Hi @Aditi_Barde and welcome in the MongoDB Community  !
!
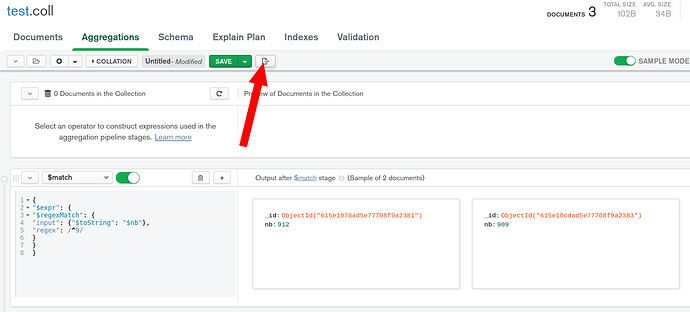
First, I created a little collection test.coll in my localhost MongoDB:
> db.coll.find()
[
{ _id: ObjectId("615e1078ad5e77708f9a2381"), nb: Long("912") },
{ _id: ObjectId("615e10c3ad5e77708f9a2382"), nb: Long("123") },
{ _id: ObjectId("615e10cdad5e77708f9a2383"), nb: Long("909") }
]
I used your existing aggregation in MongoDB Compass to test it. Looks like it is working just fine.
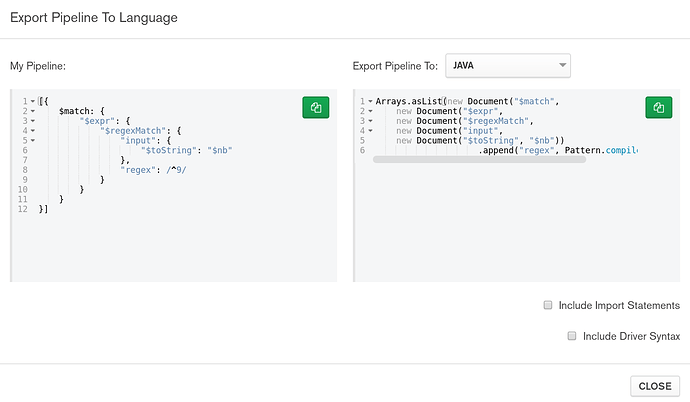
Using the export pipeline code to language button, I export the code into the Java language:
Now I copy paste this into a little Java class using the MongoDB Driver Sync 4.3.3.
I end up with something like this:
import com.mongodb.client.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoClients;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import org.bson.Document;
import org.bson.json.JsonWriterSettings;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import static java.util.Collections.singletonList;
public class Community {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String connectionString = "mongodb://localhost";
try (MongoClient mongoClient = MongoClients.create(connectionString)) {
MongoDatabase db = mongoClient.getDatabase("test");
MongoCollection<Document> coll = db.getCollection("coll");
List<Document> pipeline = singletonList(new Document("$match", new Document("$expr", new Document("$regexMatch",
new Document(
"input",
new Document(
"$toString",
"$nb")).append(
"regex",
Pattern.compile(
"^9"))))));
coll.aggregate(pipeline).forEach(printDocuments());
}
}
private static Consumer<Document> printDocuments() {
return doc -> System.out.println(doc.toJson(JsonWriterSettings.builder().indent(true).build()));
}
}
Once executed, it returns only the 2 documents starting with a “9”.
{
"_id": {
"$oid": "615e1078ad5e77708f9a2381"
},
"nb": 912
}
{
"_id": {
"$oid": "615e10cdad5e77708f9a2383"
},
"nb": 909
}
I can now improve the generated Java code and use the driver helpers a bit more to make the code easier to read.
Actually, before I do that, I can simplify the pipeline a little bit so it’s easier to read & write:
[
{
'$addFields': {
'nb': {
'$toString': '$nb'
}
}
}, {
'$match': {
'nb': /^9/
}
}
]
In Java now it looks like this when I use the Aggregates helpers + static imports:
package com.mongodb.quickstart;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoClients;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Field;
import org.bson.Document;
import org.bson.conversions.Bson;
import org.bson.json.JsonWriterSettings;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import static com.mongodb.client.model.Aggregates.*;
import static com.mongodb.client.model.Filters.regex;
import static java.util.Arrays.asList;
public class Community {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String connectionString = "mongodb://localhost";
try (MongoClient mongoClient = MongoClients.create(connectionString)) {
MongoDatabase db = mongoClient.getDatabase("test");
MongoCollection<Document> coll = db.getCollection("coll");
Bson set = set(new Field<>("nb", new Document("$toString", "$nb")));
Bson match = match(regex("nb", "^9"));
List<Bson> pipeline = asList(set, match);
coll.aggregate(pipeline).forEach(printDocuments());
}
}
private static Consumer<Document> printDocuments() {
return doc -> System.out.println(doc.toJson(JsonWriterSettings.builder().indent(true).build()));
}
}
As you can see, it’s much better & easier to read  ! I think this is the easiest way to write this pipeline using the MongoDB Java driver. I don’t know if your version or mine are equivalent in performances, but I don’t expect a big difference between the 2 to be honest.
! I think this is the easiest way to write this pipeline using the MongoDB Java driver. I don’t know if your version or mine are equivalent in performances, but I don’t expect a big difference between the 2 to be honest.
I don’t think there is an helper in the Java Driver to write the $expr combined with the $regexMatch. There is Filters.expr that you can use but the regexMatch will have to be written with Document & BsonDocuments I guess.
Cheers,
Maxime.