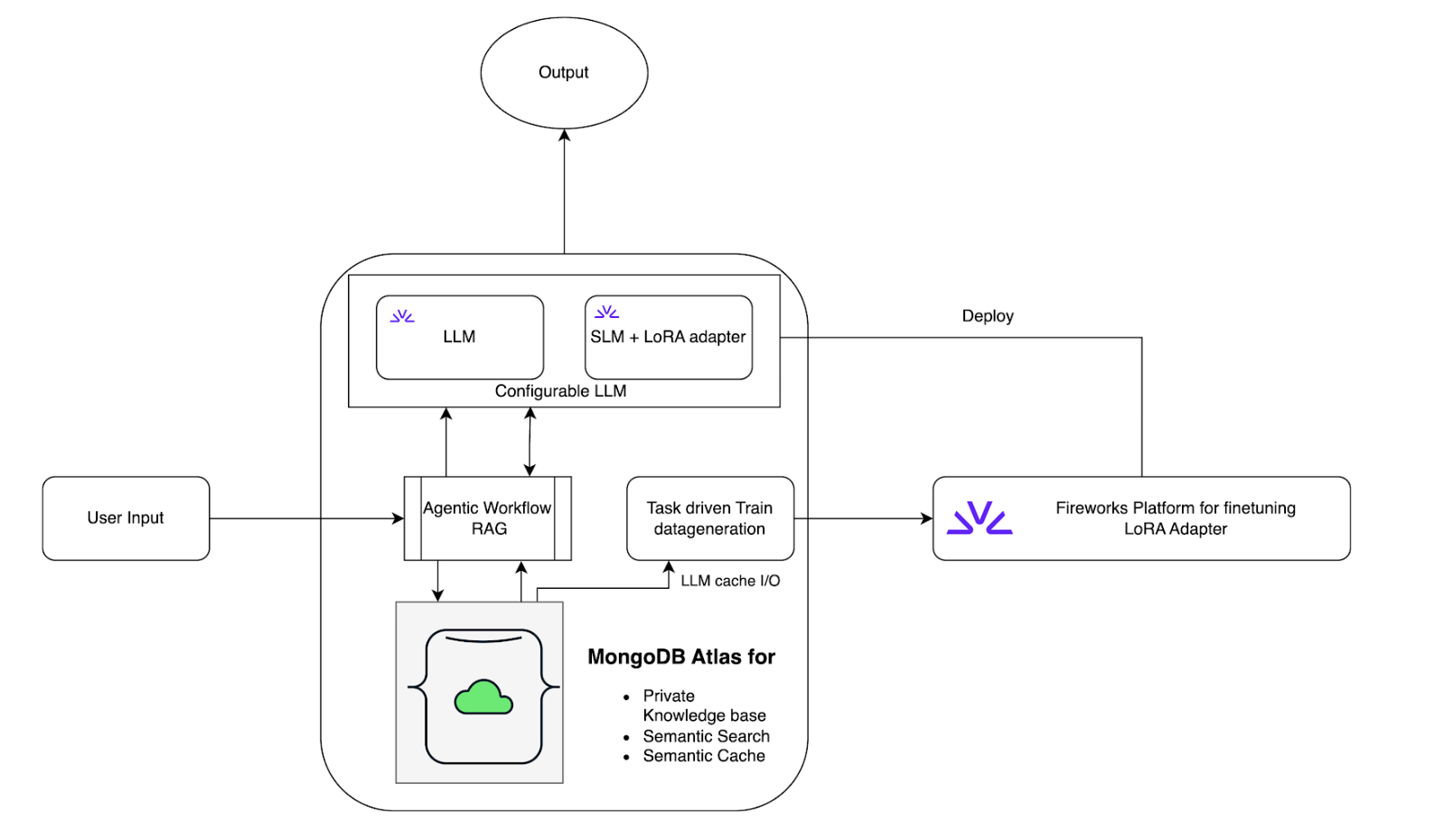
To demonstrate the practical implications of using a small language model (SLM), we will build an agentic RAG application using MongoDB Atlas and illustrate how MongoDB can be used to power semantic search capabilities and also be leveraged as a semantic caching layer. The application serves as a demonstration to follow along with a step-by-step guide to build a simple application that is task-driven by using a Frontier LLM model, such as Llama Maverick, and they fine-tune using data generated out of this setting to fine-tune an SLM that will satisfactorily perform a similar operation while consuming fewer resources.
Step-by-Step guide for building an Agentic RAG application with MongoDB Atlas
The sample code below demonstrates an end-to-end Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) workflow using LangChain, MongoDB Atlas Vector Search, and Fireworks LLMs. Below is a summary of the key steps and components:
1. Data loading & preprocessing
- PDF loading: The EU Act regulations PDF is loaded using PDFLoader.
- Text splitting: The document is split into manageable chunks using RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter for efficient retrieval and embedding.
2. Embedding & vector store setup
- Embeddings: Sentence-transformers MPNet model is used to generate vector embeddings for each text chunk.
- MongoDB Atlas Vector Search: The embeddings and text chunks are stored in MongoDB, and a vector search index is created for similarity search.
3. LLM & caching
- LLM setup: Meta Llama Maverick is used as the main LLM, with a custom output parser to clean up responses.
- Semantic cache: MongoDB Atlas Semantic Cache is configured to cache LLM responses and avoid redundant computation./li>
4. Agentic RAG workflow
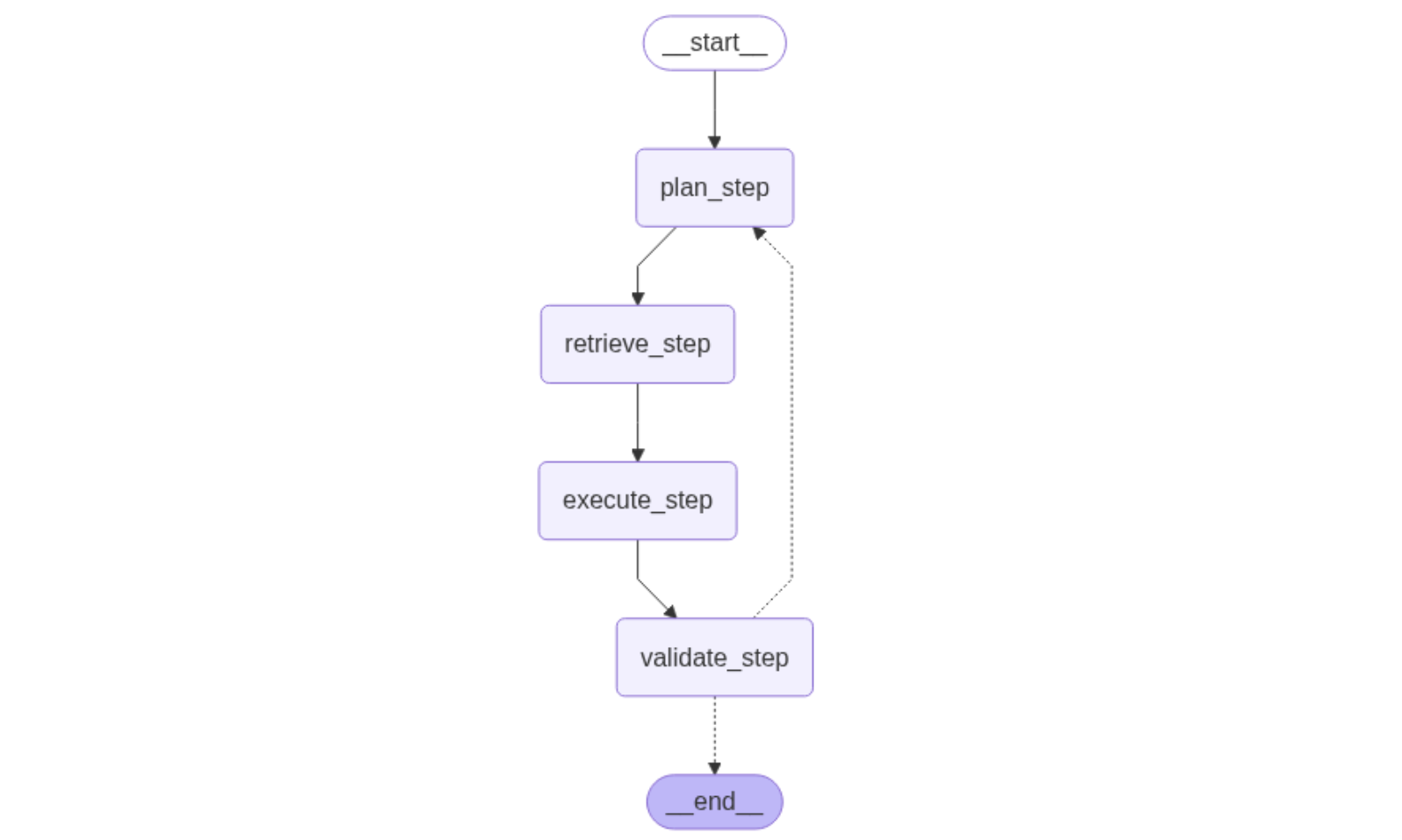
- StateGraph Construction: The workflow is modeled as a state machine with the following steps:
- plan_step: Reformulates the user query for optimal retrieval.
- retrieve_documents_step: Retrieves relevant documents from the vector store.
- execute_step: Generates an answer using the LLM and the retrieved context.
- validate_step: Uses the LLM to validate the relevance of the answer.
- should_continue: Decides whether to proceed to the execute step or go back to the plan step.
Steps to build the Agentic RAG as described above are available in the notebook here.
Once built, the graph for your agentic workflow looks as shown in Figure 2.
Running the Agentic RAG Workflow
Invoke the workflow with a user query:
Response:
Validation Score:
This notebook provides a modular, agentic RAG pipeline that can be adapted for various document retrieval and question-answering tasks using MongoDB and LLMs.
Step-by-Step guide for fine-tuning a small language model with Fireworks AI
Current challenges with frontier models
The large language model used in the preceding example, accounts/fireworks/models/deepseek-r1, can result in slow application response times due to the significant computational resources required for its billions of parameters. An agentic RAG task involves multiple LLM invocations for steps such as generating retrieval questions, producing answers, and comparing user questions to the generated results. This process involves several LLM queries, extending the total response time to 30-40 seconds, with each query potentially taking 5 or more seconds. Additionally, deploying and scaling LLMs for a large user base can be complex and expensive. To mitigate this issue, the example code demonstrates the use of a semantic cache; however, this only addresses repeated queries to the system.
By leveraging small language models (SLMs), enterprises can achieve significant gains in processing speed and cost-efficiency. SLMs require less computational power, making them ideal for resource-constrained devices, while delivering faster response times and lower operational costs. But there is a huge caveat using SLM; they come with several limitations, such as reduced generalization, limited context retention, and lower accuracy on complex tasks compared to larger models. They may struggle with nuanced reasoning, exhibit increased biases, and generate hallucinations due to their constrained training data and fewer parameters. While they are computationally efficient and well-suited for lightweight applications, their ability to adapt across domains remains restricted; for example, a pretrained SLM such as accounts/fireworks/models/deepseek-r1-distill-qwen-1p5b does not produce results which is satisfactory in our agentic RAG setting. It is not able to perform validation scoring or tends to hallucinate, which generatesa response even when context is provided.
Adapting a pre-trained Small Language Model (SLM) for specialized applications such as agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) utilizing private knowledge bases offers a cost-effective alternative to frontier models while maintaining similar performance levels. This strategy also provides scalability for numerous clients, ensuring Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are met.
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning(PEFT) i.e. QLoRA techniques, including Quantized Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), substantially improve efficiency by focusing optimization on a limited set of parameters. This method lowers memory demands and operational expenses. Integrating with MongoDB streamlines data management and supports efficient model fine-tuning workflows.
MongoDB's unique value
MongoDB is integral, providing seamless data management and real-time integration that improves operational efficiency. By storing trace data as JSON and enabling efficient retrieval and storage, MongoDB adds substantial value to the process of fine-tuning models. MongoDB also doubles up as a caching layer to avoid unnecessarily invoking LLM on repeated requests for the same data.
The following steps will go through step-by-step how one can make use of the platform to fine-tune an SLM.
Here’s how to leverage this platform and tool:
To enhance RAG applications, the initial step involves collecting data relevant to the specific task for fine-tuning. MongoDB Atlas, a flexible database, can be utilized to store LLM responses in a cache. For example, in our agentic RAG approach, we can create questions using diverse datasets and store their corresponding answers in MongoDB Atlas. While a powerful LLM might be useful for generating these initial responses or task-specific data during this simulation phase, a smaller scale fine-tuning process requires at least 1000 examples.
Subsequently, these generated responses need to be converted into the required format for the Fireworks.ai platform to begin the fine-tuning process. The cache.jsonl file, used later in fine-tuning, can be created by executing the provided code.
Now that we have prepared the dataset and generated our cache.jsonl file, we can fine-tune the pre-trained deepseek-r1-distill-qwen-1p5b model by following the steps below.
Prerequisites:
- Install firectl: Use the command pip install firectl to install the Fireworks command-line tool.
- Authenticate: Log in to your Fireworks account using firectl login.
- Prepare Dataset: Ensure your fine-tuning dataset (created during the data generation process) is ready.
Steps:
1. Upload dataset: Upload your prepared dataset to the Fireworks platform using the following command, replacing
3. Create fine-tuning job: Initiate a fine-tuning job by specifying the base model, dataset, output model name, LoRA rank, and number of epochs. For example:
6. The output will provide details about the job, including its name, creation time, dataset used, current state, and the name of the output model.
7. Monitor fine-tuning: Track the progress of your fine-tuning job using the Fireworks AI portal. This allows you to ensure the process is running as expected.
8. Deploy fine-tuned model: Once the fine-tuning is complete, deploy the model for inference on the Fireworks platform. This involves two steps:
Deploy the base model used for fine-tuning:
Deploy the fine-tuned LoRA adapter:
9. Use deployed model: After deployment, the model ID (e.g., models/ragmodel) can be used to invoke the fine-tuned language model via your preferred LLM framework, leveraging the Fireworks platform's serverless API.
Summary
Fine-tuning smaller language models (SLMs) for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) using platforms like Fireworks AI offers significant advantages over relying solely on large frontier models. This approach drastically improves response times, reducing latency from around 5 seconds with a large LLM to 2.3 seconds with a fine-tuned SLM, while also substantially decreasing memory and hardware requirements. By leveraging parameter-efficient fine-tuning techniques and integrating with data management solutions like MongoDB, businesses can achieve faster, more cost-effective AI performance for RAG applications, making advanced AI capabilities more accessible and sustainable.
Conclusion
The collaboration between MongoDB and Fireworks AI offers a powerful synergy for enhancing the efficiency and affordability of Large Language Model (LLM) training and deployment. Fireworks AI's utilization of Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) techniques like LoRA and qLoRA significantly curtails the computational resources necessary for fine-tuning LLMs by focusing on low-rank adaptation and quantization. This directly translates to substantial reductions in the costs associated with this crucial process. Complementarily, MongoDB's robust infrastructure, characterized by its distributed architecture, flexible schema, and efficient indexing capabilities, provides the ideal data management foundation. It allows for on-demand scaling of data infrastructure while minimizing storage expenses, thereby contributing to lower capital and operational expenditures.
This integration further fosters streamlined workflows between data and AI processes. MongoDB's capacity for real-time data integration ensures that AI models have immediate access to the most current information, thereby improving operational efficiency and the relevance of the models' insights. When combined with Fireworks AI's fine-tuning tools, this creates a cohesive environment where AI models can be continuously updated and refined. Moreover, the partnership simplifies the development of robust Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) solutions. MongoDB Atlas offers a scalable platform for storing embeddings, while Fireworks AI provides managed LLM hosting and other essential features. This seamless combination enables the creation of scalable and intelligent systems that significantly enhance user experience through more effective and relevant information retrieval.
Organizations adopting this strategy can achieve accelerated AI performance, resource savings, and future-proof solutions—driving innovation and competitive advantage across different sectors.
Further reading:
- Atlas Vector Search
- FireAttention V4
- FireOptimizer